Humanity’s journey through time is intrinsically tied to the evolution of technology. In the late 20th and early 21st centuries, this connection between tech history, technological innovation, and the ushering in of the digital age became particularly pronounced. This period is a testament to the relentless pursuit of progress and innovation that defines our modern world.
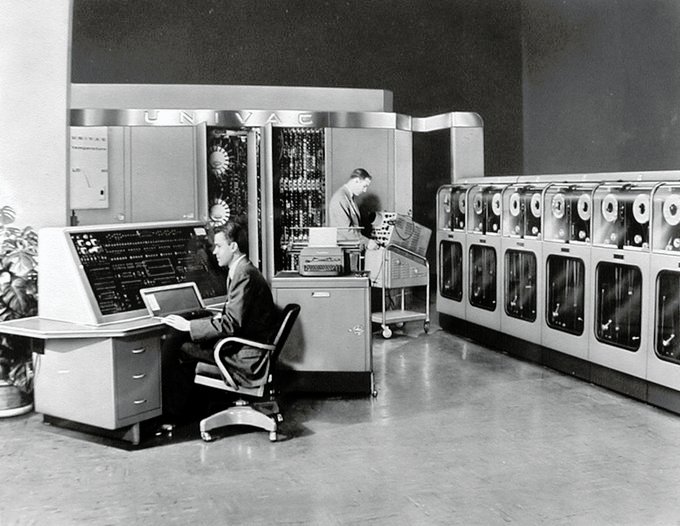
Tech history during this era unfolded like an epic narrative. It was when personal computing, a term synonymous with household names like Apple and IBM, shifted from science fiction to reality.
With the birth of personal computers and the development of graphical user interface (GUI) transformed how individuals interacted with technology. Suddenly, the once cryptic world of coding became accessible to the masses.
The internet, perhaps the most transformative invention of this era, was instrumental in knitting. The world is closer together. Tim Berners-Lee’s creation of the World Wide Web in 1991 marked a new era in communication, business, and entertainment. The dot-com bubble and its subsequent burst showcased the incredible potential of online businesses while underscoring the importance of sustainable growth.
The advent of smartphones, led by the iconic iPhone in 2007, redefined personal and professional landscapes. These devices, which doubled as communication tools, personal assistants, and entertainment hubs, became integral to daily life, exemplifying the continuous convergence of technology and society.
As we delve into this captivating period of tech history, we will trace the threads of innovation that wove together to create the tapestry of the modern digital age.
We will explore the triumphs and challenges, the trailblazing entrepreneurs and tech giants, and the profound societal shifts technology drives. In doing so, we aim to understand better how technology has shaped and continues to shape our world.
Table of Contents
What technology is the most interesting?
Determining the most exciting technology is highly subjective and can vary greatly depending on individual interests and perspectives. However, one technology that consistently garners widespread fascination is artificial intelligence (AI). AI represents a frontier of human achievement where machines are designed to mimic human cognitive functions, such as learning, problem-solving, and decision-making.

AI’s intrigue lies in its multifaceted impact on nearly every aspect of modern life. It powers voice assistants like Siri and Alexa, enhances medical diagnostics, enables self-driving cars, and even influences art and creativity through generative algorithms. AI’s ability to transform industries, address complex challenges, and raise ethical questions about automation and job displacement makes it a topic of universal interest.
The continuous evolution of AI, from machine learning to deep learning and neural networks, ensures a steady stream of breakthroughs and possibilities. Whether it’s for its transformative potential, capacity to push the boundaries of human understanding, or ethical implications, AI unquestionably ranks among the most captivating and thought-provoking technologies of our time.
Why is it important to study the history of technology?
Exploring the history of technology is essential for several compelling reasons. Firstly, it provides invaluable insights into the evolution of human civilization. Technology has been a driving force behind societal progress, shaping economies, cultures, and lifestyles. Understanding how various inventions and innovations emerged, developed, and impacted society allows us to appreciate the interconnectedness of history and technology.
Secondly, tech history offers valuable lessons for the present and future. Examining past successes and failures in technological advancements helps us make informed decisions about technology adoption and development. It allows us to anticipate potential challenges and ethical dilemmas as we innovate.
Moreover, tech history promotes innovation itself. Learning about the innovative thinking of the past inspires creativity and problem-solving in the present. It fosters a culture of continuous improvement and sparks new ideas and approaches.
Lastly, the history of technology underscores the importance of ethics and responsibility in innovation. Understanding the consequences of technological choices made in the past can guide ethical decision-making in contemporary technology development, ensuring that our advancements benefit humanity while minimizing harm.
In sum, studying technology’s history is crucial for preserving knowledge, guiding ethical decision-making, fostering innovation, and recognizing the profound impact of technology on our world.
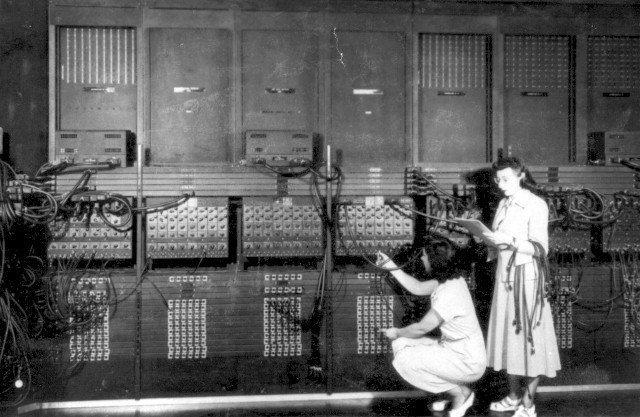

A Journey Through Tech History and Technological Innovation
Determining the most interesting period of tech history is subjective and can vary depending on individual perspectives and interests. However, one period often considered highly fascinating is the era of the late 20th and early 21st centuries, particularly from the 1970s to the early 2000s. Several reasons contribute to the significance and interest in this period:
The Birth of Personal Computing (1970s-1980s)
This period marked a technological revolution with the emergence of personal computers such as the Apple II, IBM PC, and Commodore 64. These devices transformed how individuals approached work and interacted with technology, bringing computing power into homes and offices. One of the pivotal developments was the introduction of the graphical user interface (GUI) by Xerox PARC., a breakthrough that revolutionized user-friendly computing.
Apple’s adoption of the GUI for the Macintosh not only made computers more accessible but also set the standard for intuitive and visually oriented interactions with technology. This shift laid the foundation for modern computing interfaces and shaped how we engage with digital devices today.
The Internet Revolution (1990s)
The 1990s marked a transformative period in the world of technology as the Internet experienced an explosive expansion. The crowning achievement of this era was the creation of the World Wide Web by Tim Berners-Lee in 1991, which democratized access to information and revolutionized communication on a global scale. However, this digital revolution had its challenges.
The dot-com bubble, a speculative frenzy around internet-related companies, reached its zenith in the late 1990s, leading to soaring stock prices and excessive investments. Its subsequent burst in the early 2000s resulted in the collapse of numerous Internet startups, revealing the fragility of the booming Internet economy. These events profoundly influenced the modern tech landscape, highlighting both the immense potential and inherent risks of internet-based businesses.

The Rise of Mobile Technology (2000s)
The introduction of smartphones, with the iconic iPhone leading the charge in 2007, marked a watershed moment in the history of technology. These pocket-sized marvels fundamentally transformed how people connect, communicate, and access information. With the advent of mobile apps, a veritable revolution ensued, altering how we shop, socialize, work, and seek entertainment.
Industries across the spectrum were profoundly affected. The entertainment industry embraced streaming services, while healthcare saw the emergence of telemedicine apps. From education to transportation, smartphones, and their apps became indispensable tools. This seismic shift underscores how a single device catalyzed an era of unprecedented connectivity, convenience, and innovation, forever altering how we navigate the modern world.
Open Source and Free Software Movement
During this period, the growth of the open-source and free software movements marked a profound shift in the software industry. Linux, developed by Linus Torvalds, became a symbol of collaborative software development, where a global community of volunteers contributed to creating a powerful and versatile operating system.
The GNU Project, initiated by Richard Stallman, championed the principles of software freedom, emphasizing users’ rights to access, modify, and share software. Alongside these, the Apache web server, an open-source project, became a dominant force in web hosting. These initiatives challenged traditional proprietary software models by promoting transparency, accessibility, and collective innovation, laying the foundation for a more open and collaborative digital landscape.
E-commerce and Digital Transformation
Companies like Amazon and eBay, which emerged during the late 20th and early 21st centuries, represent transformative forces in commerce. Their innovative approaches to e-commerce disrupted traditional retail and business models, setting the stage for a new era of online shopping and trade. This shift towards e-commerce and digital transformation has had a ripple effect, impacting a multitude of sectors beyond just retail.
Industries such as logistics, payment processing, advertising, and even manufacturing have been profoundly influenced by the digital revolution. The ability to connect with customers globally, streamline operations, and harness data-driven insights has become central to staying competitive in today’s business landscape.

Emerging Technologies
The late 20th and early 21st centuries witnessed a remarkable surge in emerging technologies that have not only transformed industries but also reshaped how we live and work. Artificial intelligence (AI) has become a linchpin in various sectors, from healthcare and finance to autonomous vehicles and personalized recommendations.
Virtual reality (VR) has redefined how we experience entertainment and training, while blockchain technology has introduced new paradigms in secure and decentralized record-keeping, notably in cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin. These innovations continue to evolve and hold the potential to revolutionize even more aspects of our daily lives, promising a future where technology plays an increasingly integral role.
Cybersecurity Challenges
During the late 20th and early 21st centuries, the proliferation of technology brought about unprecedented connectivity and convenience but also heightened cybersecurity threats. High-profile hacking incidents, such as the 2000 “ILOVEYOU” virus and the more recent Equifax data breach, exposed vulnerabilities in digital systems and underscored the urgency of cybersecurity.
This period witnessed the rapid development of cybersecurity measures and industries, driven by the need to protect sensitive data and critical infrastructure. Cybersecurity has become an essential component of technology, with governments, businesses, and individuals investing heavily in safeguarding digital assets, making it a critical concern in the ever-evolving tech landscape.
Social and Cultural Impact
The late 20th and early 21st centuries witnessed profound social and cultural transformations driven by technological advancements. Communication underwent a seismic shift, with email, instant messaging, and later, social media platforms like Facebook and Twitter redefining how people interacted and shared information. These platforms facilitated global connectivity and influenced political discourse, activism, and news dissemination.
The rise of digital media and streaming services transformed entertainment consumption, while e-commerce revolutionized shopping habits. These changes underscored the pervasive influence of technology on culture, communication, and daily life, shaping how we connect, create, and consume in the modern era.

Tech Giants and Entrepreneurship
The founding and meteoric growth of tech giants such as Microsoft, Apple, Google, and Facebook were pivotal in the late 20th and early 21st century tech history. These companies, often born in garages or college dorm rooms, epitomized their founders’ entrepreneurial spirit and innovative drive.
Each founder’s story, from Bill Gates and Paul Allen’s creation of Microsoft to Steve Jobs and Steve Wozniak’s iconic Apple, is a testament to visionary leadership and perseverance. Their innovations revolutionized computing and transformed entire industries, from software to consumer electronics and online advertising.
Furthermore, these tech giants’ influence on the global economy cannot be overstated. They reshaped markets, generated unprecedented wealth, and established themselves as household names, leaving an indelible mark on how we live, work, and connect in the digital age.
Scientific Advancements
During the late 20th and early 21st centuries, advancements in biotechnology, space exploration, and materials science were instrumental in shaping the trajectory of human progress. Biotechnology revolutionized healthcare, leading to breakthroughs like gene therapy and personalized medicine. Space exploration expanded our understanding of the cosmos, with missions to Mars and beyond pushing the boundaries of human exploration.
Materials science yielded innovations in lightweight, durable materials that enhanced everything from aerospace engineering to consumer products. In all these fields, technology played a pivotal role as an enabler, providing the tools and methodologies necessary to push the boundaries of scientific knowledge and usher in a new era of discovery and application.
Overall, the late 20th and early 21st centuries are often considered the most exciting period of tech history because of the rapid pace of technological innovation, the transformative impact on society and business, and the myriad of stories, personalities and events that have shaped the modern digital age. However, what one finds most interesting can vary greatly, and other periods in tech history may hold particular appeal to different individuals based on their specific interests and perspectives.