The United States has a rich and storied history of military aviation, with the American Air Force, now officially known as the U.S. Air Force, as a cornerstone of the nation’s defense capabilities. Since its inception in 1947, the U.S. Air Force has played a pivotal role in safeguarding American interests at home and abroad. With a focus on aerospace superiority, it has been at the forefront of technological advancements and operational excellence in the skies and the boundless realm of space.
The history of the U.S. Air Force is a testament to American innovation, determination, and commitment to national security. From its early days as part of the U.S. Army Air Forces during World War II to its evolution into a separate military branch, the U.S. Air Force has consistently demonstrated its adaptability and readiness to meet evolving challenges. Its contributions extend beyond traditional air warfare, as it has been a driving force in the exploration and utilization of space, becoming an integral part of the nation’s space endeavors.
This introduction sets the stage for a deeper exploration of the U.S. Air Force’s journey from its origins to its role in modern space operations. It underscores the significance of the U.S. Air Force’s history and its enduring impact on American military capabilities, technology, and national security, all while highlighting its pivotal role in the ever-expanding domain of space. In the following pages, we will delve into the pivotal moments and key achievements that have shaped the U.S. Air Force’s legacy as a guardian of the skies and a pioneer in the final frontier.
Table of Contents
What was the first U.S. Air Force?
The first U.S. Air Force was not a separate military branch but a component of the U.S. Army. It was known as the United States Army Air Forces (USAAF) during World War II. Established in 1941, the USAAF was responsible for all aviation-related operations within the U.S. Army. Its primary mission was to provide air support to ground forces, conduct strategic bombing campaigns, and engage in aerial reconnaissance.
The USAAF played a pivotal role in World War II, with iconic units like the Eighth Air Force conducting extensive bombing raids over Europe. During this time, the USAAF began to develop the foundation for future air and space capabilities, including early missile and rocket programs.
In 1947, following the end of World War II, the USAAF was separated from the Army and became an independent branch of the military known as the United States Air Force (USAF). This marked the beginning of the modern USAF as a distinct and separate service responsible for air and space operations.

Why is the U.S. Air Force important?
The U.S. Air Force is vital for several reasons. Firstly, it protects American airspace, defending against potential threats and intrusions. Secondly, it plays a pivotal role in projecting military power globally, enabling rapid response and force projection in times of crisis. Thirdly, the Air Force conducts critical intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR) operations, gathering vital information to support military decision-making.
The Air Force is also integral to nuclear deterrence, maintaining a robust intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) and nuclear bomber fleet. Furthermore, it spearheads innovation in aerospace technology, fostering advancements with civilian applications, such as GPS and satellite communication.
The Air Force’s contributions extend into space, including satellite operations, GPS, and missile warning systems, crucial for modern warfare and everyday life. The U.S. Air Force is indispensable for national security, global stability, technological innovation, and maintaining America’s leading role in aerospace and defense.
Who has the largest Air Force?
As of my last knowledge update in September 2021, the United States Air Force (USAF) is the most significant air force in the world. It is a United States Armed Forces branch responsible for aerial warfare and space operations. The USAF has a vast and technologically advanced fleet of aircraft, including fighter jets, bombers, transport planes, and reconnaissance aircraft, along with a significant presence in space.
The USAF’s size and capabilities make it the most extensive air force on the global stage. It is crucial in the United States’ defense, power projection, and global security efforts. However, it’s worth noting that the rankings of the world’s largest air forces can change over time due to developments in military capabilities, budgets, and geopolitical factors. To get the most up-to-date information on this topic, it’s advisable to consult more recent sources and reports.
The United States Air Force (USAF) has played a significant role in space exploration and operations since the inception of the space age. Here’s a brief overview of the U.S. Air Force’s involvement in space from 1945 to the twenty-first century:

Early Developments
The U.S. Air Force’s significant involvement in space can be traced back to the formative years of space exploration during World War II. At that time, the U.S. Army Air Forces (USAAF) was at the forefront of technological innovation, particularly in experimental rocketry and missile programs. These groundbreaking initiatives served wartime purposes and unwittingly laid the foundation for the nation’s future endeavors beyond Earth’s atmosphere.
The USAAF’s interest in rocketry and missile technology emerged from the need for more advanced weaponry during the war. This interest led to developing projects like the V-2 rocket, captured from Nazi Germany and studied by American scientists and engineers. The knowledge gained from these endeavors eventually found applications beyond military use, propelling the U.S. into space exploration.
In essence, the USAAF’s early forays into rocketry and missile development were the precursors to the U.S. Air Force’s subsequent role in space, marking the inception of a journey that would ultimately see the USAF at the forefront of global space capabilities.
In 1947, a pivotal moment in the history of the United States military occurred with the official establishment of the United States Air Force (USAF) as a separate and independent branch. This significant transition marked the culmination of years of development and transformation in aviation and military strategy. Before this, the USAF was known as the United States Army Air Forces (USAAF), functioning as a component of the U.S. Army.
The decision to create a distinct Air Force was based on recognizing the unique capabilities and evolving airpower mission. With World War II showcasing the strategic importance of air superiority and long-range bombing campaigns, the USAAF had proven its significance in modern warfare. By becoming a separate branch, the USAF gained the autonomy to focus exclusively on air and space operations, research, and development, ultimately shaping the nation’s aerospace capabilities and global reach.
This transformation marked the USAF’s formal emergence as a guardian of American skies and space, setting the stage for its pivotal role in space exploration, satellite operations, missile defense, and more in the years to come.
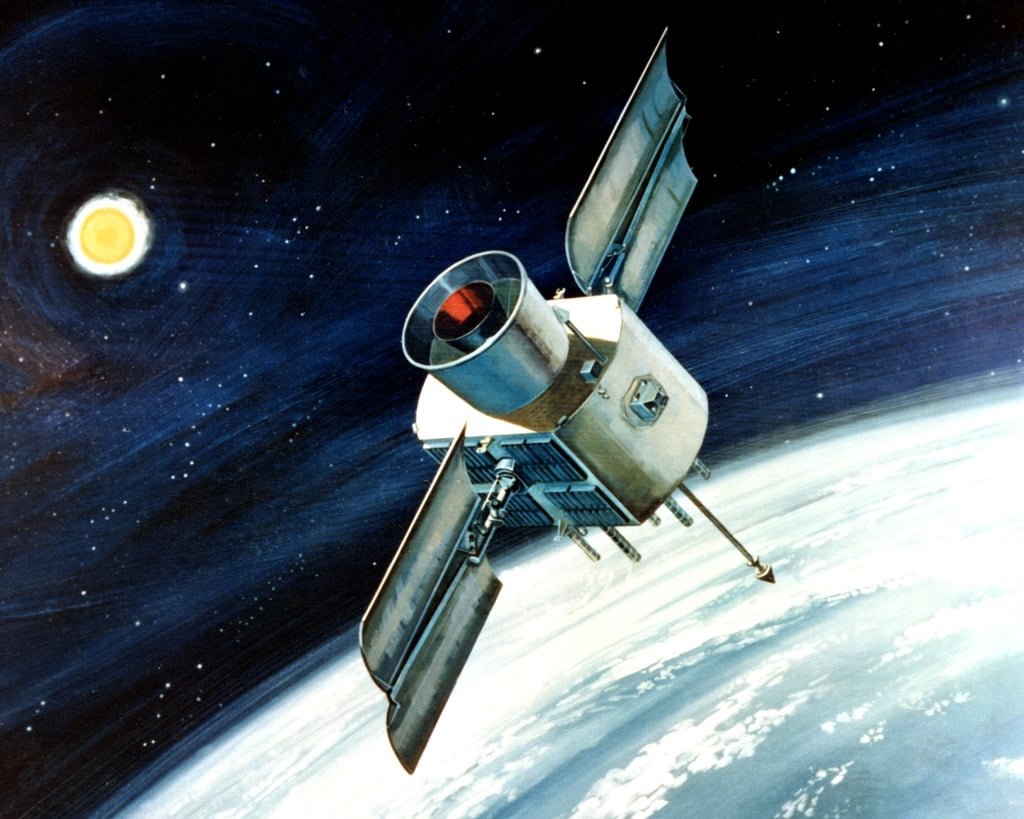

Early Satellites
The United States Air Force (USAF) played an instrumental role in the developing years of space exploration, leaving an indelible mark on the trajectory of human space endeavors. A pivotal moment in this history occurred on January 31, 1958, when the USAF achieved a milestone that would alter our understanding of the Earth’s environment and cosmic phenomena.
On that historic day, the USAF successfully launched its first Explorer 1 satellite into Earth’s orbit. Beyond its initial mission objectives of studying cosmic rays and micrometeorite impacts, Explorer 1 made an unexpected and groundbreaking discovery. It identified the existence of the Van Allen radiation belts, named after the project’s lead scientist, Dr. James Van Allen. This discovery revolutionized our understanding of the Earth’s magnetosphere and the radiation environment in space.
Explorer 1’s findings opened new avenues for space research and underscored the USAF’s pioneering spirit in space exploration. In the following decades, this event marked the USAF’s entry into space science, setting the stage for the broader exploration and utilization of space for civilian and military purposes. The USAF’s role in this significant achievement remains a testament to its commitment to advancing our knowledge of the cosmos and securing our capabilities in space.
Military Reconnaissance and Communications
Amid the intense Cold War rivalry between the United States and the Soviet Union, the United States Air Force (USAF) played a pivotal role in developing and operating reconnaissance satellites, most notably the Corona series. This covert and technologically advanced program was instrumental in gathering critical intelligence about the Soviet Union and its activities.
The Corona series of reconnaissance satellites, officially known as the “Discoverer” program, was initiated in the late 1950s and continued into the 1960s. These satellites were designed to capture images of the Earth’s surface from orbit and then eject photographic film canisters, which would be retrieved in mid-air by specially equipped aircraft.
The intelligence gathered by Corona satellites provided invaluable information about Soviet military installations, nuclear weapon facilities, and missile sites. This data was crucial for monitoring arms control agreements, assessing the Soviet Union’s military capabilities, and gaining an upper hand in the Cold War’s geopolitical chess game.
The Corona program exemplifies the USAF’s commitment to technological innovation and its vital role in national security during a tumultuous era. It also marked a significant milestone in the history of satellite surveillance, laying the groundwork for future generations of reconnaissance and surveillance satellites.
In addition to its pioneering efforts in space exploration, the United States Air Force (USAF) has been instrumental in establishing and maintaining a robust network of communication satellites, a vital component of military operations and global communication infrastructure.
Recognizing the strategic importance of reliable and secure communication, the USAF embarked on a mission to deploy a constellation of communication satellites. These satellites serve a dual purpose: enhancing military operations and supporting global civilian communication needs.
The USAF’s communication satellites provide a resilient and secure means of transmitting vital data for military operations, including command and control information, intelligence, and reconnaissance data. This capability ensures that military forces maintain effective communication even in remote or hostile environments, bolstering national security.
On the civilian front, the USAF’s contribution to global communication is equally significant. These satellites have connected people worldwide, enabling international voice, data, and video communication and facilitating internet access. They are crucial for disaster response, humanitarian efforts, and commercial activities that rely on satellite communication services.
Overall, the USAF’s network of communication satellites is a testament to its commitment to national defense and global connectivity, making it an essential player in shaping the modern communication landscape.

Human Spaceflight
During the early days of human spaceflight, the United States Air Force (USAF) played a pivotal role in shaping the path to the stars. Notably, several USAF test pilots transitioned into the elite ranks of astronauts, embodying the military’s commitment to advancing aerospace exploration.
Astronauts like John Glenn and Gus Grissom, both USAF officers, exemplified this transition. John Glenn, a Marine Corps aviator, later joined the USAF and became the first American to orbit the Earth in 1962 as part of NASA’s Mercury program. Gus Grissom, a USAF pilot, was one of NASA’s original seven astronauts and flew on the Mercury and Gemini missions.
Moreover, the USAF’s involvement in the X-15 program, led by NASA and the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA), marked a crucial step in bridging the gap between atmospheric flight and space exploration. This experimental aircraft, piloted by several USAF test pilots, including Neil Armstrong, provided invaluable data on high-speed flight, aerodynamics, and the challenges of re-entry, laying the foundation for future space missions such as the Apollo program. The USAF’s contributions to early human spaceflight underscored its dedication to pushing the boundaries of aerospace science and technology.
GPS (Global Positioning System)
The United States Air Force (USAF) played a pivotal and pioneering role in developing and operating the Global Positioning System (GPS). This satellite-based navigation system has transformed how we navigate and conduct various military and civilian activities.
In the 1970s and 1980s, the USAF initiated and oversaw the development of GPS as a critical military technology. The system initially aimed to provide precise positioning, navigation, and timing information to support various military operations. It involved launching a constellation of satellites into orbit around the Earth, which would broadcast signals that GPS receivers could receive and triangulate on the ground, in the air, and at sea.
However, the significance of GPS extended far beyond military use. As the system became operational and accessible for civilian applications, it revolutionized the transportation, agriculture, surveying, and telecommunications industries. GPS has become integral to daily life, enabling accurate navigation in vehicles, smartphones, and countless other devices and systems.
The USAF’s stewardship of GPS showcases its role as a technological innovator, with the system’s accuracy and reliability contributing to advancements in numerous sectors worldwide. Today, GPS remains a critical asset for military and civilian users, exemplifying the USAF’s enduring impact on space technology and its global applications.
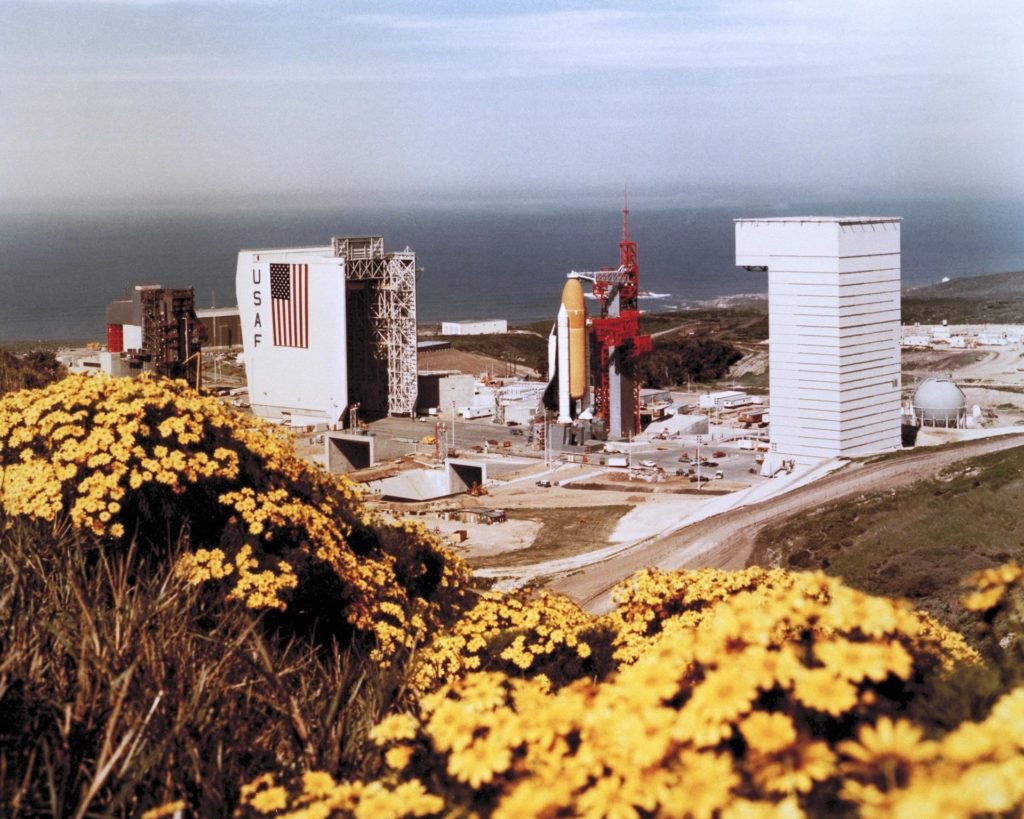

Space Launch Operations
The United States Air Force (USAF) has played a pivotal role in space access and exploration by operating various space launch facilities. Cape Canaveral and Vandenberg Space Force Base are key players in the nation’s space endeavors.
Cape Canaveral, located on Florida’s eastern coast, is synonymous with America’s space launch heritage. The USAF’s presence at Cape Canaveral dates back to the early days of the space age, and it has since become a hub for launching a diverse array of military and civilian satellites into orbit. Cape Canaveral has successfully launched crewed missions, robotic spacecraft, scientific probes, and national security payloads.
Vandenberg Space Force Base, situated on California’s central coast, is the USAF’s primary launch site for missions to polar and sun-synchronous orbits. This strategic location allows for a wide range of orbital inclinations and is essential for Earth observation and reconnaissance satellites.
These launch facilities exemplify the USAF’s commitment to space access, national security, and scientific exploration. They continue to play pivotal roles in ensuring the United States’ presence in space and its ability to meet diverse mission objectives, both military and civilian, in the ever-expanding frontier of space.
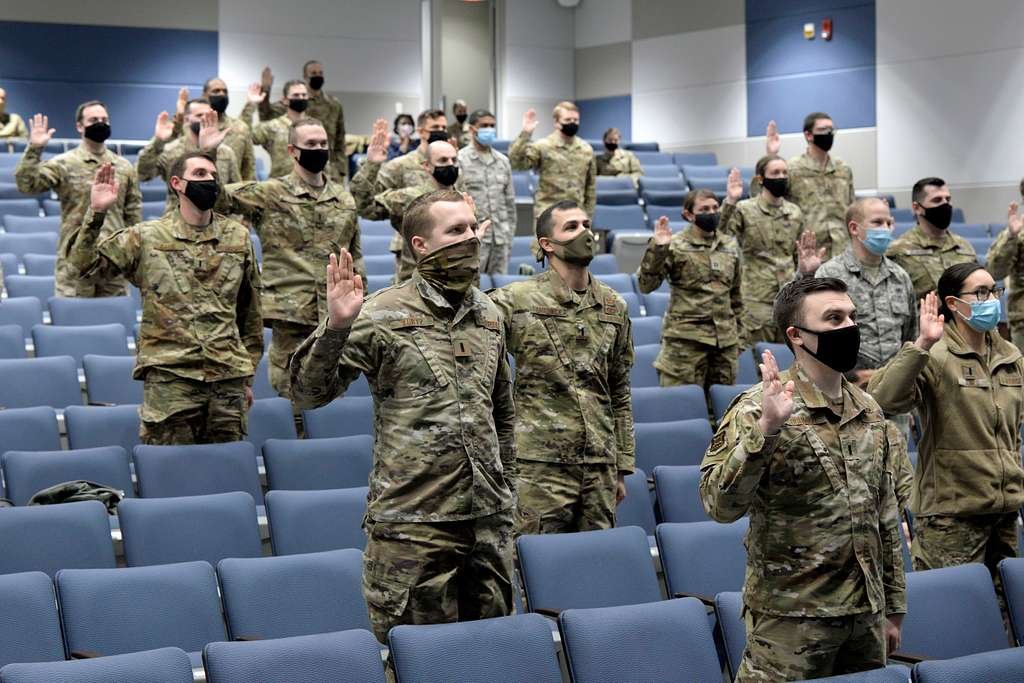

Space Force Establishment
In a significant milestone for the United States’ space endeavors, the United States Space Force (USSF) was officially established as the sixth branch of the U.S. military in December 2019. This momentous decision represented a recognition of space as a distinct and critical national security and defense domain, setting the stage for a new era of space-focused operations.
The USSF, separate from the United States Air Force (USAF), organizes, trains, and equips military personnel specifically for space operations. This includes various tasks, from safeguarding American satellites and space assets to conducting space-based intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance missions.
By creating the USSF, the United States acknowledged the evolving challenges posed by potential adversaries in space and the need to protect its interests in orbit. Establishing this dedicated branch underlines the nation’s commitment to maintaining supremacy in space while ensuring the peaceful and secure use of outer space for the benefit of all. The USSF’s role in securing American interests in the cosmos is a testament to the ever-growing importance of space in modern military strategy.
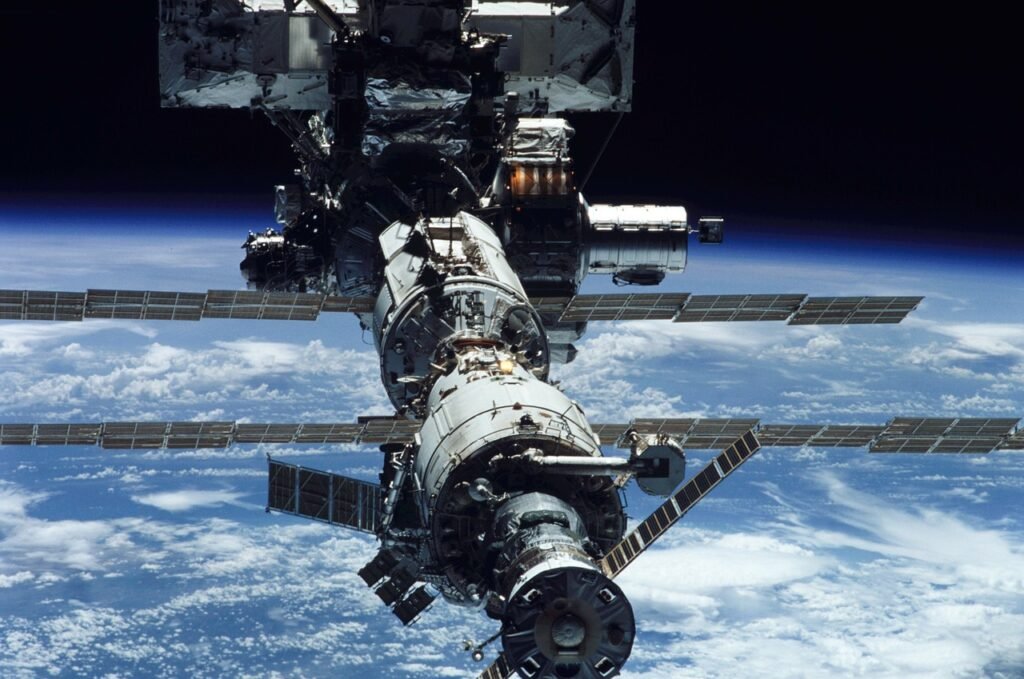

Modern Space Operations
As the nation’s dedicated space branch, the United States Space Force (USSF) is critical in safeguarding and advancing U.S. interests in the space domain. Central to its mission is overseeing and operating diverse military satellites. These satellites serve multifaceted purposes, including communication, surveillance, and missile warning systems, ensuring the nation’s information superiority and defense capabilities.
Furthermore, the USSF operates in close collaboration with other government agencies, most notably NASA, to further the exploration and utilization of outer space. This partnership extends to various space missions, encompassing crewed and robotic endeavors. Notably, the USSF contributes to the launching and supporting missions to the International Space Station (ISS), facilitating scientific research, technology development, and international cooperation in low Earth orbit. Beyond the ISS, this collaboration extends to missions exploring the moon, Mars, and beyond, demonstrating the integrated approach to space activities that define contemporary space exploration efforts.
The USAF and its successor, the USSF, have played a critical role in shaping the United States presence and capabilities in space. They continue to be at the forefront of space exploration and defense in the twenty-first century, with an increasing emphasis on space as a contested domain and the need for space security.













