In the ever-evolving world of space exploration, the launch of Luna 21 stands as a significant milestone that captures the imagination of scientists, space enthusiasts, and curious minds alike. As we delve into the intricacies of this groundbreaking mission, we uncover the technological marvels, scientific objectives, and the potential impact Luna 21 could have on our understanding of the moon and beyond.
Table of Contents
When was Luna 21 launched?
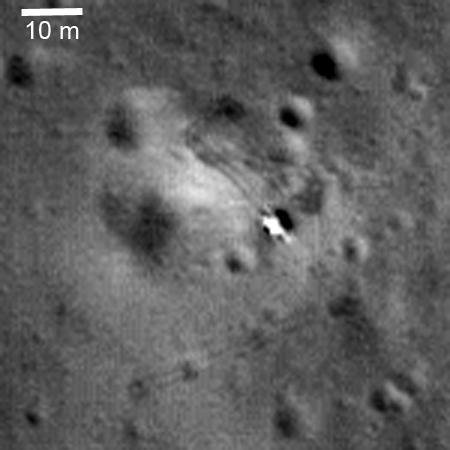
Luna 21 (Ye-8 series) was an uncrewed space mission and its spacecraft of the Luna program, also called Lunik 21, in 1973. The spacecraft landed on the Moon and deployed the second Soviet lunar rover, Lunokhod 2. The primary objectives of the mission were to collect images of the lunar surface, examine ambient light levels to determine the feasibility of astronomical observations from the Moon, perform laser ranging experiments from Earth, observe solar X-rays, measure local magnetic fields, and study mechanical properties of the lunar surface material.

What country launched Luna 21?
The Soviet Union launched Luna 21 on January 8, 1973. As part of the Luna program it aimed to explore the lunar surface using the Lunokhod 2 rover. The mission’s objectives included conducting experiments and analyzing soil samples, contributing valuable scientific data that enhanced our understanding of the Moon’s geological composition and surface conditions.
The Historical Context
In the tapestry of space exploration, the moon’s allure has fascinated civilizations for centuries. The climax came in 1969 with NASA’s Apollo 11, marking the first human-crewed moon landing. Subsequent robotic missions unveiled lunar secrets, from iconic images of Armstrong’s steps to rovers probing its crannies. Luna 21, continuing this cosmic quest, stands as the latest chapter in humanity’s persistent exploration, contributing to the ongoing narrative of lunar mystery. With each mission, we unravel the ancient secrets concealed within the moon’s craters, adding layers to our cosmic understanding and reinforcing the profound significance of lunar exploration in our shared history.
Luna 21: A Brief Overview
Luna 21, launched on 8 January 1973, marks the pinnacle of technological prowess in lunar exploration. As a robotic spacecraft, its advanced capabilities are tailored to unravel the moon’s geological and mineralogical mysteries. The mission’s multifaceted objectives encompass a comprehensive approach to lunar study:
Lunar Surface Exploration
Luna 21’s suite of cutting-edge instruments is a scientific marvel, enabling in-depth surface analysis. Scientists eagerly anticipate scrutinizing the moon’s topography, soil composition, and mineral content, providing a nuanced understanding of its geological makeup.
Sample Collection
A pivotal aspect of Luna 21’s mission is the collection of soil and rock samples from the lunar surface. These specimens hold the potential to unlock invaluable insights into the moon’s geological history and evolutionary processes, shedding light on the forces that shaped our celestial neighbor.
Advanced Imaging
Equipped with high-resolution cameras, Luna 21 captures detailed images of the lunar landscape, contributing to a comprehensive catalog of the moon’s features. From the rugged beauty of craters to the majestic expanse of mountains and plains, these images enrich our visual understanding of the moon’s complex terrain.
Technology Demonstration
Luna 21 isn’t merely a scientific mission; it serves as a trailblazer for future lunar and deep-space exploration endeavors. The incorporation of innovative technologies, spanning robotics, communication systems, and autonomous navigation, positions Luna 21 as a pioneering force shaping the landscape of space exploration for years to come. The mission stands as a testament to human ingenuity, pushing the boundaries of what is technologically achievable in our quest to explore the cosmos.
Technological Marvels on Board

A critical aspect of Luna 21’s significance lies in the cutting-edge technologies it employs. Some of the noteworthy features include:
1. Autonomous Navigation Systems
Luna 21’s advanced autonomous navigation systems represent a breakthrough in space exploration technology. These systems are designed to function without continuous guidance from Earth, relying on sophisticated algorithms and sensors. The spacecraft can analyze its surroundings, identify obstacles, and adjust its course in real time, allowing it to navigate the lunar terrain independently.
This autonomy significantly reduces the need for constant communication with Earth, which is especially crucial during the time delays in signal transmission to and from the Moon. By relying on autonomous navigation, Luna 21 can make decisions on the spot, adapting to unforeseen challenges and ensuring a more efficient exploration process. This capability is a cornerstone for future space missions, paving the way for more extended and complex operations in distant celestial bodies.
2. Precision Landing Systems
The precision landing systems on Luna 21 mark a milestone in lunar exploration. These systems utilize advanced sensors and guidance technology to target specific regions on the lunar surface with unparalleled accuracy. Precision landing is crucial for several reasons:
Mission Objectives
Space missions often have specific objectives, such as exploring particular geological features or studying specific lunar environments. Precision landing allows Luna 21 to reach these designated locations with precision, maximizing the chances of mission success.
Scientific Data Collection
Accurate landing ensures that scientific instruments and payloads are deployed in optimal locations. This is especially important for collecting diverse and meaningful data, contributing to our understanding of the Moon’s composition, history, and potential resources.
Operational Efficiency
Precision landing minimizes the need for the spacecraft to traverse long distances on the lunar surface, conserving energy and extending the operational lifespan of the mission.
3. Robotic Arm for Sample Collection
Luna 21’s robotic arm is a marvel of engineering tailored for the delicate task of collecting soil and rock samples from the lunar surface. This robotic arm is equipped with a range of tools and sensors, allowing it to perform precise movements and manipulate objects with great accuracy.
Sample Accessibility
The robotic arm extends Luna 21’s reach, enabling it to access lunar areas that would be challenging or impossible to reach without direct physical contact. This capability is crucial for exploring rugged or uneven terrains that might harbor unique geological features.
Scientific Exploration
By collecting samples with precision, scientists can gain valuable insights into the Moon’s geological composition, history, and potential resources. These samples are invaluable for furthering our understanding of the lunar environment and can contribute to broader scientific knowledge about the solar system.
Mission Flexibility
The versatility of the robotic arm enhances the mission’s adaptability, allowing scientists to adjust their sample collection strategy based on unexpected discoveries or changing mission priorities.
Scientific Significance
The scientific community eagerly anticipates the data Luna 21 is poised to deliver. Some of the key scientific questions the mission aims to address include:
Lunar Evolution
Scientists are eager to delve into the collected samples to uncover the moon’s geological evolution. This involves investigating the processes that have shaped the lunar surface over time, such as volcanic activity, tectonic movements, and the impact of celestial bodies. By understanding these mechanisms, researchers can piece together a comprehensive timeline of the moon’s geological history, shedding light on how it transformed from its early state to the terrain we observe today.
Resource Exploration
Luna 21’s meticulous examination of the moon’s soil and mineral composition is not just a scientific endeavor; it holds practical implications for potential future lunar exploration and colonization. The mission aims to identify and characterize resources that could be crucial for sustaining human activities on the moon. Whether it’s the presence of water ice, rare minerals, or other valuable substances, this information could guide future missions in selecting landing sites and planning resource utilization strategies.
Impact Crater Studies
Luna 21’s advanced imaging capabilities provide an unprecedented opportunity to scrutinize lunar impact craters with remarkable detail. By studying these craters, scientists can gain insights into the frequency, size, and effects of asteroid and meteoroid impacts on the moon. This data not only contributes to our understanding of lunar geology but also has broader implications for planetary defense, offering valuable information about the history of impact events in our solar system.
Global Collaboration and Partnerships
Embarking on the mission to explore the lunar landscape, Luna 21 stands as a testament to the power of global collaboration. In this joint effort, space agencies, research institutions, and private entities from across the globe come together, pooling their resources and expertise to advance humanity’s understanding of the Moon.
Global Collaboration Across Sectors
- Luna 21 represents a globally collaborative initiative involving space agencies, research institutions, and private entities from around the world.
- International space agencies, including NASA, ESA, Roscosmos, and CNSA, contribute unique expertise, technology, and resources, fostering a shared effort in lunar exploration.
Fostering Global Cooperation for Scientific Advancement
- The collaborative approach not only advances lunar exploration objectives but also contributes to a global pool of space exploration knowledge.
- By promoting international cooperation, Luna 21 sets a precedent for future joint endeavors, strengthening relations and building a foundation for shared scientific achievements in space exploration and beyond.
Public Engagement and Education

Recognizing the significance of engaging the public, space agencies, and educational institutions have orchestrated outreach programs. These initiatives, including virtual tours, live broadcasts, and educational resources, provide a captivating avenue for individuals of all ages to delve into Luna 21’s mission objectives and discoveries.
Holistic Outreach Strategies
Space agencies and educational institutions collaboratively engineer comprehensive outreach programs for missions like Luna 21. Integrating virtual tours, live broadcasts, and educational resources, these initiatives cater to diverse audiences, ensuring an immersive and accessible experience for the public.
Virtual Tours
Immerse the audience in Luna 21’s mission by offering virtual tours of the spacecraft, rover, and mission control. This interactive experience allows individuals to explore the intricacies of the mission, fostering a deeper understanding and connection.
Live Broadcasts
Beyond mere observation, live broadcasts enable real-time participation in Luna 21’s key events. From rover landings to groundbreaking discoveries, these broadcasts create a shared experience, emphasizing the collaborative nature of space exploration.
Real-Time Interactive Experiences
Live broadcasts play a central role in establishing a real-time connection between Luna 21’s mission and the public. By broadcasting key events, such as rover landings and discoveries, across various platforms, agencies enable a broad audience to actively witness and engage in the exhilaration of Luna 21’s exploration.
Broad Accessibility
Broadcasting events on diverse platforms, including social media and online streaming services, ensures that a broad and global audience can participate. This accessibility democratizes the experience, allowing individuals from different backgrounds to share in the excitement of lunar exploration.
Interactive Engagement
Beyond passive viewership, live broadcasts often incorporate interactive elements such as Q&A sessions with scientists and engineers. This fosters a sense of community engagement, as the public can pose questions, receive insights, and feel directly connected to the mission’s progress.
Education for All Ages
Crafted to be inclusive and aligned with educational standards, resources are designed to appeal to individuals of all ages. These accessible materials not only inform but also inspire a diverse audience, fostering interest in STEM fields. Through these initiatives, there is a concerted effort to contribute to a broader cultural appreciation for the wonders of space exploration.
Diverse Learning Materials
Educational resources go beyond traditional formats, incorporating diverse mediums such as videos, interactive simulations, and online games. This multi-faceted approach ensures engagement across various learning styles and preferences.
Inspiring STEM Interest
By aligning educational resources with science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) principles, the initiatives aim to inspire the next generation of scientists, engineers, and space enthusiasts. This strategic focus contributes to the broader goal of cultivating a workforce interested in advancing human knowledge and exploration.
Challenges and Solutions
The journey to launch and operate Luna 21 faced formidable challenges, including the harsh lunar environment and complexities of autonomous navigation. The mission’s success stands as a testament to the resilience and ingenuity of the scientific and engineering teams involved.
Navigating Harsh Lunar Conditions
Luna 21 faced challenges associated with the unforgiving lunar environment, requiring the scientific and engineering teams to develop solutions for spacecraft durability and functionality in extreme conditions, such as temperature variations and surface irregularities.
Overcoming Autonomous Navigation Complexities
The mission grappled with the complexities of autonomous navigation, demanding innovative solutions to ensure Luna 21’s ability to navigate and operate independently. The successful execution of the mission underscores the resilience and ingenuity of the teams involved, highlighting their capacity to overcome intricate technical challenges in the realm of space exploration.
Future Implications
As Luna 21 continues its mission, its gathered data is poised to have far-reaching implications for future lunar exploration, influencing spacecraft design, guiding landing site selection, and shaping the trajectory of scientific inquiry in lunar and planetary science.
Informing Spacecraft Design
The ongoing mission of Luna 21 is poised to impact the design of future spacecraft. The data collected, including information on the lunar environment and operational challenges, will serve as a valuable resource for engineers and designers. This knowledge will contribute to the refinement and optimization of spacecraft, enhancing their capabilities for future lunar exploration endeavors.
Guiding Site Selection for Future Missions
Luna 21’s findings play a crucial role in guiding the selection of landing sites for upcoming lunar missions. The data gathered about the lunar surface, geological features, and potential resource availability will inform strategic decisions about where to deploy future spacecraft. This precision in site selection is vital for maximizing the scientific return and mission success in subsequent lunar exploration initiatives.
Shaping the Trajectory of Scientific Inquiry
The insights derived from Luna 21’s mission will have a lasting impact on the direction of scientific inquiry in the realm of lunar and planetary science. The data will contribute to a deeper understanding of lunar processes, geological history, and potential resource utilization. As a result, future research questions and exploration objectives in lunar and planetary science will be shaped by the discoveries made during Luna 21’s mission, influencing the trajectory of scientific advancements in these fields.
The launch of Luna 21 marks a historic moment in the ongoing human quest for knowledge and exploration. This robotic spacecraft, laden with advanced technologies and scientific instruments, promises to unravel the mysteries of the moon and contribute to our broader understanding of the cosmos. As Luna 21 continues its mission, the world awaits the groundbreaking discoveries that will shape the future of space exploration.