In the early 1980s, “Pac-Man Fever” swept across the globe, symbolizing more than just the craze for the iconic arcade game. This phenomenon marked the dawn of video gaming as a mainstream cultural movement, capturing the imaginations of millions. People of all ages flocked to arcades, mesmerized by the simple yet addictive gameplay of Pac-Man, turning it into a cultural icon that transcended the boundaries of gaming.
Pac-Man wasn’t just a game; it was a social experience, a conversation starter, and a symbol of the burgeoning video game industry. Merchandise, music, and even television shows were inspired by the game, reflecting its pervasive influence. Pac-Man Fever became a cultural touchstone, showcasing the power of video games to shape entertainment and pop culture on a global scale.
Table of Contents
The Birth of Pac-Man

Pac-Man’s creation in the early 1980s marked a revolutionary moment in the video game industry. Developed by Toru Iwatani, a young game designer at Namco, Pac-Man was officially released in Japan in May 1980. The game quickly became a sensation, captivating players with its simple yet engaging mechanics. By October of the same year, Pac-Man had made its way to North America, thanks to the efforts of Midway Games, and its popularity skyrocketed. Toru Iwatani’s goal was to design a game that appealed to a broader audience, including women, which was a significant departure from the predominantly male-targeted, violence-themed arcade games of the time. His vision was to create something that anyone could enjoy, regardless of age or gender, making Pac-Man a universal hit.
Who Created Pac-Man?
Toru Iwatani’s innovative approach to game design was the driving force behind Pac-Man’s creation. His desire to break away from the violent and aggressive themes common in arcade games led him to develop something entirely new. Toru Iwatani envisioned a game that was not only fun but also accessible to everyone. His efforts paid off as Pac-Man quickly became one of the most beloved video games in history. Iwatani’s creation resonated with people across the world, setting a new standard for the gaming industry and paving the way for future games that sought to appeal to a diverse audience.

What Inspired Pac-Man?
The inspiration for Pac-Man’s design is as iconic as the game itself. The concept originated from a simple yet universal activity: eating. Toru Iwatani has often shared the story of how the idea came to him while he was eating a pizza. After removing a slice, the remaining shape of the pizza resembled a mouth, which sparked the creation of Pac-Man’s distinct character design. Originally named “Puck Man” in Japan, the game’s title was derived from the Japanese term “paku-paku,” an onomatopoeic expression that mimics the sound of eating. However, the name was changed to “Pac-Man” for the international market to prevent potential vandalism of arcade cabinets by altering the “P” in “Puck” to an “F.” This small change ensured the game’s title remained playful while avoiding any unintended associations.
Game Mechanics and Innovation
How Does Pac-Man Work?
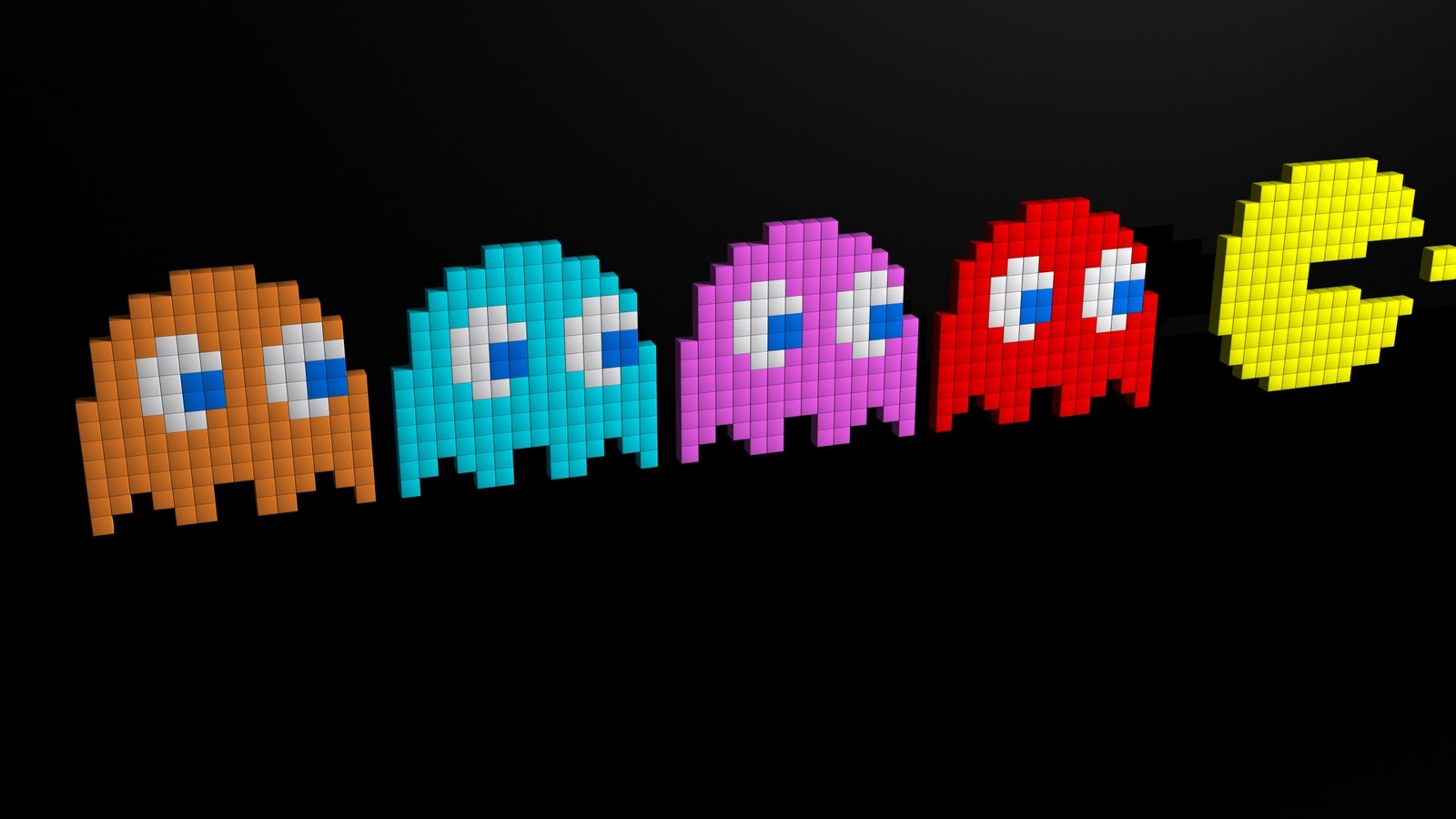
Pac-Man’s gameplay is deceptively simple yet incredibly engaging. The player controls Pac-Man, a yellow, circular character, through a maze filled with tiny dots known as pellets. The objective is to navigate the maze and eat all the pellets while avoiding four ghosts: Blinky, Pinky, Inky, and Clyde. Each ghost has its distinct personality and behavior, which adds a strategic element to the game. The player must constantly stay alert as the ghosts move through the maze in pursuit of Pac-Man. The game also includes four larger pellets called “Power Pellets,” which, when consumed, give Pac-Man the temporary ability to eat the ghosts, turning the tables on his pursuers and earning extra points. The challenge lies in clearing the maze while managing the threat posed by the ghosts, requiring both quick reflexes and strategic thinking.
What Made Pac-Man Unique?
Pac-Man stood out in the crowded arcade game market of the early 1980s for several reasons, all of which contributed to its widespread appeal and enduring legacy.
Character Design
One of Pac-Man’s most innovative features was the distinct personalities and behaviors assigned to the ghosts. Each ghost followed a unique strategy, which added depth to the gameplay. Blinky, the red ghost, was relentless, always chasing Pac-Man directly. Pinky, the pink ghost, tried to anticipate Pac-Man’s movements and positioned itself ahead of him, making it more challenging to evade. Inky, the cyan ghost, was unpredictable, using a combination of Blinky’s and Pinky’s strategies, making him the most difficult to outmaneuver. Finally, Clyde, the orange ghost, would sometimes chase Pac-Man but would also randomly move away, adding an element of surprise. These distinct behaviors made each game unpredictable and kept players engaged, as they had to adapt their strategies depending on which ghosts were closest.
Non-Violent Theme
At a time when many arcade games focused on shooting, fighting, and destruction, Pac-Man offered something refreshingly different. The game’s non-violent premise—eating pellets and avoiding ghosts—made it accessible and appealing to a much broader audience, including women and younger players. Pac-Man’s focus on evasion and survival rather than combat also made it a family-friendly game, contributing to its massive popularity.
Memorable Music
Pac-Man’s sound design played a crucial role in its success. The game’s catchy theme music and distinctive sound effects were instantly recognizable and added to its charm. The sounds of Pac-Man eating pellets, the tension-building chase music when ghosts pursued him, and the triumphant jingles when he consumed a Power Pellet or completed a level all created a memorable auditory experience. The music and sounds were integral to the game’s identity, making it not only fun to play but also enjoyable to listen to. This combination of engaging gameplay and iconic audio elements helped solidify Pac-Man’s status as a cultural phenomenon.
Pac-Man Fever: Cultural Impact

Who Are the Characters in Pac-Man Fever?
“Pac-Man Fever” refers not only to the cultural craze surrounding the game but also to the beloved characters that made it so memorable. At the center is Pac-Man, the iconic yellow character whose simple design and engaging gameplay captivated players worldwide. Alongside him are the four ghosts—Blinky, Pinky, Inky, and Clyde—each with their unique behavior patterns. Blinky, the relentless red ghost, directly chases Pac-Man, while Pinky, the pink ghost, tries to ambush him. Inky, the cyan ghost, combines elements of both strategies, making him unpredictable, and Clyde, the orange ghost, behaves erratically, sometimes chasing and other times retreating.
These characters added depth and strategy to Pac-Man, turning a simple maze game into a dynamic and challenging experience. Their distinct personalities not only contributed to the game’s addictive quality but also helped solidify Pac-Man’s place in pop culture. The phenomenon extended beyond the arcade, with these characters appearing in various media, merchandise, and even music, embodying the era’s fascination with video gaming.
The Arcade Craze
When Pac-Man debuted in arcades in 1980, it quickly became a cultural phenomenon. The game’s distinctive sound effects and upbeat music, combined with the constant beeping of high scores, created an immersive and lively atmosphere that drew crowds. Pac-Man’s appeal transcended the usual gaming demographic, attracting players of all ages and backgrounds. The game’s easy-to-understand mechanics made it accessible to newcomers, while its strategic elements kept more experienced players engaged. As a result, Pac-Man contributed significantly to the communal and social aspects of gaming, making arcades a central part of entertainment culture during that era.
Pac-Man Merchandise
The explosive popularity of Pac-Man soonspiltd over into a vast array of merchandise. From T-shirts and lunchboxes to action figures and even a breakfast cereal, Pac-Man’s image was everywhere. This wave of merchandise made him one of the first video game characters to achieve significant recognition outside of the gaming world. The simplicity and distinctiveness of Pac-Man’s design—his round yellow shape with a wedge-shaped mouth—proved to be highly adaptable and marketable. As a result, Pac-Man became a symbol of 1980s pop culture, with his likeness appearing on a wide range of products and solidifying his status as an iconic figure.
Media Presence
Pac-Man’s influence extended into various media formats, amplifying his presence and impact. The hit single “Pac-Man Fever,” released by Buckner & Garcia in 1981, captured the game’s widespread appeal and reached number 9 on the Billboard Hot 100 chart. The song’s catchy tune and playful lyrics humorously portrayed the addictive nature of the game and the obsession with high scores, reflecting the broader cultural impact of Pac-Man.
Additionally, Pac-Man was featured in his animated television series produced by Hanna-Barbera. The show, which aired in the early 1980s, expanded on the game’s universe by introducing Pac-Man and his family into new storylines and adventures. This media presence further cemented Pac-Man’s status as a cultural icon, showcasing his influence beyond just the arcade and into mainstream entertainment.
What Position Was Pac-Man Fever in the Charts?
“Pac-Man Fever,” a song by Buckner & Garcia, became a significant part of the early 1980s pop culture, climbing to number 9 on the Billboard Hot 100 chart in March 1982. The song’s success was fueled by its catchy tune and lyrics that perfectly captured the excitement and obsession surrounding the Pac-Man arcade game. It resonated with an abroade audience, from avid gamers to those who had never set foot in an arcade. It made it a crossover hit that extended the game’s influence beyond just the gaming community.
The chart success of “Pac-Man Fever” underscored how deeply Pac-Man had infiltrated popular culture. The game was no longer just an arcade sensation; it had become a cultural phenomenon, influencing everything from music to merchandise. The song served as an anthem for the era, symbolizing how video games had started to shape entertainment and daily life in ways previously unimaginable. This crossover into the music world was a clear indication of the game’s broad appeal and its role in defining a new age of pop culture.
Legacy of Pac-Man
Influence on Game Design
Pac-Man’s groundbreaking success reshaped the landscape of game design in several key ways. First and foremost, it demonstrated that video games could appeal to a broader demographic, including women and younger players, which was a significant shift from the predominantly male-oriented arcade games of the time. The game’s engaging design, characterized by its unique maze navigation and colorful, memorable characters, highlighted the importance of character design and personality in crafting compelling gaming experiences.
The distinctive ghosts with their behaviors and Pac-Man’s simple yet iconic appearance set a precedent for developing characters with personality and backstory. This approach influenced future game developers to create more relatable and immersive characters, leading to the emergence of other gaming icons. Pac-Man’s success showed that a well-designed character could become a central element of a game’s appeal, encouraging a focus on narrative and personality in game development.
Ongoing Popularity
Pac-Man’s enduring popularity is a testament to its timeless appeal and adaptability. Since its debut, the game has been ported to virtually every gaming platform, from early home consoles like the Atari 2600 to modern smartphones and tablets. The franchise has continued to evolve with new versions and spin-offs, such as Ms. Pac-Man, which introduced new gameplay elements and expanded on the original concept, and Pac-Man Championship Edition, which modernized the classic game with updated graphics and features. Pac-Man 256, inspired by the endless runner genre, introduced a fresh twist on the original gameplay. These adaptations have ensured that Pac-Man remains relevant, continuously introducing new generations to the beloved character and keeping the franchise alive in the gaming world.
Honors and Recognition
Pac-Man’s impact on the gaming industry has been widely recognized. In 2005, it was inducted into the World Video Game Hall of Fame, a testament to its significance in the history of video games. Beyond gaming, Pac-Man has become a cultural icon, frequently appearing in various forms of media, including movies, TV shows, and other cultural references. This widespread recognition underscores Pac-Man’s role as a symbol of the growth and evolution of the gaming industry. The character’s influence extends beyond the arcade, reflecting its deep integration into popular culture and its enduring legacy as a pioneering force in gaming history.
The Psychology of Pac-Man Fever
Why Was Pac-Man So Addictive?
Pac-Man’s addictive nature stems from a combination of simple yet engaging gameplay and psychological motivators. The game features easy-to-understand mechanics: players navigate a maze, eat pellets, and avoid ghosts. This simplicity made Pac-Man accessible to a broad audience, while the game’s increasing difficulty kept players continually challenged.
The short, discrete levels allowed players to experience quick bursts of success and gratification, encouraging them to keep playing. Clear goals, such as achieving high scores and progressing through levels, provided tangible rewards and a sense of accomplishment. This constant reinforcement of progress and the opportunity to improve skills contributed to the game’s addictive quality, as players were driven to beat their previous scores and master the game.
The Social Aspect
Pac-Man Fever extended beyond the individual gaming experience to create a rich social environment. Arcades became vibrant social hubs where players gathered not only to play but to share strategies, compete for high scores, and engage in friendly banter. This communal aspect of arcade gaming fostered a sense of camaraderie and competition among players. The shared enthusiasm for Pac-Man created bonds between individuals who might not otherwise have interacted, turning arcade visits into social events. This social interaction added an extra layer of enjoyment to the game, as players relished the opportunity to connect with others and be part of a larger gaming community. The collective experience of Pac-Man Fever, therefore, was as much about the social connections formed as it was about the gameplay itself.
Pac-Man in the Digital Age

Modern Adaptations
In the digital era, Pac-Man has undergone numerous adaptations that breathe new life into the classic game while preserving its beloved core mechanics. The game has been adapted for mobile platforms, allowing it to reach a new generation of players who can enjoy Pac-Man on smartphones and tablets. These modern versions often feature enhanced graphics and updated gameplay elements, such as new mazes, power-ups, and improved soundtracks, to appeal to contemporary tastes while retaining the original charm.
However, digital adaptations have introduced online features like leaderboards and multiplayer modes, adding competitive and social dimensions to the gameplay. Players can now compete globally for high scores or enjoy cooperative and competitive play with friends, expanding the game’s appeal beyond its arcade roots. These updates have helped Pac-Man remain relevant and engaging in a rapidly evolving gaming landscape, ensuring that the game continues to captivate audiences, both old and new.
Cultural References
Pac-Man’s influence extends far beyond the arcade, manifesting in numerous cultural references across various media and art forms. His distinctive design, featuring the simple yet iconic yellow character, remains instantly recognizable and has made its mark on movies, TV shows, advertisements, and more. Pac-Man has been featured in everything from nostalgic references in popular films and television series to creative uses in modern art and fashion.
The game’s mechanics and visual elements have inspired countless homages and parodies, reflecting its enduring appeal and cultural significance. Pac-Man-themed merchandise continues to be popular, and his image is often used in contemporary designs and promotional materials. This ongoing presence in popular culture highlights Pac-Man’s status as a timeless figure whose impact on entertainment and media continues to resonate across generations.
Pac-Man’s rise from a simple arcade game to a cultural icon highlights the impact of innovative design and broad appeal. Designed to engage a wide audience with its non-violent, maze-based gameplay, Pac-Man quickly became a sensation, fostering community in arcades and inspiring diverse adaptations. Its distinctive features and challenging mechanics ensured lasting popularity. Today, Pac-Man’s legacy endures through his presence in music, television, and merchandise. This enduring relevance underscores the joy video games can bring and the power of creative design to create lasting cultural phenomena. Pac-Man remains a timeless symbol of gaming’s impact on popular culture.