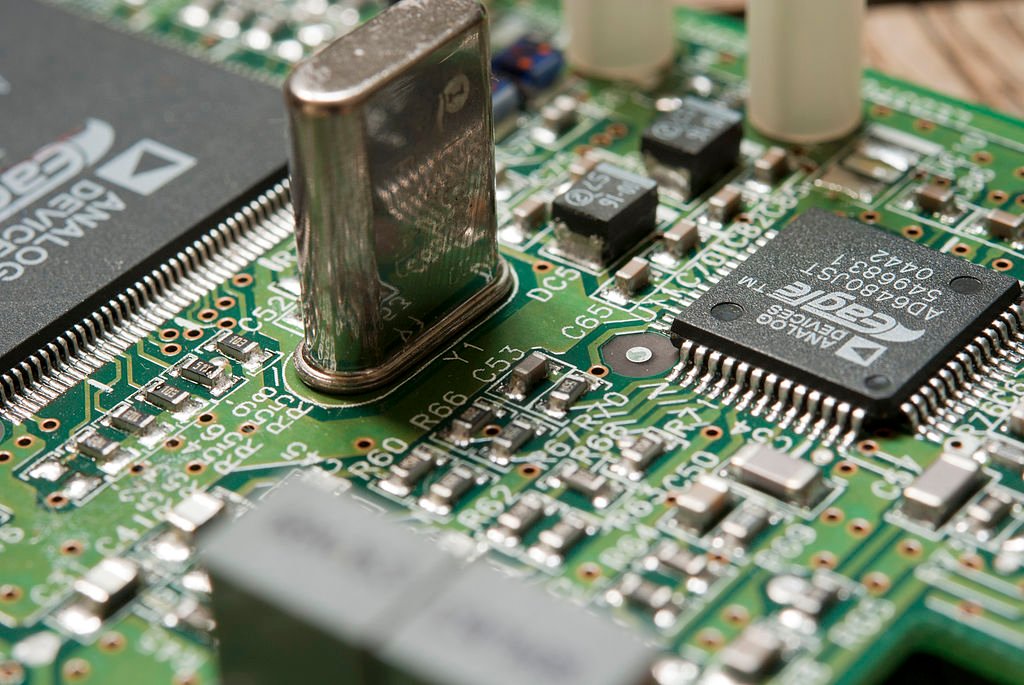
Few innovations have had as profound an impact in the relentless pursuit of technological advancement as Integrated Circuits (ICs). These microscopic marvels have catalyzed a transformative shift in computing, enabling the creation of smaller, more efficient, and incredibly capable computers. In this comprehensive guide, we journey through time and technology, unraveling the story of integrated circuits, from their origins and development to their profound role in making smaller computers a reality.
Table of Contents
Who made the first small computer?
The title of “the first small computer” can be attributed to several early inventions, but one notable example is the “Kenbak-1.” Designed by John Blankenbaker in 1970, the Kenbak-1 is often considered the world’s first commercially available personal computer. It was a minimalist machine, using integrated circuits to perform basic tasks, including calculations and logical operations. Though primitive by today’s standards, the Kenbak-1’s compact size and user-friendly design set the stage for developing smaller, more accessible computers. It paved the way for the personal computing revolution in the coming decades, making computing accessible to individuals and businesses.

The Birth of Integrated Circuits
The Early Days of Computing
The roots of integrated circuits can be traced back to the early days of computing when computers were massive, room-filling monoliths. While groundbreaking in their own right, these formidable machines were far from the vision of compact and portable computing we enjoy today.
The dream of a computer that could fit on a desk, alone in one’s pocket, seemed like a distant fantasy. But within this landscape of bulky machinery lay the seeds of innovation that would eventually give birth to the integrated circuit.
The Spark of Innovation
The advent of integrated circuits can be attributed to two brilliant minds: Jack Kilby and Robert Noyce. In 1958, Jack Kilby, working at Texas Instruments, created the first functioning integrated circuit. His invention integrated several electronic components onto a single semiconductor material, marking a pivotal moment in the history of electronics.
Simultaneously, Robert Noyce, co-founder of Fairchild Semiconductor and later Intel, developed a similar concept but with a crucial advancement – he used a silicon wafer as the base, allowing for the mass production of integrated circuits.
These groundbreaking inventions set the stage for a technological revolution that would change the world forever.
Which technology made the size of computer smaller?
The technology that made the size of computers smaller is the development and integration of microelectronics and integrated circuits (ICs). Integrated circuits, often referred to as microchips or simply chips, allowed for the miniaturization of electronic components. This miniaturization made it possible to pack more computing power into smaller spaces, creating smaller and more portable computers. Integrated circuits are the fundamental technology that revolutionized computing by reducing the size and increasing the efficiency of electronic components within computers.
Understanding Integrated Circuits
What Are Integrated Circuits?
Before diving deeper into the history and impact of integrated circuits, it’s essential to grasp the fundamental concept of integrated circuits and how they function.
At their core, integrated circuits are tiny circuits that incorporate various electronic components, such as transistors, resistors, capacitors, and diodes, onto a single semiconductor substrate. This consolidation of features onto a single chip results in a compact, efficient, and powerful electronic device.
Integrated circuits come in various forms, including microprocessors, memory chips, and application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs), each tailored to specific functions and applications.
The Building Blocks
To truly appreciate the significance of integrated circuits, it’s essential to understand the role of their constituent components:
Transistors
Transistors are the workhorses of integrated circuits. These semiconductor devices amplify or switch electronic signals. They act as digital switches, allowing for the representation of binary information (0s and 1s) that underpins all computing operations.
Resistors
Resistors control the flow of electrical current within a circuit. They are vital for setting voltage levels and regulating the behavior of various components.
Capacitors
Capacitors store and release electrical energy. They play a crucial role in smoothing out electrical signals providing stability to integrated circuits.
Diodes
Diodes are semiconductor devices that allow the flow of electrical current in one direction while blocking it in the opposite direction. They are essential for rectifying alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC) and protecting components from reverse voltage.
The Miniaturization Miracle
The Size Revolution
One of the most significant contributions of integrated circuits to computing is their ability to miniaturize electronic components. This miniaturization, often called “scaling down,” is a defining feature of integrated circuits and has led to the creation of smaller, more efficient computers.
The miniaturization of components within integrated circuits made it possible to shrink computers from room-sized behemoths to portable devices in our pockets. This evolution not only revolutionized computing but also transformed the way we interact with technology.
Moore’s Law
The remarkable progress in miniaturization owes much to Moore’s Law, a prediction made by Gordon Moore, co-founder of Intel, in 1965. Moore’s Law states that the number of transistors on an integrated circuit would double approximately every two years while the cost per transistor would decrease.
This prediction became a self-fulfilling prophecy, driving the semiconductor industry to innovate and scale down electronic components continuously. The relentless pursuit of Moore’s Law led to the development of smaller, faster, and more energy-efficient integrated circuits, laying the foundation for the computing devices we use today.

Applications of Integrated Circuits
Computers on the Go
One of the most visible impacts of integrated circuits is the transformation of computing devices into portable and handheld marvels. The development of smaller and more power-efficient integrated circuits paved the way for laptops, tablets, and smartphones.
Laptops
The miniaturization of components allowed for the creation of laptops, which combined the power of traditional desktop computers with portability. Laptops became indispensable tools for professionals and consumers alike, enabling work and entertainment on the go.
Tablets
Tablets emerged as a new category of computing devices, characterized by their compact form factor and touch-based interfaces. Integrated circuits played a pivotal role in making tablets lightweight, responsive, and capable of handling various tasks.
Smartphones
Perhaps the smartphone is the most iconic manifestation of integrated circuits’ impact. These pocket-sized supercomputers are powered by highly efficient integrated circuits that enable communication, photography, navigation, and countless other functions.
The Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things (IoT) represents another dimension of integrated circuits’ influence. Internet of Things is a network of interconnected devices that communicate and share data, leading to smart homes, cities, and industries.
Integrated circuits are at the heart of IoT devices, making it possible for everyday objects like thermostats, appliances, and wearable devices to collect, process, and transmit data. This connectivity enhances efficiency, convenience, and sustainability across various domains.
The proliferation of IoT devices is a testament to integrated circuits’ ability to enable seamless communication and data exchange, revolutionizing how we interact with our surroundings.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Power Efficiency
While integrated circuits have made remarkable strides in miniaturization and performance, they have also faced challenges related to power consumption. As components continue to shrink, minimizing power consumption becomes increasingly crucial to prevent overheating and extend battery life in portable devices.
Researchers and engineers are exploring various strategies to enhance power efficiency, including new materials, innovative transistor designs, and advanced cooling solutions. These efforts aim to strike a balance between performance and energy consumption in future integrated circuits.
Beyond Silicon

As we look to the future, the limits of traditional silicon-based integrated circuits are becoming apparent. Researchers are actively exploring alternative materials and technologies to push the boundaries of computing.
- Quantum Computing
Quantum computing represents a groundbreaking frontier. Quantum bits, or qubits, can exist in multiple states simultaneously, potentially enabling quantum computers to solve complex problems exponentially faster than classical computers. Integrated circuits for quantum computing are a focal point of research, potentially revolutionizing fields such as cryptography, materials science, and drug discovery.
- Molecular Electronics
Molecular electronics is another exciting avenue. Researchers are investigating the use of individual molecules as electronic components, potentially leading to ultra-compact and energy-efficient integrated circuits. This frontier offers new possibilities for computing and could redefine the future of electronics.
Impact on Society
Education and Accessibility
Integrated circuits have made the widespread availability of smaller computers possible, transforming education and accessibility. Students worldwide can access powerful computing tools that facilitate learning, research, and collaboration. Integrated circuits have democratized knowledge and opened doors to new opportunities for people around the globe.
Innovation and Industry
The impact of integrated circuits extends far beyond consumer electronics. They have fueled innovation in various industries, from healthcare and automotive to aerospace and manufacturing. Advanced integrated circuits enable the development of cutting-edge technologies, making processes more efficient, products more capable, and industries more competitive.
Which invention allowed computers to become smaller in size?
The invention that allowed computers to become smaller in size is the “Integrated Circuit” or “Microchip.”
- Integrated Circuits (ICs)
Integrated circuits, commonly known as microchips or chips, were a groundbreaking invention that transformed computing. They allowed electronic components such as transistors, resistors, and capacitors to be miniaturized and combined onto a single semiconductor substrate.
- Miniaturization
ICs enabled the miniaturization of electronic components, reducing the physical size of computer circuitry.
- Increased Density
By packing more components into a smaller space, computers could perform complex tasks with greater processing power while occupying less physical volume.
- Portability
Smaller components made laptops, tablets, and smartphones possible, revolutionizing the computing industry.
Which of the modern day computer is the smallest in size?
The smallest computers are often associated with microcontrollers and microcomputers used in embedded systems and the Internet of Things (IoT). These tiny computing devices are designed for specific applications and are highly compact. Examples of such small computers include
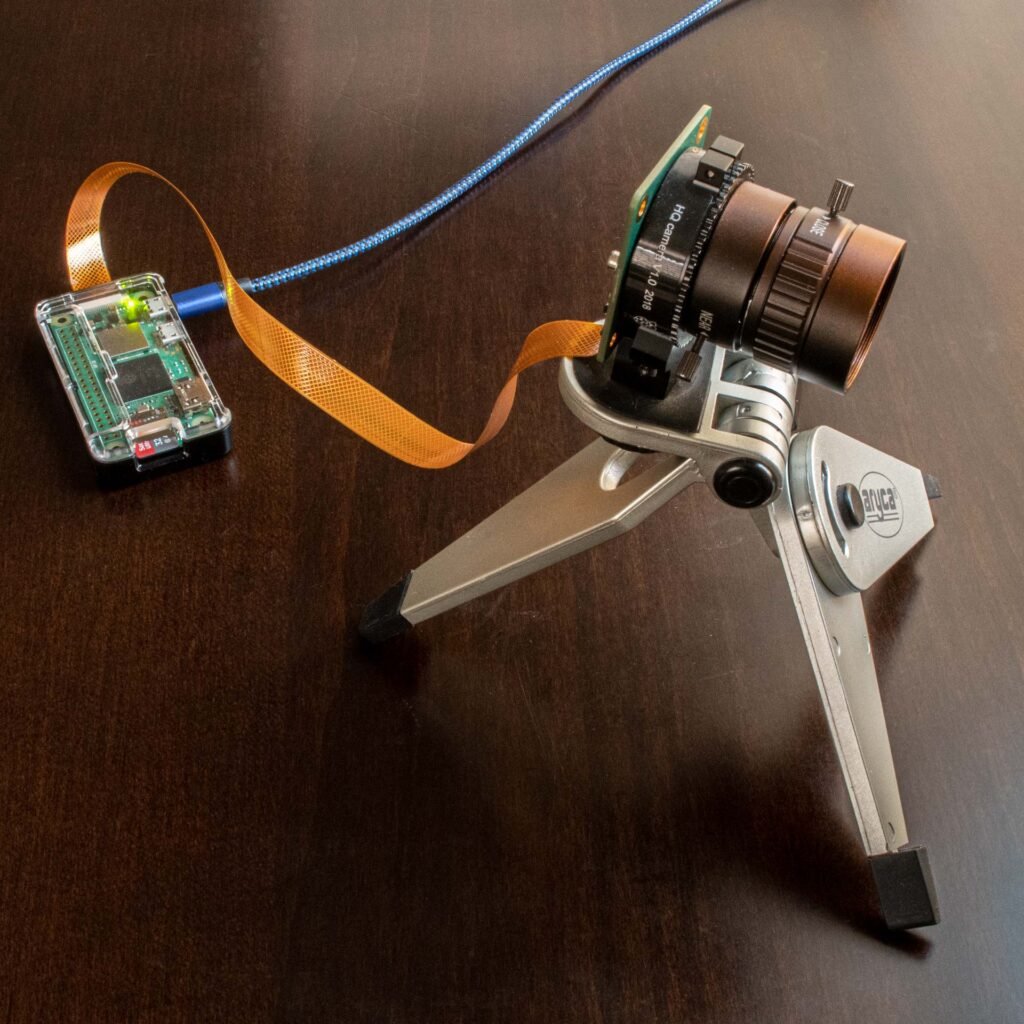
Raspberry Pi Zero
The Raspberry Pi Zero is an extremely small, credit card-sized single-board computer used for various DIY projects and IoT applications.
Arduino Nano
Arduino Nano is a small microcontroller board popular for embedded projects and known for its compact size.
Micro:bit
The BBC micro:bit is a pocket-sized computer designed for educational purposes. It encourages students to learn programming and electronics.
ESP8266 and ESP32
These are Wi-Fi and Bluetooth-enabled microcontrollers often used in IoT applications. They are tiny and power-efficient.
In this extensive exploration of integrated circuits technology, we have unveiled the remarkable journey that has led to smaller, more powerful computers becoming an integral part of our daily lives. Integrated circuits have revolutionized technology and transformed how we connect, work, and envision the future.
As we navigate this ever-evolving technological landscape, it’s clear that the role of integrated circuits remains central in shaping our world. Their relentless miniaturization and increasing capabilities promise a future where the boundaries of what’s possible expand, making our lives more efficient, connected, and exciting. Integrated circuits have made a more miniature computer possible, and their influence will continue to shape our future in ways we can only imagine. The journey of integrated circuits is an ongoing saga of innovation, and its following chapters promise even more incredible advancements that will reshape our world once again.