During the tumultuous era of the Cold War, military advancements became pivotal in the global power play. Among the array of formidable war machines, the T-64 stood as a testament to Soviet engineering prowess and strategic innovation. Renowned as one of the most significant battle tanks of its time, the T-64 emerged as a groundbreaking marvel in the realm of armored warfare.
Designed and developed during the mid-20th century, the T-64 was a pivotal addition to the Soviet arsenal. This highly classified and technologically advanced tank was a manifestation of the USSR’s determined effort to surpass the capabilities of contemporary battle tanks. It epitomized a blend of revolutionary design elements and cutting-edge features that redefined the standards for armored combat vehicles.
Distinctively, the T-64 boasted an array of pioneering attributes that set it apart from its predecessors. Notably, its revolutionary composite armor, combining steel and non-metal materials, enhanced its defensive capabilities without compromising agility—a technological leap that bolstered its position as a formidable force on the battlefield. Equipped with a potent 125mm smoothbore main gun and an innovative autoloader system, the T-64 showcased superior firepower and reduced crew requirements, setting a new benchmark in tank design.
Despite its revolutionary features and technological advancements, the T-64 remained shrouded in secrecy, its deployment limited within the Soviet Union. This secrecy contributed to its mystique, leaving behind a legacy of intrigue and fascination among military enthusiasts and historians alike.
The T-64’s significance in the narrative of Cold War-era military might, its impact on subsequent tank development, and its role as a symbol of Soviet engineering excellence make it an indispensable chapter in the annals of armored warfare. This exploration delves into the intricacies of the T-64—a Soviet battle tank that transcended boundaries and left an indelible mark on the history of tanks and military technology.
Table of Contents
How many T-64s does Ukraine have?
As of my last knowledge update in January 2022, Ukraine possessed a significant number of T-64 tanks due to its historical ties with the Soviet Union. However, the exact count of operational T-64 tanks in Ukraine’s inventory can fluctuate due to various factors, including modernization, decommissioning, or sales.
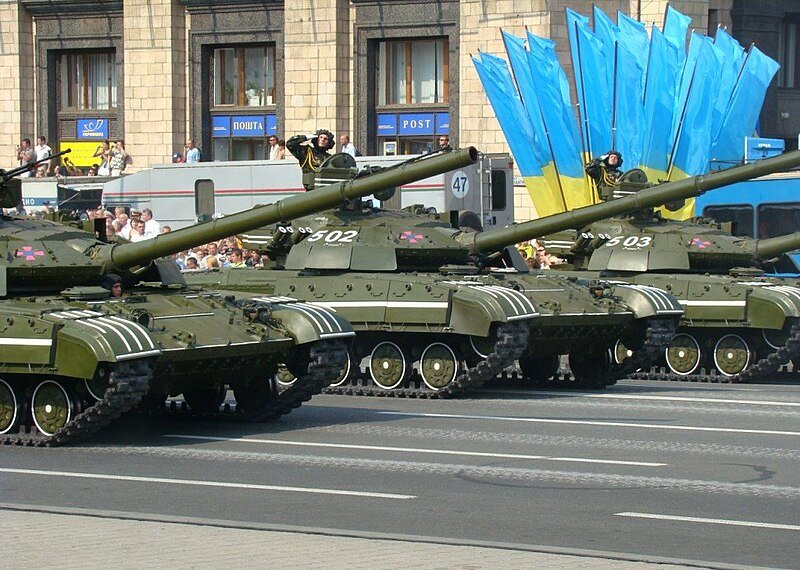

During the dissolution of the Soviet Union, Ukraine inherited a substantial portion of the Soviet military’s equipment, including T-64 tanks. Over the years, Ukraine has taken steps to modernize and maintain its armored forces. Still, the exact number of operational T-64s can be uncertain due to ongoing reforms and the country’s efforts to transition towards more modern tank models.
Moreover, Ukraine has engaged in various defense programs aimed at upgrading and modernizing its military capabilities, which might involve retiring older tank models like the T-64 in favor of more advanced and modern tanks.
It’s important to note that the specific number of T-64 tanks in Ukraine’s possession can change due to military strategies, budget allocations, and geopolitical developments. For the most current and precise information regarding Ukraine’s inventory of T-64 tanks, one would need to refer to the latest reports or official statements from the Ukrainian government or defense authorities.
Was the T-64 a good tank?
The T-64 considered a revolutionary tank for its time, showcased several groundbreaking features that positioned it as an advanced combat vehicle. Its composite armor, integrating steel and non-metal materials, provided enhanced protection without compromising its mobility—a significant advantage over contemporary tanks. Additionally, the introduction of an autoloader system reduced crew size, allowing for a three-person crew instead of the traditional four, enhancing operational efficiency.
In terms of firepower, the T-64’s 125mm smoothbore main gun was a substantial improvement over previous Soviet tank armaments, offering increased lethality and versatility on the battlefield.
However, the T-64 faced certain challenges. Its innovative design led to complexities in maintenance and production, making it more expensive compared to other Soviet tanks.
Furthermore, its sophisticated technology sometimes resulted in reliability issues, impacting its overall operational effectiveness.
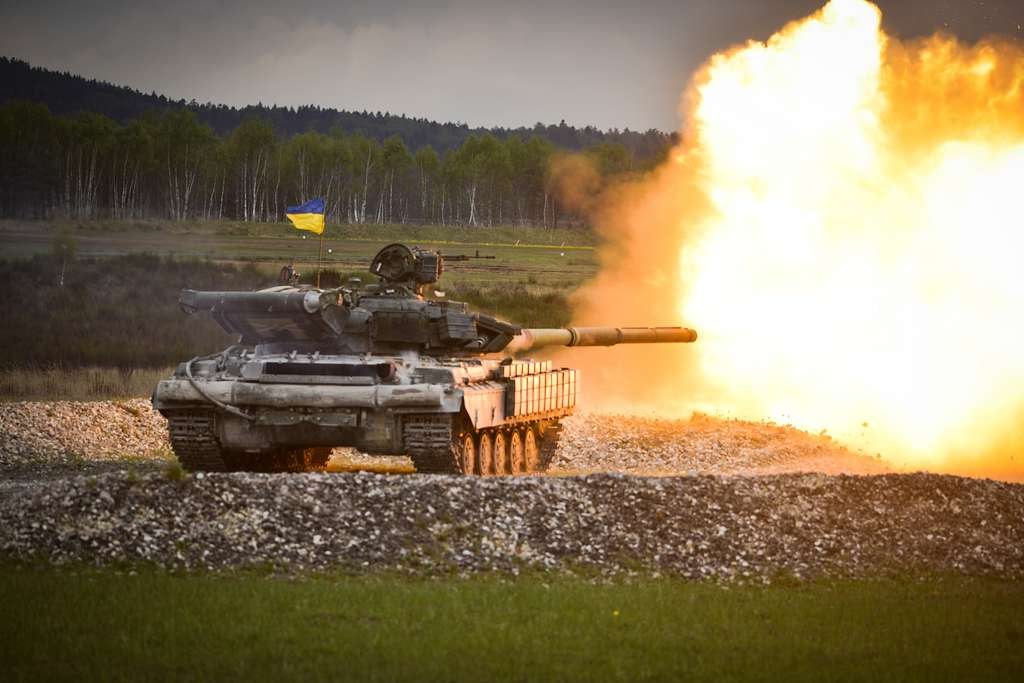

Despite its advancements, the T-64 had limited deployment and was surpassed by subsequent tank models like the T-72 and T-80, which addressed some of its shortcomings while incorporating certain features. While the T-64 showcased groundbreaking elements and influenced tank design, its mixed legacy reflects a combination of advanced capabilities and practical challenges, ultimately placing its effectiveness in a nuanced context within the evolution of armored warfare.
T 64 Battle Tank: The Cold War’s Most Secret Tank
The T-64 was indeed one of the most significant tanks developed during the Cold War era by the Soviet Union. It was a highly advanced and secretive tank, designed to counter the perceived threats posed by NATO tanks at the time.
Here are some key points about the T-64:
Innovation and Features
The T-64, a revolutionary creation in the realm of armored warfare, heralded a new era of tank design by pioneering the integration of composite armor. Unveiled as the world’s inaugural tank to embrace this innovative approach, the T-64 marked a paradigm shift in defensive capabilities without compromising the tank’s mobility or agility.
What set the T-64 apart was its trailblazing composite armor, a fusion of steel and non-metallic materials. This groundbreaking construction fundamentally altered the traditional understanding of tank protection, offering an unparalleled blend of resilience and reduced weight. Unlike conventional armor solely reliant on steel plates, this composite composition provided enhanced defense against enemy fire while maintaining the tank’s maneuverability, a critical factor in dynamic battlefield scenarios.
The ingenious application of composite armor in the T-64 not only fortified its defenses but also presented a template for subsequent tank designs worldwide. This innovation not only bolstered the tank’s survivability against anti-tank weaponry but also laid the foundation for future armored vehicles seeking to optimize protection without compromising speed and agility.
The T-64’s adoption of composite armor epitomized a watershed moment, showcasing the fusion of cutting-edge materials science with military engineering. Its legacy reverberated throughout the evolution of tank technology, influencing the design philosophies of subsequent generations of armored vehicles seeking to strike a delicate balance between protection and mobility on the battlefield.
Autoloader System
The T-64’s automatic loading system represented a watershed moment in tank design, revolutionizing crew operations and efficiency. Unlike its predecessors, which required a four-person crew—comprising a commander, gunner, loader, and driver—the T-64 introduced a pioneering advancement: an automated loading mechanism integrated into the tank’s design. This innovation eliminated the need for a dedicated human loader, resulting in a streamlined crew configuration of three members.
The implementation of this automatic loading system had far-reaching implications. By eliminating the human loader, the tank’s interior was meticulously reconfigured to accommodate the reduction in crew size. The absence of the fourth crew member not only optimized internal space but also significantly enhanced crew safety and operational effectiveness. With a reduced crew, the tank’s overall profile was compacted, granting it a more petite silhouette on the battlefield—an advantageous attribute for both offensive and defensive maneuvers.
Moreover, the automatic loading system vastly improved the tank’s rate of fire. The mechanized process facilitated quicker and more precise ammunition loading, enabling the crew to engage targets with increased rapidity and accuracy. This transformative feature not only minimized crew fatigue during prolonged engagements but also contributed to the T-64’s reputation for being a highly lethal and agile combat vehicle.
The T-64’s pioneering automatic loading system, symbolizing a leap forward in crew efficiency and combat effectiveness, underscored its status as an innovative and forward-thinking Soviet tank during the Cold War era.
Powerful Armament

The T-64, a pioneering marvel of Soviet tank design during the Cold War, revolutionized armored warfare with its formidable armament. At its core lay a 125mm smoothbore main gun, a substantial upgrade from the 100mm cannons featured in earlier Soviet tank models. This significant enhancement in firepower marked a pivotal advancement, allowing the T-64 to wield increased destructive potential on the battlefield.
The 125mm smoothbore gun served as the centerpiece of the T-64’s offensive capabilities, boasting versatility in ammunition deployment. Its ammunition repertoire encompassed a diverse array, ranging from armor-piercing rounds meticulously crafted to penetrate enemy armor defenses to high-explosive anti-tank (HEAT) shells designed to unleash devastating impact upon impact. This diversity in ammunition not only augmented the tank’s ability to engage and neutralize various targets but also ensured adaptability in combat scenarios.
The sheer potency of the 125mm smoothbore main gun positioned the T-64 as a formidable adversary capable of confronting and outmatching contemporary tanks fielded by rival forces. Its firepower, coupled with other technological innovations like the autoloader system and composite armor, consolidated the T-64’s status as a groundbreaking asset in armored warfare, solidifying its place in the annals of military history as a symbol of Soviet engineering excellence and tactical superiority.
Mobility
The T-64, a pinnacle of Soviet tank engineering during the Cold War, was propelled by a robust 700-horsepower engine. This technological marvel endowed it with exceptional speed and maneuverability across diverse landscapes. This powerful engine was a cornerstone of the tank’s mobility, enabling it to navigate terrains with agility and efficiency.
The 700-horsepower engine, integrated into the T-64’s design, represented a significant leap forward in tank propulsion systems. Its robust power output not only facilitated impressive speeds on flat terrain but also endowed the tank with the ability to traverse challenging landscapes, including rugged terrain, snow-covered regions, and urban environments. This exceptional mobility afforded the T-64 a strategic advantage, allowing it to respond to dynamic battlefield scenarios and outmaneuver adversaries swiftly.
Moreover, the engine’s efficiency, in conjunction with the tank’s relatively low weight compared to other contemporary designs, optimized its overall performance. This amalgamation of power and agility granted the T-64 a distinct edge, ensuring it could swiftly position itself for offensive maneuvers or tactically retreat when necessary, thereby solidifying its reputation as a versatile and formidable armored asset within the Soviet military arsenal. Ultimately, the potent 700-horsepower engine emerged as a defining feature that empowered the T-64, contributing significantly to its operational success and battlefield dominance during its service tenure.
Secrecy and Limited Deployment
The T-64, a pinnacle of Soviet tank engineering during the Cold War, remained veiled in secrecy, its deployment intentionally restrained by the Soviet Union. This strategic decision was rooted in the tank’s cutting-edge technology and the regime’s sincere intent to safeguard its advanced features from falling into the hands of adversaries.
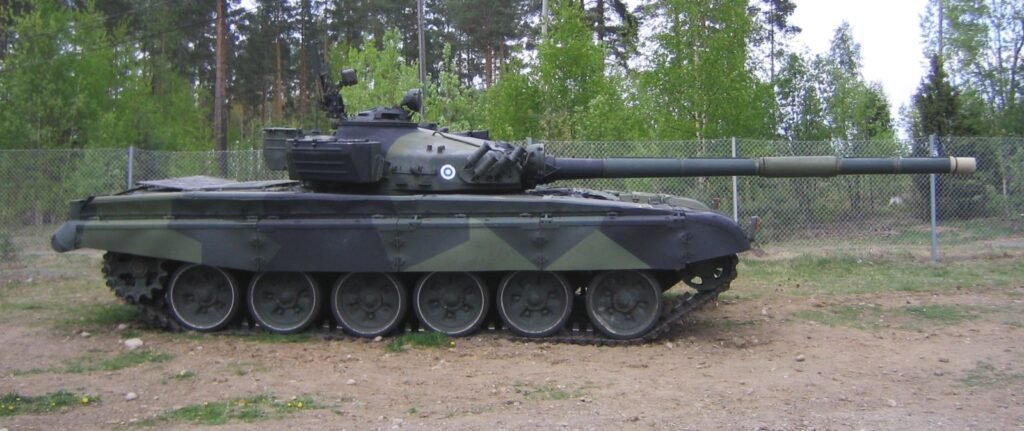

In contrast to the more prevalent and exported T-72, the T-64 was deliberately confined within the borders of the Soviet Union. This deliberate limitation in its distribution prevented its widespread usage and exportation to Warsaw Pact nations, marking a departure from the conventional practice of sharing military technology among allied states.
The Soviet Union’s insistence on preserving the secrecy surrounding the T-64 stemmed from its innovative design elements, which included the pioneering use of composite armor and an automatic loading system. Such advancements were considered strategically significant and were safeguarded to maintain a tactical advantage on the battlefield.
By retaining the T-64 predominantly for domestic use, the Soviet Union ensured tighter control over its technological edge, relegating it to a select few operational units. Consequently, while the T-72 gained international recognition and adoption, the T-64’s limited deployment within the Soviet borders contributed to its enigmatic status, sparking curiosity and intrigue among military experts and enthusiasts for decades to come.
Successor to the T-62
The introduction of the T-64 into Soviet service marked a crucial transition in armored warfare, intending to supersede the aging T-62 tank while heralding a new era of technological advancements. Tasked with replacing its predecessor, the T-64 was engineered to deliver substantial improvements across multiple facets of combat capability—firepower, protection, and mobility.
Compared to the T-62, the T-64 presented a paradigm shift in armored warfare dynamics. Its 125mm smoothbore main gun provided increased firepower, offering enhanced penetration capabilities and the ability to fire a diverse range of ammunition, thereby significantly augmenting its combat effectiveness against contemporary and potential adversaries. Moreover, the innovative composite armor integrated into the T-64’s design significantly bolstered its defensive capabilities without compromising agility, offering a higher level of protection against anti-tank weaponry.
In terms of mobility, the T-64 featured a powerful 700-horsepower engine that not only provided superior speed but also ensured efficient maneuverability across various terrains. This emphasis on improved mobility further solidified its position as a modernized and versatile combat vehicle capable of adapting swiftly to diverse battlefield scenarios.
Overall, the T-64’s introduction represented a pivotal step forward for Soviet armored forces, manifesting in a tank that seamlessly amalgamated advancements in firepower, protection, and mobility—an embodiment of the Soviet Union’s commitment to staying at the forefront of military innovation during the intense geopolitical climate of the Cold War.
Despite its technological advances, the T-64 also faced specific challenges, including complexities in maintenance and production, which made it more expensive compared to other Soviet tank models. Over time, it was succeeded by newer tank designs like the T-72 and later the T-80, which incorporated some of its features while addressing its limitations.
Overall, the T-64 remains a symbol of Soviet engineering prowess and innovation during the Cold War, albeit one that was shrouded in secrecy and limited in its widespread deployment.