World War II, a dark chapter in human history, brought about a remarkable silver lining in the form of scientific and technological advancements. As nations mobilized their resources and intellect to secure victory, they inadvertently propelled humanity into a new era of innovation and discovery. This blog post will delve into the scientific and technological breakthroughs that emerged during World War II and their profound impact on today’s world.
Table of Contents
The Dawn of Radar Technology
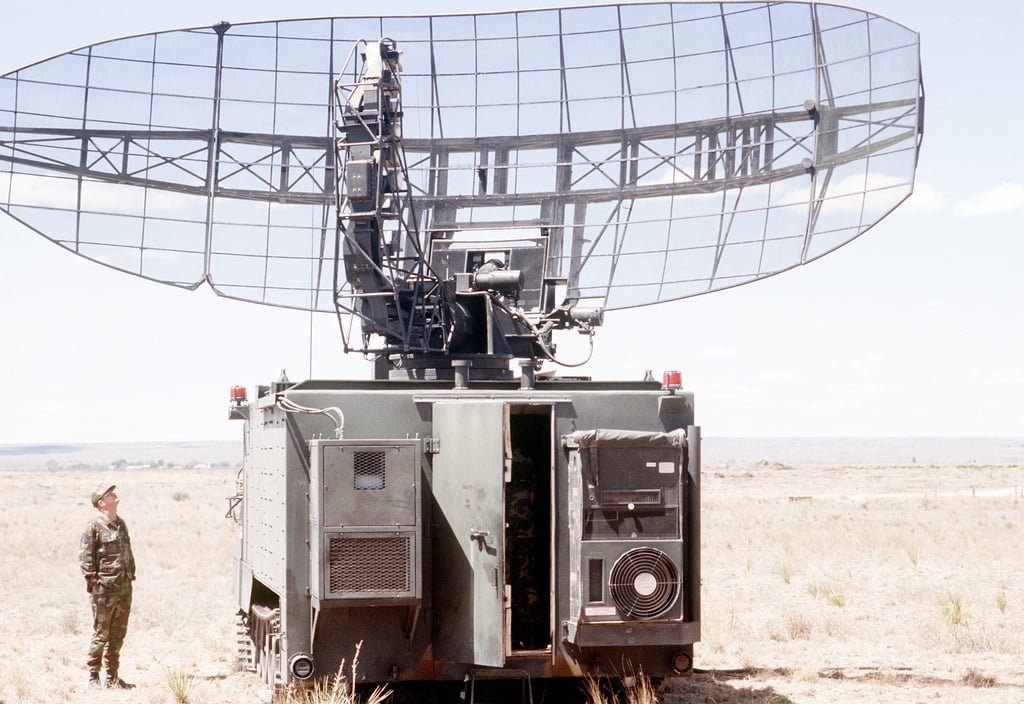

One of the most significant technological leaps during World War II was the development and implementation of radar technology. Radar, short for “Radio Detection and Ranging,” revolutionized military operations by enabling the detection of incoming enemy aircraft and ships long before they could pose a threat. This proved crucial in defense and laid the foundation for modern air traffic control and weather forecasting systems.
Innovation Catalyst
Radar Technology, abbreviated “Radio Detection and Ranging,” catalyzed innovative advancements during World War II.
Military Revolution
Radar Technology revolutionized military strategies by enabling the early detection of approaching enemy aircraft and ships, providing a strategic advantage in defense.
Enhanced Preparedness
Radar’s capability to detect threats from afar significantly improved military preparedness, allowing timely responses and preserving valuable resources and lives.
Enduring Impact
Radar’s profound influence extended well beyond the war, laying the groundwork for crucial systems such as air traffic control and modern meteorology.
Weather Forecasting
Radar technology’s ability to accurately track weather patterns contributed to the evolution of meteorology, enhancing weather forecasting capabilities and disaster preparedness.
Scientific Advancements
Radar’s deployment fostered scientific research and technological innovation, leading to further breakthroughs in various fields.
The Birth of Nuclear Science

The Manhattan Project, a top-secret research endeavor during World War II, led to the creation of the world’s first atomic bomb. This project catapulted nuclear science into the limelight and forever changed the course of human history. While the destructive power of nuclear weapons is undeniable, nuclear energy has also become a vital source of power generation with applications in various fields, including medicine and space exploration.
Manhattan Project
A covert World War II operation leading to the development of the atomic bomb, thrusting nuclear science into prominence.
Atomic Bomb
The first atomic bombs detonated over Hiroshima and Nagasaki demonstrated the devastating power of nuclear science, concluding the war.
Nuclear Energy
Beyond weaponry, nuclear science evolved to provide a significant source of electricity generation through nuclear power plants, contributing to global energy needs.
Multifaceted Applications
Nuclear science’s influence extends into medicine, enabling radiation therapy for cancer treatment and space exploration, powering spacecraft on interstellar missions.
Transformational Legacy
The Manhattan Project’s legacy, marred by its destructive origins, reshaped scientific understanding and continues to impact diverse fields, promising a better future through responsible nuclear applications.
Advances in Communication
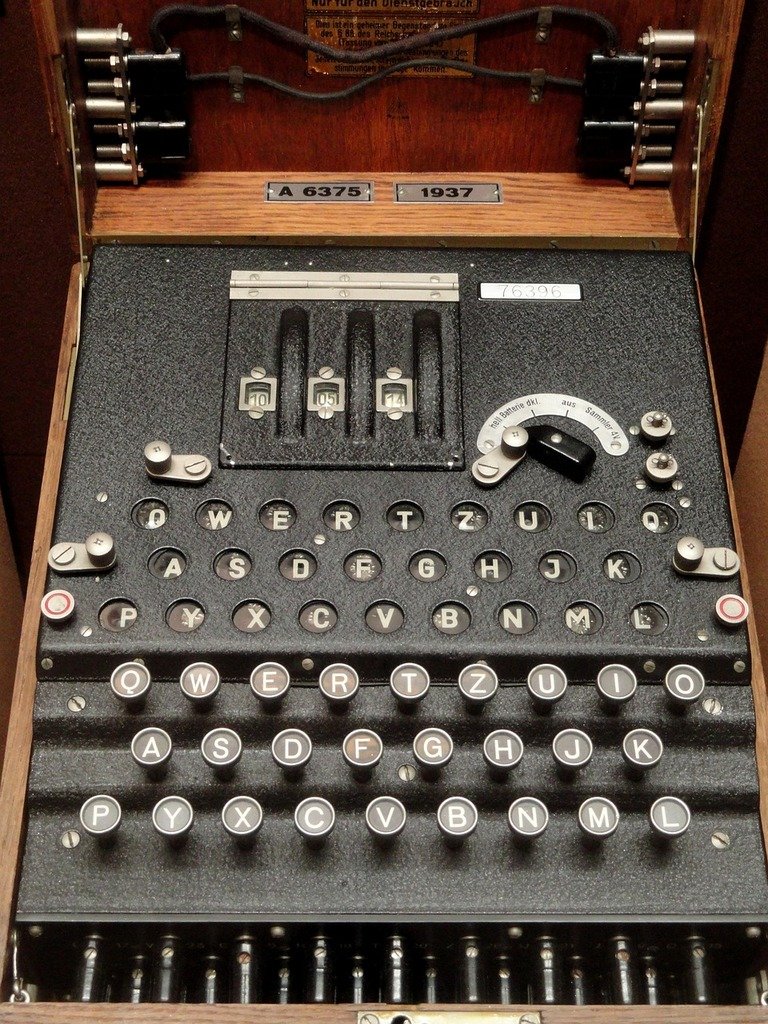

World War II also spurred major advancements in communication technology. Allied cryptanalysts’ development of encryption machines like the Enigma and cracking their codes were pivotal in intelligence operations. These achievements laid the groundwork for modern cryptography, cybersecurity, and the development of digital computing.
Encryption Machines
World War II saw the development of advanced encryption machines, notably the Enigma machine used by the Germans. These machines were instrumental in securing sensitive military communications.
Allied Codebreaking
Allied cryptanalysts made significant breakthroughs in deciphering the Enigma code, a pivotal achievement that allowed them to intercept and decode critical enemy messages, gaining a substantial intelligence advantage.
Cryptography Foundation
The wartime use of encryption and codebreaking laid the foundation for modern cryptography, the science of securing information through encryption and decryption techniques.
Cybersecurity Implications
The lessons learned during WWII played a crucial role in the evolution of cybersecurity. The need for secure communication during wartime translated into the development of strategies and technologies to protect digital information in the post-war era.
Digital Computing Emergence
The quest for efficient codebreaking and information processing during the war drove research into early digital computing devices. This research laid the groundwork for the development of modern computers, shaping the technological landscape we rely on today.
Lasting Impact
The advances in communication technology during World War II continue to influence how we secure and transmit information in the digital age, emphasizing the enduring impact of wartime innovation on our modern world.
Jet Propulsion and Rocketry

World War II served as a pivotal period for the advancement of aviation, mainly through the introduction of jet engines in military aircraft. This innovation, driven by jet propulsion, revolutionized the field, profoundly affecting both military and commercial aviation while laying the foundation for rocketry research and the subsequent space age.
Jet Engines Transform Aviation
The conflict marked a significant turning point in aviation history, witnessing the emergence of jet engines powered by jet propulsion. These engines, exemplified by aircraft like the German Messerschmitt Me 262 and the British Gloster Meteor, ushered in an era of faster and more efficient flight. Jet propulsion technology propelled aircraft by expelling high-speed exhaust gases, a stark departure from traditional propeller-driven aviation.
Commercial Aviation Soars
Post-war, jet propulsion technology seamlessly transitioned into the civilian sector, fueling the birth of commercial jet aviation. Iconic aircraft like the Boeing 707 and Douglas DC-8 made global travel more accessible and comfortable for passengers. Jet propulsion technology drastically reduced travel time, ushering in an era of mass international air travel and connecting the world like never before.
Rocketry and the Space Age
Simultaneously, during World War II, significant strides were made in rocketry, particularly in Nazi Germany with the V-2 rocket. The development of rocketry, intimately tied to the principles of jet propulsion, laid the groundwork for the space age that followed. Post-war, captured German scientists, led by Wernher von Braun, played pivotal roles in advancing rocket technology in the United States. This laid the groundwork for the launch of Sputnik 1, the first artificial satellite, and ultimately, human spaceflight.
Satellite Technology Flourishes
The rocketry research that emerged during World War II, powered by jet propulsion principles, was a precursor to the development of satellite technology. The launch of Sputnik 1 by the Soviet Union in 1957 marked the commencement of the space race, driving the rapid expansion of satellite technology. Today, satellite technology is indispensable for communication, navigation, and Earth observation, all thanks to the enduring legacy of jet propulsion-driven rocketry research.
Medical Breakthroughs

The wartime effort accelerated medical research, developing antibiotics like penicillin, which saved countless lives on and off the battlefield. These discoveries marked the beginning of modern pharmaceuticals and profoundly impacted healthcare worldwide.
Penicillin Revolutionizes Medicine
One of World War II’s most significant medical breakthroughs was penicillin development and mass production. This antibiotic, discovered by Sir Alexander Fleming in 1928 but not widely used until the war, was pivotal in saving countless lives during the conflict. Penicillin’s ability to combat bacterial infections effectively revolutionized medicine, turning previously deadly diseases and disorders into treatable conditions.
On and Off the Battlefield
Penicillin’s impact extended far beyond the battlefield. Soldiers wounded in combat, who would have previously faced life-threatening infections, now had a fighting chance at recovery. Moreover, civilians worldwide benefited from this breakthrough, as penicillin became readily available post-war, dramatically reducing mortality rates from common infections.
Birth of Modern Pharmaceuticals
The successful mass production of penicillin marked the birth of modern pharmaceuticals. Once a modest enterprise, the pharmaceutical industry began to flourish, leading to the development of a wide range of life-saving drugs and therapies. This paved the way for future medical innovations and the quest for new treatments and cures.
Global Impact on Healthcare
The impact of penicillin and subsequent antibiotic discoveries cannot be overstated. These drugs transformed healthcare worldwide, making surgery safer and reducing mortality from infectious diseases, and extending life expectancy. They also led to the development of antibiotics to combat a wide range of bacterial infections, ensuring that humanity could face health challenges with improved resilience.
Post-War Technological Transfer
After the curtains fell on World War II, the world witnessed an unprecedented transformation as the scientific and technological breakthroughs made during the conflict transitioned from military applications to civilian life. This transition, often called the “post-war technological transfer,” brought about remarkable changes and left an indelible mark on society.
Transition of Innovations
After World War II, many scientific and technological advancements developed for military purposes transitioned into civilian applications.
Rapid Industrial Growth
This transition led to the rapid growth of various industries. For instance, innovations in aviation, such as jet propulsion and rocketry, were adopted in commercial aviation, making air travel faster, safer, and more accessible.
Healthcare Revolution
Wartime medical research yielded antibiotics like penicillin, which transformed healthcare by providing effective treatments for infectious diseases. This significantly improved public health and extended life expectancy.
Diverse Applications
The transfer of technology and knowledge spanned multiple fields, including electronics, telecommunications, and materials science, resulting in advancements such as the development of computers, telecommunications networks, and new materials.
Economic Boom
The infusion of wartime innovation into civilian sectors contributed to the post-war economic boom. It stimulated economic growth, job creation, and increased productivity, laying the foundation for prosperity in the post-war era.
Quality of Life Improvement
These technological advancements improved the quality of life for people worldwide. They made transportation more efficient and accessible, enhanced healthcare, and facilitated communication, ultimately contributing to a higher standard of living.
How did scientific and technological advances contribute to destruction during World War 2?
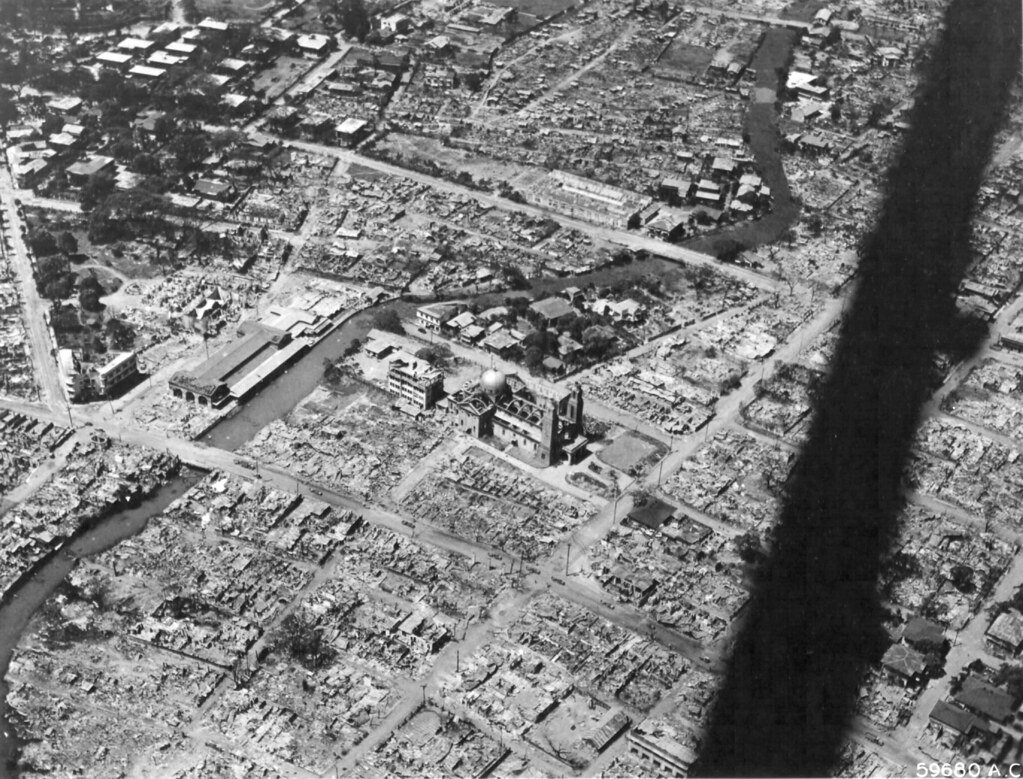

During World War II, various countries made significant technological advancements. Determining a single “best” in technology is challenging as each nation excels in specific areas. However, here’s a breakdown of some notable technological strengths:
Germany
1. Advanced Rocketry
Germany’s V-2 rocket was groundbreaking and laid the foundation for future space exploration.
2. Jet Propulsion
The Messerschmitt Me 262 became the world’s first operational jet-powered fighter.
3. Tanks
The Tiger and Panther tanks were formidable regarding firepower and armor.
United States
1. Atomic Bomb
The Manhattan Project developed the world’s first atomic bomb.
2. Aircraft
The B-29 Superfortress was a long-range bomber, and the P-51 Mustang was an exceptional fighter.
3. Naval Technology
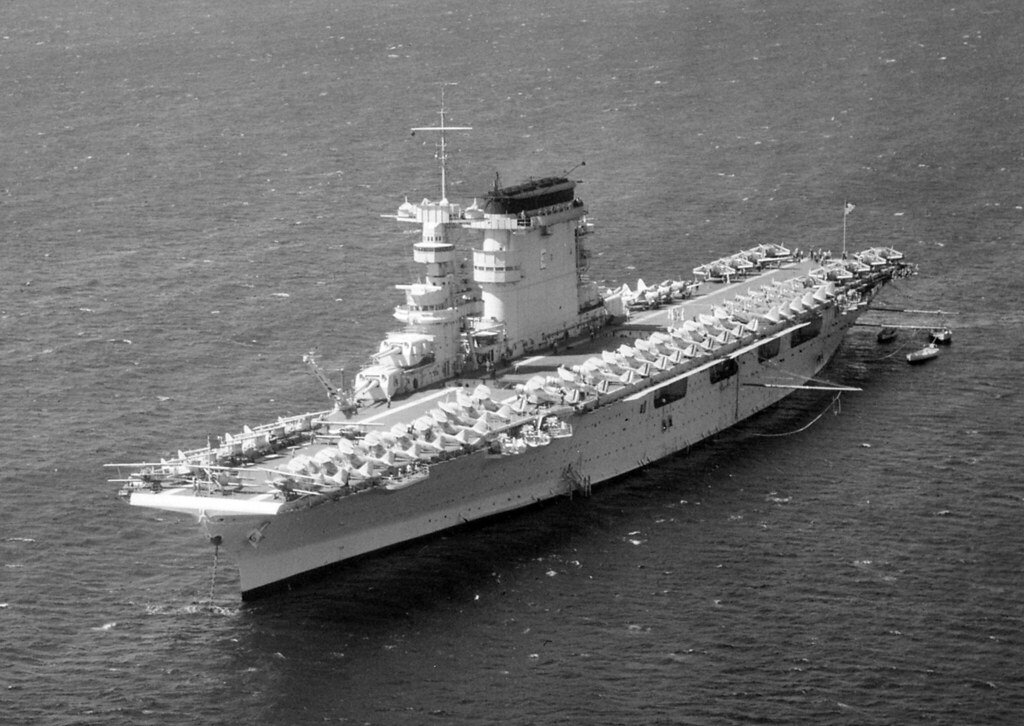
The U.S. had superior aircraft carriers, such as the USS Enterprise.
Soviet Union
1. Tanks
The T-34 was renowned for its durability and effectiveness on the Eastern Front.
2. Artillery
Soviet artillery was powerful and vital to their defensive strategies.
3. Small Arms
The Mosin-Nagant rifle and PPSh-41 submachine gun were widely used.
United Kingdom
1. Radar Technology
The British developed radar systems that were crucial for air defense.
2. Codebreaking
Bletchley Park was pivotal in breaking the German Enigma code.
3. Aviation
The British had innovative aircraft like the Spitfire and Lancaster bomber.
Japan
1. Naval Technology
The Yamato-class battleships were among the largest and most heavily armed ever built.
2. Aircraft
The Mitsubishi A6M Zero was highly maneuverable and effective in the early years of the war.
3. Submarines
Japan had advanced submarines, such as the I-400 class, capable of carrying seaplanes.
How much has technology advanced since WW2?
Since World War II, technology has advanced dramatically. The era has witnessed the invention of the internet, smartphones, space exploration, and significant progress in medicine, computing, and transportation. These innovations have transformed communication, daily life, and global connectivity, reshaping the world in ways unimaginable in the mid-20th century.
While World War II is synonymous with tragedy and devastation, it also represents human ingenuity and the capacity for innovation during the darkest times. That era’s scientific and technological advancements continue to shape our world today, reminding us of the remarkable progress that can arise even from the most challenging circumstances.