Sony Corporation, a name synonymous with cutting-edge innovation and groundbreaking technology, has left an indelible mark on the world of consumer electronics and entertainment. Founded in 1946 by two visionaries, Masaru Ibuka and Akio Morita, Sony embarked on a journey to reshape how we interact with the world of sound and vision.
Masaru Ibuka and Akio Morita, with a mere 190,000 yen in capital and a team of just 20 employees, dared to dream beyond the constraints of post-World War II Japan. Originally known as Tokyo Tsushin Kogyo (Tokyo Telecommunications Engineering Corporation), the company soon adopted the name “Sony” in 1950, derived from the Latin word “sonus,” meaning sound, and the colloquial term “sonny,” reflecting youthful energy and innovation.
Sony’s early forays into electronics were marked by their pioneering spirit. In 1955, they introduced Japan’s first transistor radio, the TR-55, a portable marvel that symbolized the dawn of a new era in electronics. This innovation was followed by the TR-63, the world’s smallest transistor radio in 1957, which not only captured the hearts of consumers but also established Sony as a global electronics leader.
As the years passed, Sony’s commitment to innovation only grew stronger. The company ventured into reel-to-reel tape recorders, revolutionizing the way people recorded and played back audio. In 1963, Sony unveiled the world’s first portable cassette tape recorder, the TC-50, further solidifying their reputation as a pioneer in consumer electronics.
In 1968, Sony made its mark in television by introducing the Trinitron color television. The Trinitron’s superior picture quality set new standards in the industry and became a global sensation.
Meanwhile, Sony continued to expand its product offerings, delving into videocassette formats and other emerging technologies.
The 1980s saw the iconic Sony Walkman, a portable cassette player that changed how people experienced music. Sony’s collaboration with Philips led to the creation of the compact disc (CD) in 1982, setting new standards for audio quality and durability.
Sony’s journey didn’t stop with consumer electronics. In 1994, they entered the video game industry with the PlayStation console, marking the beginning of a new era in gaming. The company further diversified, acquiring Columbia Pictures Entertainment in 1989, forming Sony Pictures Entertainment, and establishing Sony Music Entertainment as a major player in the music industry.
This introduction barely scratches the surface of Sony’s remarkable history. Join us as we delve deeper into the milestones and innovations that have made Sony Corporation a global powerhouse in electronics and entertainment.
Table of Contents
What was Sony initially made for?
Sony, founded initially as Tokyo Tsushin Kogyo (Tokyo Telecommunications Engineering Corporation) in 1946, had its roots in telecommunications equipment. The company’s early focus was repairing and developing innovative devices for the post-World War II Japanese market. Its first major product was the Type-G magnetic recording and tape recorder, used for business and professional purposes.

However, Sony’s most significant early breakthrough came in consumer electronics. In the mid-1950s, Sony engineers, led by co-founder Masaru Ibuka and his team, developed Japan’s first transistor radio, the TR-55, released in 1955. This portable radio marked a pivotal moment in Sony’s history. It was smaller, lighter, and more energy-efficient than traditional vacuum tube radios, making it a tremendous success and setting the stage for Sony’s future in consumer electronics.
Recognizing the potential of miniaturization and solid-state technology, Sony continued to innovate in the electronics industry. The company’s subsequent endeavors included the development of portable cassette tape recorders, color televisions, and iconic products like the Walkman and the Trinitron TV, solidifying its reputation as a pioneer and leader in consumer electronics. While Sony’s origins may have been in telecommunications, its pivot to consumer electronics ultimately defined the company and laid the foundation for its future success in a wide range of industries.
What made Sony famous?

Sony became famous for its relentless commitment to innovation and groundbreaking contributions to the consumer electronics and entertainment industries. Several key factors contributed to Sony’s fame:
Transistor Radios
Sony gained early recognition with the release of Japan’s first transistor radio, the TR-55, in 1955. This portable and energy-efficient radio was a technological marvel and set the stage for Sony’s reputation for quality electronics.
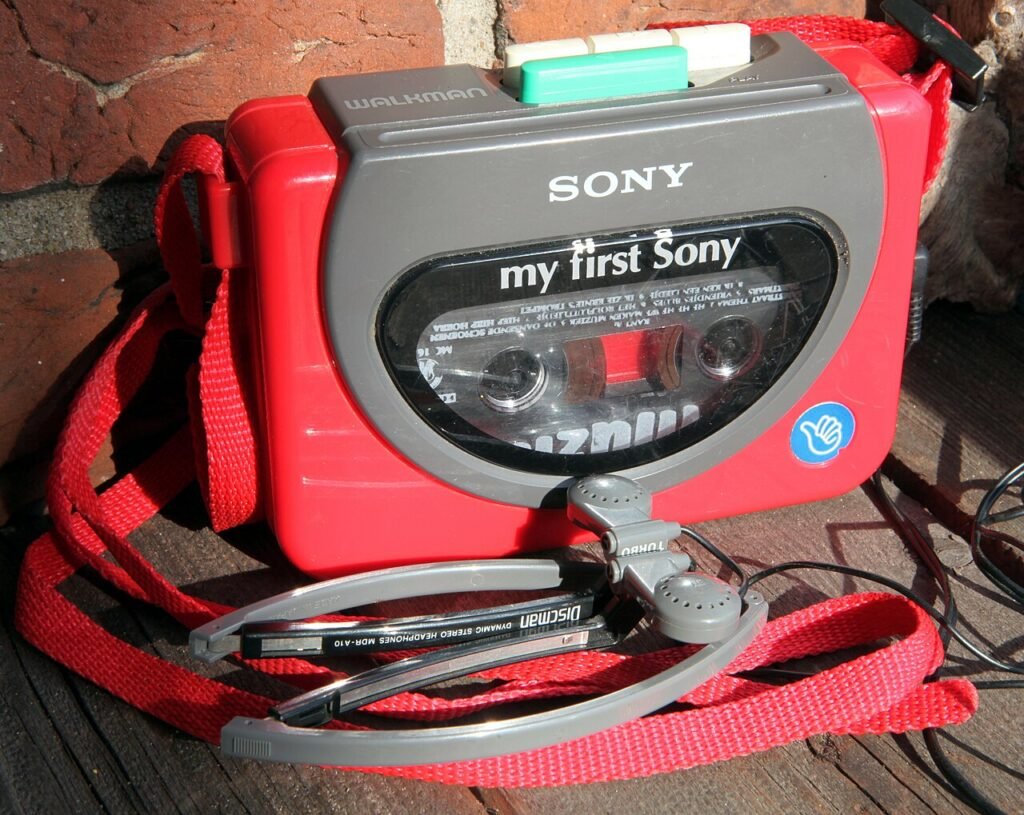
Sony Walkman Revolution
In 1979, Sony introduced the Walkman, a portable cassette player that revolutionized how people listened to music. The Walkman became an iconic cultural phenomenon symbolizing Sony’s commitment to personal entertainment.
Trinitron TVs
Sony’s Trinitron color televisions, introduced in 1968, offered superior picture quality and became highly popular worldwide. They set new standards in television technology.
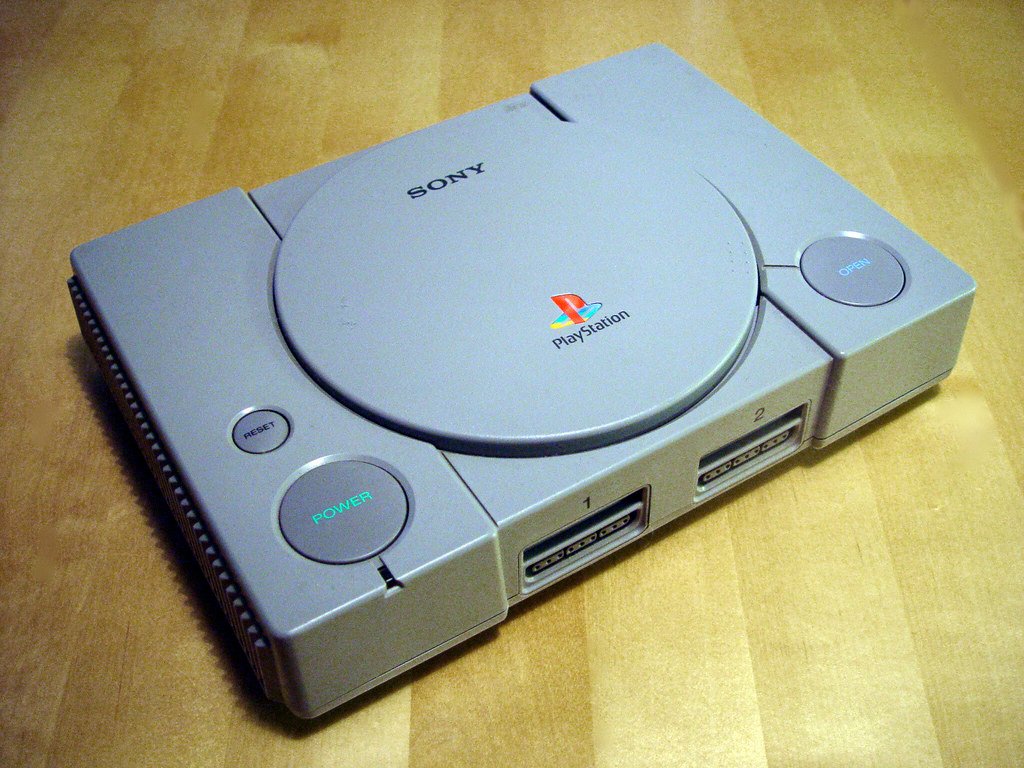
PlayStation
Sony entered the video game industry with the PlayStation console in 1994. The PlayStation series achieved tremendous success, with each iteration pushing the boundaries of gaming technology.
Compact Disc (CD) Technology
Sony, in collaboration with Philips, developed the CD format in 1982. This format revolutionized the music industry by setting new audio quality and durability standards.
Diversification
Sony expanded its presence beyond electronics into entertainment, acquiring companies like Columbia Pictures and establishing Sony Music Entertainment. This diversification allowed Sony to significantly influence the global entertainment industry.
Innovation Culture
Sony’s culture of innovation and quality control has been a driving force behind its success. The company consistently invested in research and development, ensuring its products were forefront of technological advancements.
Sony’s commitment to pushing the boundaries of technology and its ability to create iconic products that resonate with consumers have made it a globally recognized and respected brand, solidifying its fame in electronics and entertainment.
Sony’s Legacy of Innovation

Sony Corporation, commonly known as Sony, is a Japanese multinational conglomerate that has significantly contributed to various industries, including electronics, entertainment, and technology. Its history is marked by innovation and groundbreaking consumer electronics and entertainment developments. Here is a detailed history of Sony:
Foundation and Early Years (1946-1950s)
Sony’s inception in 1946 marked the birth of a company that would eventually become a global powerhouse in electronics and entertainment. Founded with a modest capital of 190,000 yen and a mere 20 employees, Masaru Ibuka and Akio Morita laid the foundation for what would become Sony Corporation.
In 1950, recognizing the need for a name that embodied their vision of innovation in sound technology, they officially rebranded the company as Sony Corporation. The name “Sony” was a fusion of two elements: “Sonus,” representing the Latin word for sound, and “sonny,” reflecting the youthful, innovative spirit that would come to define the company.
Sony’s early ventures included the creation of the G-Type tape recorder, a groundbreaking innovation that marked Japan’s entry into the world of audio technology. This tape recorder showcased Sony’s commitment to pushing the boundaries of what was possible and laid the groundwork for the company’s future as a trailblazer in the realm of consumer electronics.
Transistor Radios (1950s-1960s)
Sony’s release of the TR-55 in 1955 marked a transformative moment in the consumer electronics industry. This pioneering transistor radio was a game-changer, boasting a compact and lightweight design that shattered the dominance of bulky vacuum tube radios. Not only was the TR-55 more portable, but it was also significantly more energy-efficient, providing users with unparalleled convenience and mobility.
Building on this success, Sony continued to push the boundaries of innovation by introducing the TR-63 in 1957. This radio’s claim to fame was its distinction as the world’s smallest transistor radio at the time. Its diminutive size didn’t compromise performance, making it a global sensation and cementing Sony’s reputation as a trailblazer in consumer electronics. These early achievements laid the foundation for Sony’s ongoing legacy of innovation and set the stage for various groundbreaking products.
Reel-to-Reel Tape Recorders (1960s)
In the early 1960s, Sony made significant strides in audio technology by introducing the TC-100, a portable reel-to-reel tape recorder. This innovation marked a notable milestone in the company’s history, as it offered consumers the ability to record and playback audio content with unprecedented convenience and portability.
However, Sony didn’t stop there. In 1963, they further pushed the boundaries of audio innovation by introducing the TC-50, the world’s first portable cassette tape recorder. This invention was nothing short of revolutionary, transforming the way people captured and enjoyed sound. The compact and user-friendly design of the TC-50 made audio recording and playback accessible to a broader audience, setting the stage for the cassette tape’s domination of the music and recording industry in the coming decades. Sony’s relentless pursuit of innovation in audio technology during this period solidified its reputation as a pioneering force in consumer electronics.
Consumer Electronics and Trinitron TVs (1960s-1970s)
In 1968, Sony made a significant foray into the television market with the launch of the Trinitron color television. This innovative technology marked a turning point in television history, offering superior picture quality and enhanced color accuracy, quickly attracting consumers worldwide. The Trinitron TVs became a symbol of Sony’s commitment to excellence in consumer electronics.
Additionally, in 1971, Sony unveiled the U-matic videocassette format, a pioneering development that laid the foundation for the evolution of video recording technology. The U-matic format introduced the concept of compact video cassettes, setting the stage for the VHS and Betamax formats that would follow and ultimately revolutionize the way people recorded and consumed video content. Sony’s U-matic format was a crucial milestone in the history of video technology.
Walkman Revolution (1980s)

The 1980s marked a pivotal era for Sony, characterized by two revolutionary advancements that would shape the future of entertainment. In 1979, Sony introduced the Walkman, initially marketed as the Sony Soundabout in the United States. This portable cassette player liberated music enthusiasts, allowing them to carry their favorite tunes wherever they went. The Walkman swiftly achieved cultural icon status, ushering in the era of personal, on-the-go music enjoyment.
A few years later, in 1982, Sony collaborated with Philips to develop the compact disc (CD) format. This innovation set entirely new standards for audio quality and durability. The introduction of CDs signaled the beginning of the digital audio age, offering pristine sound quality and greater convenience than traditional analog formats. Together, the Walkman and the CD solidified Sony’s reputation as a pioneer in portable music technology and high-quality audio, contributing significantly to the company’s global renown and success.
PlayStation and Entertainment (1990s-Present)
Sony’s entry into the video game industry in 1994 with the PlayStation marked a pivotal moment in gaming history. The PlayStation’s cutting-edge technology, extensive game library, and strategic marketing allowed it to challenge and ultimately surpass the dominance of established rivals like Nintendo and Sega.
In 1989, Sony’s acquisition of Columbia Pictures Entertainment formed Sony Pictures Entertainment. This move transformed Sony into a major player in the global entertainment industry, enabling it to produce and distribute a wide range of films and television shows.

Additionally, Sony Music Entertainment, another subsidiary of the conglomerate, has emerged as one of the world’s largest music companies, representing a diverse array of artists and contributing significantly to the global music landscape. Together, these strategic expansions into gaming and entertainment solidified Sony’s position as a multimedia powerhouse.
Digital Era and Diversification (2000s-Present)
Throughout its history, Sony’s commitment to innovation has extended beyond its early successes. In the realm of imaging technology, Sony has consistently pushed boundaries with its digital cameras and camcorders, offering consumers cutting-edge solutions for capturing and preserving memories. The introduction of the PlayStation 2 in 2000 marked another milestone, as it became the best-selling video game console in history, underscoring Sony’s influence in the gaming world.
Sony’s diversification efforts have seen the company enter the smartphone market with the Xperia series, offering consumers a blend of performance and style. Additionally, Sony’s prowess in display technologies has been exemplified through its development of OLED and 4K HDR televisions, redefining home entertainment with stunning visuals and immersive viewing experiences. These endeavors showcase Sony’s ongoing commitment to technological innovation and its dedication to enhancing various facets of modern life.
Recent Developments (2010s-Present)
Sony’s release of the PlayStation 4 in 2013 and the PlayStation 5 in 2020 solidified its dominance in the gaming industry. These consoles showcased cutting-edge hardware, immersive gaming experiences, and a vast library of exclusive titles, further enhancing Sony’s reputation as a gaming powerhouse.
In addition to gaming, Sony ventured into the virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) markets with the PlayStation VR. This headset allowed players to immerse themselves in virtual worlds, expanding Sony’s influence in immersive technologies.
Furthermore, Sony’s film and music divisions have been consistent sources of popular content. Sony Pictures Entertainment has produced blockbuster films, while Sony Music Entertainment represents some of the world’s biggest music artists, ensuring the company’s influence extends beyond hardware and into entertainment and media.
Sony’s impact on the global stage transcends mere business success; it represents a profound influence on how we experience and interact with technology and entertainment. By consistently pushing the boundaries of innovation and setting new standards for quality, Sony has not only shaped the consumer electronics and entertainment sectors but has also redefined our expectations. From the iconic Walkman that revolutionized music on the go to the PlayStation, which reimagined gaming, Sony’s legacy is a testament to its unwavering commitment to enhancing our daily lives. Sony continues to inspire and lead the way as a pioneer and leader, maintaining its esteemed reputation as a global brand synonymous with innovation and excellence.