The history of self-driving cars is a compelling journey into the realm of autonomous vehicles, reshaping the landscape of transportation as we know it. The concept of autonomous transportation, once relegated to the realms of science fiction, is now an integral part of our reality. In this exploration of the history of self-driving cars, we delve into the remarkable milestones that have defined their evolution.
Self-driving cars, also known as autonomous vehicles, represent a paradigm shift in the way we think about mobility. They promise to revolutionize transportation by eliminating the need for human intervention in driving and offering safer, more efficient, and potentially more environmentally friendly alternatives.
The story begins with the seminal moment in 2005 when Stanford University’s autonomous vehicle, Stanley, triumphed in the DARPA Grand Challenge, covering 131 miles of treacherous desert terrain without human assistance. This remarkable achievement sparked widespread interest and laid the foundation for the development of self-driving cars.
Over the years, industry giants like Google, now operating under the name Waymo, made significant strides in autonomous vehicle technology. Their project, initiated in 2009, initiated rigorous testing, leading to the introduction of self-driving car prototypes onto public roads.
Nevada’s groundbreaking legislation in 2011, permitting the testing of autonomous vehicles on public roads, marked a pivotal moment for the technology’s legitimacy. Other states and countries soon followed suit, recognizing the potential benefits of autonomous transportation.
The history of self-driving cars also includes notable advancements from automakers like Audi, with its autonomous RS 7 that demonstrated high-speed capabilities, and Tesla, which introduced its Autopilot feature to consumer vehicles, showcasing the potential for mainstream adoption.
Fast-forward to the 2020s and companies like Waymo have launched fully autonomous taxi services, making it clear that self-driving cars are not just a concept but a burgeoning reality in the world of transportation.
As we journey through these pivotal milestones in the history of self-driving cars, it becomes evident that the road to autonomous transportation is paved with innovation, determination, and the unwavering pursuit of a future where self-driving cars redefine the way we move from one place to another.
Table of Contents
What was the first successful self-driving car?
The first successful self-driving car is often credited to “Stanley,” an autonomous vehicle developed by a team from Stanford University. Stanley achieved a historic milestone by winning the DARPA Grand Challenge in 2005. This competition, organized by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA), aimed to stimulate the development of autonomous vehicle technology for military applications.
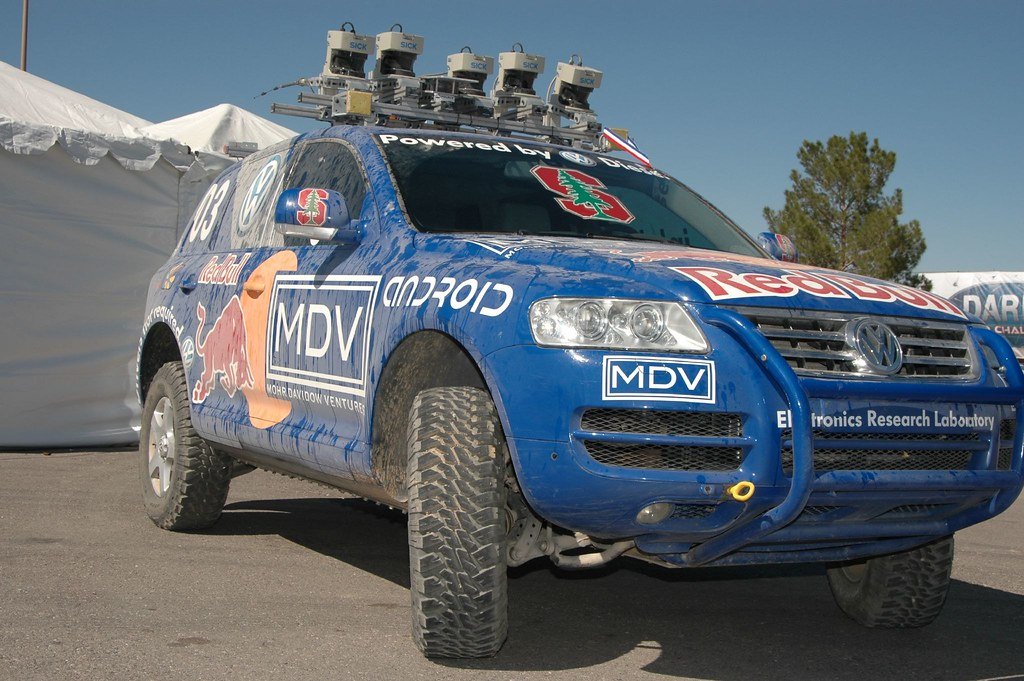

Stanley’s victory marked a significant moment in the history of self-driving cars. The vehicle was a modified Volkswagen Touareg SUV equipped with various sensors, including LIDAR, GPS, and cameras, as well as advanced navigation and obstacle avoidance software.
During the DARPA Grand Challenge, Stanley completed a 131-mile desert course in California’s harsh terrain without human intervention. It navigated through challenging obstacles, and rough terrain, and even interacted with other vehicles on the course. Stanley’s triumph demonstrated that self-driving technology had reached a level of maturity where it could tackle complex, real-world driving scenarios.
Stanley’s success sparked widespread interest in autonomous vehicle development and laid the foundation for subsequent advancements in the field. It showcased the potential of self-driving cars and encouraged further research and investment by academic institutions and industry leaders, ultimately paving the way for the development of the self-driving cars we see today.
What are the main points of self-driving cars?
Self-driving cars, also known as autonomous vehicles, represent a transformative technological advancement in the field of transportation. The main points of self-driving cars can be summarized as follows:
Safety
Self-driving cars have the potential to significantly reduce accidents caused by human error. They are equipped with sensors, cameras, radar, and advanced algorithms that can detect and react to their surroundings with greater precision and speed than humans.
Convenience
Autonomous vehicles offer unparalleled convenience. Passengers can engage in other activities, such as work or leisure, during their journeys, as there is no need for constant attention to driving.
Efficiency
Self-driving cars can optimize traffic flow by communicating with each other and traffic infrastructure. This can reduce congestion, shorten commute times, and lower fuel consumption.
Accessibility
Autonomous technology can make transportation more accessible to individuals who are unable to drive due to age, disability, or other reasons. It has the potential to improve mobility for the elderly and disabled populations.
Environmental Benefits
By optimizing routes and driving patterns, self-driving cars can contribute to reduced fuel consumption and emissions. This aligns with global efforts to combat climate change and reduce the environmental impact of transportation.
Economic Impact
The development and deployment of self-driving cars have the potential to create new industries and jobs related to technology, manufacturing, maintenance, and services.
Legislative and Ethical Challenges
The adoption of self-driving cars raises complex legal and ethical questions, including liability in the event of accidents, data privacy concerns, and the need for updated traffic regulations.
Cybersecurity
Autonomous vehicles rely heavily on software and connectivity, making them vulnerable to hacking and cybersecurity threats. Ensuring the security of self-driving car systems is a critical consideration.
Self-driving cars have the potential to revolutionize transportation by improving safety, convenience, efficiency, and accessibility while also addressing environmental and economic concerns. However, they also come with significant challenges that must be addressed for their widespread adoption and integration into our daily lives.
11 Milestones in Self-Driving Car History
The development of self-driving cars, also known as autonomous vehicles, has been a long and complex journey. Here are 11 major milestones in the history of self-driving cars:
Stanley Wins DARPA Grand Challenge (2005)
Stanford University’s groundbreaking achievement in the DARPA Grand Challenge of 2005, with their autonomous vehicle named Stanley, marked a pivotal moment in the history of autonomous vehicle technology. During this event, Stanley navigated a grueling 131-mile desert course without any human intervention, capturing the first-place prize.
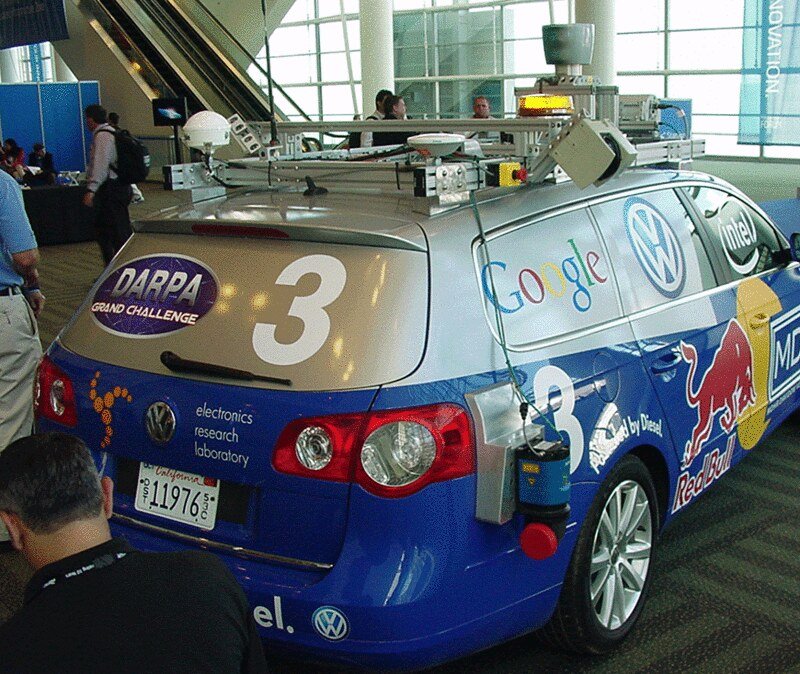

This remarkable feat served as a catalyst, igniting a newfound enthusiasm and serious interest in the development of autonomous vehicles. Before this competition, the idea of self-driving cars was largely confined to science fiction and viewed as a distant dream. However, Stanley’s success demonstrated that the concept of vehicles operating without human drivers was not only feasible but also within the realm of imminent possibility.
The DARPA Grand Challenge showcased the power of cutting-edge technologies such as advanced sensors, artificial intelligence, and precise mapping systems, which were integrated into Stanley to enable it to make real-time decisions and navigate complex, dynamic environments. This event spurred significant investment and research into autonomous vehicle technology by both academic institutions and industry leaders, setting the stage for the rapid advancements and innovations that have since reshaped the automotive landscape.
Google’s Self-Driving Car Project (2009)
In 2009, Google, the tech giant renowned for its pioneering endeavors, embarked on a groundbreaking journey into the realm of self-driving cars, a project that would later evolve into Waymo, a subsidiary under the Alphabet Inc. umbrella. The inception of this initiative marked a pivotal moment in the history of autonomous vehicles.
Google’s self-driving car project involved retrofitting conventional vehicles with an array of advanced sensors, including LiDAR, radar, and cameras, along with powerful onboard software systems. These technologies allowed the vehicles to perceive their environment in real time, making it possible for them to navigate safely and autonomously on public roads.
Through rigorous testing and continuous development, Google’s project demonstrated remarkable progress, attracting significant attention and investment. In 2015, the company unveiled a fully autonomous prototype vehicle, devoid of traditional controls like steering wheels and pedals, signaling their commitment to the vision of a future where self-driving cars were a commonplace mode of transportation.
This ambitious project laid the foundation for Waymo, which has since become a leader in the development and deployment of autonomous vehicle technology, offering ride-hailing services and forging partnerships with automakers to bring self-driving cars closer to mainstream adoption. Google’s initial foray into self-driving cars paved the way for the transformative potential of autonomous transportation.
Nevada Legalizes Autonomous Vehicles (2011)
In 2011, Nevada made history by becoming the first state in the United States to enact legislation explicitly permitting the testing and operation of autonomous vehicles on public roads. This pioneering move marked a significant turning point in the development of self-driving cars and set a precedent for other states and countries to follow suit.
Nevada’s decision to embrace autonomous vehicle testing was a testament to the state’s forward-thinking approach to technology and transportation. It recognized the potential of self-driving cars to revolutionize the automotive industry, improve road safety, and enhance mobility for individuals who may have difficulty driving due to age or disability.
By providing a legal framework for autonomous vehicle testing, Nevada not only encouraged innovation but also attracted technology companies and automakers to conduct their experiments within its borders. This, in turn, stimulated economic growth and job creation in the state while positioning Nevada as a hub for autonomous vehicle development.
Nevada’s trailblazing legislation paved the way for other states and countries to draft their own regulations, thereby accelerating the progress of self-driving car technology on a global scale. It demonstrated the importance of proactive governmental support in shaping the future of autonomous transportation.
Audi’s Autonomous RS 7 (2015)
In a groundbreaking display of the potential of self-driving technology, Audi unveiled an autonomous RS 7 that left automotive enthusiasts and experts alike in awe. This remarkable event took place at the Hockenheimring racetrack in Germany, a venue synonymous with high-speed racing and precision driving.
The Audi RS 7, a high-performance sports car, not only completed laps on the demanding racetrack but did so entirely without human intervention. It navigated sharp turns, accelerated on straightaways, and executed maneuvers with a level of precision that showcased the incredible capabilities of self-driving technology even in the world of performance-oriented vehicles.
This demonstration illustrated that self-driving technology is not limited to mundane or everyday transportation; it has the potential to enhance and redefine the very essence of high-speed driving and racing. The implications are far-reaching, from improving track performance and safety to opening up new possibilities for motorsports and enthusiast-driven experiences. Audi’s autonomous RS 7 at Hockenheimring marked a pivotal moment, highlighting that self-driving cars can be both thrilling and technologically impressive, appealing to a broader spectrum of automotive enthusiasts.
Uber’s Self-Driving Car Tests (2016)
In a groundbreaking move, Uber initiated its self-driving car testing program in the city of Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. This marked a significant step forward in the development and integration of autonomous vehicles into the realm of ride-sharing services. Users of the Uber app were given the opportunity to experience the future of transportation firsthand, as they could now hail autonomous vehicles as part of their regular ride-hailing service.

Pittsburgh was chosen as the testing ground due to its dynamic urban environment, which provided a real-world challenge for Uber’s self-driving technology. The program aimed to gather valuable data, refine algorithms, and enhance the safety and reliability of autonomous vehicles.
This bold venture not only demonstrated Uber’s commitment to innovation but also underlined the potential of self-driving cars to revolutionize the ride-sharing industry. It sparked both excitement and discussions about the future of transportation, safety, and the role of autonomous vehicles in urban mobility. While the program has evolved and faced its share of challenges, it served as a pivotal moment in the ongoing development of autonomous transportation solutions.
Tesla’s Autopilot (2015)
In 2015, Tesla made a significant stride in the realm of self-driving technology with the introduction of its Autopilot feature. While not a fully autonomous system, Autopilot represented a groundbreaking advancement in driver-assistance capabilities for consumer vehicles.
Autopilot leveraged a suite of sensors, cameras, and radar to enable semi-autonomous driving functions. These included adaptive cruise control, which automatically adjusted the vehicle’s speed to match traffic, and lane-keeping assistance, which helped the car stay within its lane. The combination of these features allowed for a more relaxed and comfortable driving experience, particularly during long highway stretches.
What made Tesla’s Autopilot system unique was its ability to receive over-the-air software updates, enhancing and expanding its capabilities over time. This feature allowed Tesla vehicles to evolve and improve, pushing the boundaries of what was possible in terms of advanced driver-assistance systems.
However, it’s crucial to note that while Autopilot was a significant step toward self-driving technology, it still required the driver to remain engaged and alert, with hands on the steering wheel. Tesla made it clear that the system was not fully autonomous, and drivers were responsible for maintaining control and monitoring the vehicle’s actions.
Tesla’s Autopilot not only set the stage for further advancements in self-driving technology but also raised important questions and challenges related to driver trust, safety, and regulatory considerations in the emerging landscape of autonomous vehicles.
Waymo’s Fully Self-Driving Taxi Service (2020)
Waymo, a subsidiary of Alphabet Inc., made a groundbreaking stride in the world of autonomous transportation by launching a fully autonomous ride-hailing service in Phoenix, Arizona. This marked a significant milestone in the development of self-driving technology and its integration into everyday life.
What sets Waymo apart is its distinctive feature: the service operates without human safety drivers behind the wheel. This bold move signified a high level of confidence in the technology’s safety and reliability. Passengers were now able to summon a self-driving Waymo vehicle, and, without the presence of a human driver, experience a truly autonomous journey.
The launch of this service was not only a technological achievement but also a testament to the rigorous testing and refinement that autonomous vehicles underwent over the years. It was a clear indication that self-driving cars were no longer confined to the realm of experiments but had become a practical mode of transportation accessible to the public.
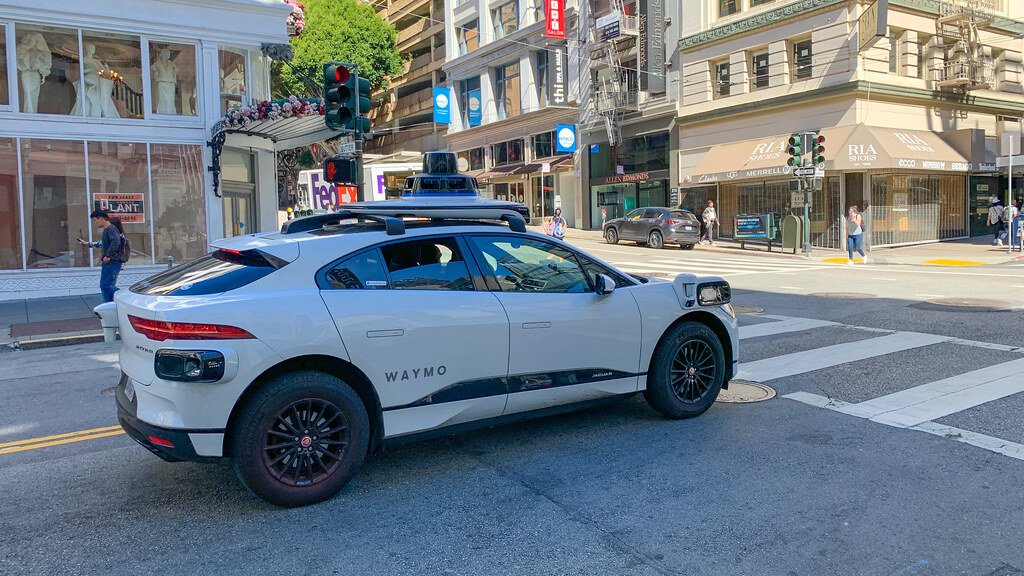

Waymo’s initiative in Phoenix provided valuable insights into the future of mobility, reshaping how people perceive and interact with transportation services. It also encouraged other companies in the autonomous vehicle space to further develop and deploy their self-driving technologies, driving the industry toward a future where self-driving cars are a common sight on the roads.
Cruise Origin Unveiled (2020)
General Motors’ subsidiary, Cruise, made a significant leap forward in the realm of autonomous transportation when it unveiled the Cruise Origin, an innovative self-driving electric vehicle meticulously crafted for the future of shared mobility. What sets the Origin apart is its striking departure from traditional vehicles – it lacks a conventional steering wheel and pedals, emblematic of its commitment to full autonomy.
Designed with a focus on ride-sharing and ride-hailing services, the Cruise Origin is poised to revolutionize urban transportation. Its spacious, cabin-like interior is intended to foster a communal atmosphere, with seating for multiple passengers. The absence of a human-centric driving apparatus not only maximizes interior space but also signals Cruise’s unwavering belief in the capabilities of autonomous technology.
The Cruise Origin embodies the fusion of cutting-edge hardware and software, equipped with a suite of sensors, cameras, and advanced AI algorithms that afford it an exceptional ability to perceive and navigate the complexities of urban environments. This pioneering approach to mobility holds the promise of reducing congestion, emissions, and the cost of transportation while advancing the vision of a self-driving future.
Legislation and Regulation (Ongoing)
Various countries and regions around the world have recognized the transformative potential of autonomous vehicles and are actively working on legislation and regulations to govern their deployment and operation. These rules are essential to ensure the safe integration of self-driving cars onto public roads and to establish clear accountability in the event of accidents or incidents.
The primary objectives of these regulations include defining the technical and safety standards that autonomous vehicles must meet, specifying the conditions under which testing and deployment are allowed, and outlining the roles and responsibilities of both manufacturers and users. They address critical aspects such as vehicle design, cybersecurity measures, data privacy, and liability frameworks.
These regulatory efforts are crucial for fostering public trust in self-driving technology. By establishing rigorous safety standards and accountability mechanisms, governments aim to minimize risks while maximizing the benefits of autonomous transportation. The collaborative approach involving government agencies, industry stakeholders, and experts is key to developing a robust regulatory framework that enables the responsible and safe deployment of autonomous vehicles in various countries and regions.

Robo-Taxis in China (2020s)
Companies like Baidu and Pony.ai are at the forefront of the autonomous vehicle revolution, extending their reach beyond their home country of China and showcasing the global expansion of self-driving technology. Their deployment of autonomous taxi services in several Chinese cities is a testament to the rapid advancements in this field and the increasing acceptance of self-driving cars worldwide.
These companies have harnessed cutting-edge technologies, including artificial intelligence and sensor systems, to develop autonomous vehicles capable of safely navigating complex urban environments. By offering taxi services operated by these self-driving cars, they are not only demonstrating the maturity of their technology but also providing a practical glimpse into the future of urban transportation.
The global expansion of self-driving technology is not limited to China alone. Similar efforts are underway in various parts of the world, including the United States and Europe, with companies like Waymo, Cruise, and Tesla actively testing and deploying autonomous vehicles. This worldwide push toward autonomous transportation signifies a shift in how we perceive and interact with mobility, with self-driving cars poised to play a central role in the future of transportation on a global scale.
Partnerships and Industry Collaboration (Ongoing)
The race to develop self-driving technology has spurred a wave of collaborations between automakers, tech companies, and startups, all aimed at accelerating the advancement and deployment of autonomous vehicles. These partnerships have become a key strategy in navigating the complex landscape of autonomous transportation.
One notable example is the collaboration between Waymo, a subsidiary of Alphabet Inc. (Google’s parent company), and Jaguar Land Rover. Waymo leveraged Jaguar’s expertise in luxury vehicles to integrate its self-driving technology into Jaguar’s electric I-PACE SUVs. This partnership showcased the potential for combining cutting-edge autonomous systems with premium automotive brands, appealing to consumers seeking both performance and advanced autonomous capabilities.
In addition to these cross-industry partnerships, traditional automakers have joined forces with tech giants like Apple, Amazon, and Microsoft. These collaborations aim to harness the tech companies’ expertise in artificial intelligence, cloud computing, and data analytics to enhance self-driving technology.
These alliances and partnerships underscore the multifaceted nature of autonomous vehicle development, where the fusion of automotive engineering and high-tech innovation is essential. By pooling resources, knowledge, and experience, these collaborations are driving the autonomous vehicle industry forward, bringing us closer to a future where self-driving cars are a common sight on our roads.
The journey towards the realization of self-driving cars is marked by an ongoing and relentless pursuit of innovation. Researchers, engineers, and companies in the automotive and technology sectors continue to invest heavily in research and development to refine and enhance autonomous vehicle technology. The primary goal is to ensure that self-driving cars are not only safe but also accessible and reliable for the general public.
Safety remains a paramount concern, and rigorous testing and simulation are crucial components of this ongoing process. Engineers are continually refining the algorithms and artificial intelligence systems that enable self-driving cars to perceive and respond to their surroundings with precision and reliability.
Moreover, the collaboration between various stakeholders, including government agencies, automakers, and tech companies, is instrumental in addressing regulatory and ethical challenges. The development of standardized guidelines and the establishment of a legal framework are essential steps in ensuring the responsible deployment of autonomous vehicles.
As technology advances, self-driving cars hold the potential to revolutionize transportation, offering a safer and more efficient way for people to travel. While challenges persist, the dedication to overcoming them continues to drive progress in the field of autonomous transportation. The milestones achieved thus far serve as beacons of hope for a future where self-driving cars are an integral part of our daily lives.