In the history of human progress, the journey of Modern Technology stands as an awe-inspiring testament to human ingenuity. Modern Innovations have catapulted our civilization into an era defined by rapid advancements, altering the course of history and reshaping the fabric of our existence. In this exploration of the History of Technology, we embark on a captivating voyage through time, delving into the profound impacts and pivotal moments that have brought us to the present day.
Modern Technology, an omnipresent force in our lives, has transcended the limitations of mere tools and become an integral part of our identity. The relentless march of progress has seen the convergence of science, engineering, and human creativity, giving rise to many innovations that have reshaped industries, communication, and society. Our quest to understand technology’s past, present, and future takes us through centuries of ingenuity, from the Industrial Revolution’s transformative machinery to the interconnected digital realms of the World Wide Web.
As we embark on this journey through the History of Technology, we will uncover the remarkable achievements, pivotal inventions, and visionary minds that have propelled humanity forward. Join us as we explore the fascinating narrative of Modern Technology, a story still unfolding, where the lines between the possible and the impossible continue to blur, promising a future limited only by our imagination.
Table of Contents
What is modern technology?

Modern technology refers to the collection of tools, systems, devices, and techniques developed and widely adopted to facilitate and enhance various aspects of human life and industry. It encompasses multiple innovations, from digital and information technologies to manufacturing, healthcare, communication, transportation, and more.
At its core, modern technology is characterized by its integration of electronics, digitalization, and connectivity. This includes the proliferation of computers, smartphones, the internet, and various software applications that have revolutionized how we communicate, gather information, conduct business, and entertain ourselves.
Additionally, modern technology has fueled breakthroughs in fields like robotics, artificial intelligence, biotechnology, and renewable energy, transforming industries and shaping our daily lives.
Modern technology is not static; it continues to evolve rapidly, driven by ongoing research, development, and innovation. It plays a pivotal role in driving economic growth, improving living standards, and addressing complex global challenges while presenting new opportunities and ethical considerations for society.
Why is modern technology helpful?
Modern technology is beneficial for several compelling reasons. Firstly, it enhances efficiency and productivity across various sectors, from manufacturing to healthcare, by automating tasks and streamlining processes. This leads to cost savings and increased output, benefiting both businesses and consumers.
Secondly, modern technology has revolutionized communication and connectivity. The internet and smartphones have made connecting with people globally more accessible, accessing information instantly and facilitating remote work and learning. This connectivity has also facilitated rapid information dissemination during emergencies and crises.
Thirdly, technology has transformed healthcare, improving diagnoses, treatments, and patient care. Medical advancements like telemedicine and wearable health devices enable more accessible, personalized healthcare services.
Moreover, modern technology improves our quality of life. From smart homes that enhance convenience and energy efficiency to entertainment options that provide relaxation and enjoyment, technology enhances our daily experiences.
Lastly, technology is crucial in addressing global challenges like climate change through innovations in renewable energy and environmental monitoring.
In sum, modern technology’s utility lies in its capacity to improve efficiency, connectivity, healthcare, quality of life and its potential to address complex global issues.
What was the start of modern technology?
The start of modern technology is often traced back to the period known as the Industrial Revolution, which began in the late 18th century and continued into the 19th century. This transformative era shifted from rural and handcraft-based economies to industrial and manufacturing-based societies. Several key developments set the stage for what we now consider modern technology.
One pivotal invention was the steam engine. James Watt’s improvements in the late 18th century were particularly influential—the steam engine powered factories, locomotives, and ships, revolutionizing transportation and manufacturing processes.
The mechanization of textile production, such as the spinning jenny and power loom, also played a vital role—additionally, innovations in metallurgy and constructing canals and railways for efficient transportation further advanced industrialization.
The emergence of mechanized factories, mass production techniques, and the widespread use of coal and, later, electricity for powering machinery were key elements that defined the early phases of modern technology. These innovations fundamentally changed society, the economy, and how people lived and worked, setting the stage for further technological advancements in the following centuries.
History of Technology and Innovation
The history of modern technology is a complex and vast subject that spans several centuries. Still, I can provide a broad overview of key developments and milestones that have shaped the modern technological landscape:
Industrial Revolution (18th and 19th centuries)
The Industrial Revolution, a watershed moment in human history, ignited a profound transformation in the fabric of society. It shattered the agrarian and handcraft-based economies that had prevailed for centuries, ushering in the age of industrial and manufacturing-based societies. Innovations like the steam engine, which harnessed the power of steam to drive machinery, and mechanized textile production, with inventions such as the spinning jenny and power loom, propelled productivity to unprecedented levels.
Concurrently, the development of advanced transportation systems, such as railways and steamships, revolutionized the movement of goods and people, connecting distant regions and expanding markets. This seismic shift in technology not only changed the way people lived and worked but also laid the foundation for the modern world we know today.
Electricity and Telegraph (19th century)
The discovery and harnessing of electricity revolutionized communication and modern life. Samuel Morse’s invention of the telegraph in 1837 was a watershed moment, allowing for long-distance communication through electrical signals transmitted via Morse code. This breakthrough significantly accelerated the exchange of information, impacting fields ranging from journalism to business.
In the late 19th century, Thomas Edison’s pioneering work on the practical incandescent light bulb illuminated our world and showcased electricity’s versatility and utility. It paved the way for the widespread electrification of homes and businesses, fundamentally altering how people lived and worked and laying the foundation for further innovations in electrical engineering and technology. Edison’s contributions and Morse’s telegraph are pivotal chapters in the electrifying story of modern technology.
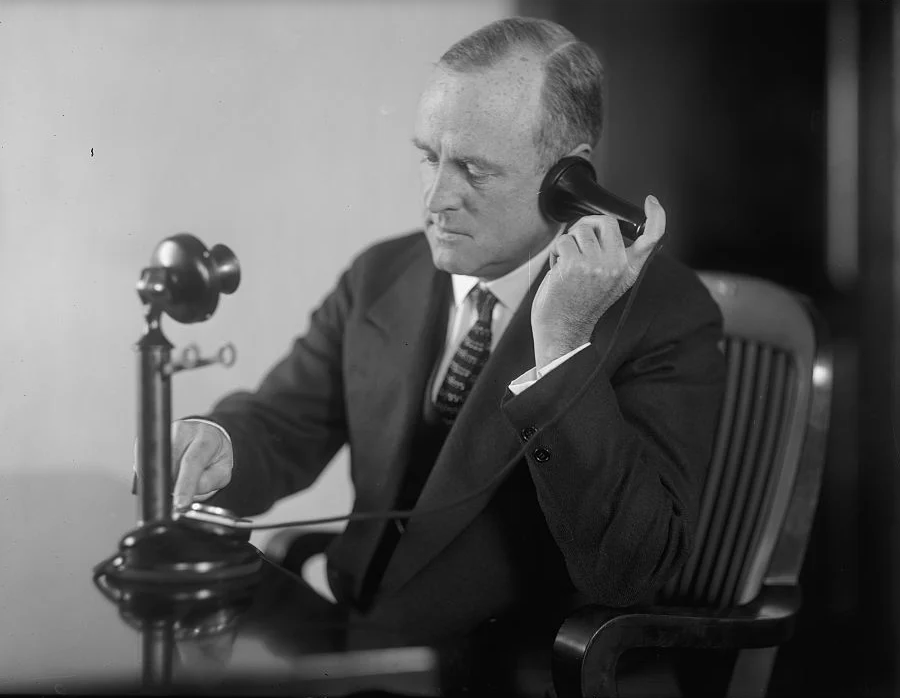

Telephone (late 19th century)
Alexander Graham Bell’s invention of the telephone in 1876 marked a monumental leap forward in communication technology. This groundbreaking invention enabled voice communication over long distances, revolutionizing how people connected and exchanged information. By transmitting sound via electrical signals, the telephone eliminated the constraints of physical proximity, opening up unprecedented possibilities for business, personal, and emergency communication. Bell’s creation laid the foundation for the modern telecommunications industry, setting in motion a trajectory of technological advancements that would ultimately lead to the development of today’s vast and interconnected global communication networks, including landlines, mobile phones, and the internet. The telephone’s legacy is an emblem of human innovation and our relentless pursuit of more efficient and effective communication.
Radio and Broadcasting (early 20th century)
Guglielmo Marconi’s groundbreaking work in wireless telegraphy marked a monumental leap in the evolution of communication technology. By successfully transmitting telegraphic signals wirelessly over long distances, Marconi laid the foundation for radio communication. This innovation revolutionized maritime communication, enabling ships to communicate with shore stations and opening the door to the broadcasting world.
In the 1920s, radio broadcasting emerged as a powerful medium of mass communication, captivating audiences worldwide. It provided a platform for news dissemination, entertainment, and cultural exchange, connecting people across the globe in ways previously unimaginable. Radio waves became the threads weaving together societies and cultures, transforming the world into a global village and fostering a shared sense of interconnectedness.
Automobile (late 19th and early 20th centuries)
The invention of the automobile, often attributed to pioneers like Karl Benz and later popularized by Henry Ford’s Model T, was a watershed moment in human history. It marked a profound revolution in transportation, liberating society from the constraints of horse-drawn carriages and transforming how people moved and connected.
The widespread adoption of automobiles revolutionized the economy, spurring the growth of industries like automotive manufacturing, petroleum, and road construction. It led to suburbanization, changing urban planning, and creating new living patterns. Additionally, the automobile fueled the growth of tourism and led to the development of an intricate network of roads and highways. This transformative technology accelerated personal mobility and catalyzed economic and social transformations that continue to shape our world today.

Aerospace and Aviation (20th century)
The Wright brothers’ historic first powered flight in 1903 indeed marked a pivotal moment in the history of aviation, symbolizing the birth of the aerospace era. Subsequent advancements in aerospace technology accelerated progress in multiple directions. Airplanes became more sophisticated, leading to commercial aviation, military aircraft, and global connectivity.
Furthermore, the development of rocketry technology paved the way for space exploration. Milestones like the launch of Sputnik in 1957, Yuri Gagarin’s first human spaceflight in 1961, and the Apollo moon landing in 1969 demonstrated the remarkable strides made in aerospace technology within a mere six decades. These achievements expanded our understanding of the universe and highlighted humanity’s capacity to push the boundaries of what is technologically possible.
Computers and Information Technology (mid-20th century)
The invention of the electronic computer, spearheaded by visionaries like Alan Turing and John von Neumann, was a pivotal moment in the history of technology. Turing’s groundbreaking work in the mid-20th century on the concept of a universal machine, the Turing machine, laid the theoretical foundation for modern computing. John von Neumann’s contributions, particularly his design of the stored-program architecture, brought these theoretical concepts into practical application.
As the 20th century progressed, the development of integrated circuits and microprocessors ushered in a new era of computing, enabling the creation of smaller, more powerful, and more accessible computers. This rapid advancement in computing technology catalyzed the digital age, transforming every aspect of modern life, from communication and entertainment to science, business, and beyond. The digital revolution continues to shape our world today, with ongoing innovations pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in technology.
Internet and World Wide Web (late 20th century)
The ARPANET, launched in the late 1960s by the U.S. Department of Defense’s Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA), was a pioneering network that laid the groundwork for the Internet. It was designed to facilitate communication and data exchange among researchers and scientists. However, it wasn’t until 1989 that the World Wide Web, invented by Tim Berners-Lee, introduced a user-friendly interface for accessing and sharing information on this network. With the introduction of web browsers and protocols like HTTP, the World Wide Web transformed the internet into a globally accessible platform. This innovation revolutionized how people communicate, conduct commerce, and disseminate information, fundamentally reshaping modern society and business operations.

Mobile Technology (late 20th century to present)
The introduction of mobile phones in the 1980s marked a pivotal moment in the history of technology. While bulky and limited in functionality compared to today’s standards, these early mobile devices revolutionized communication by offering unprecedented mobility and convenience. However, it was the subsequent evolution into smartphones that genuinely transformed the way people interact with technology. With their powerful computing capabilities and internet connectivity, smartphones have become ubiquitous, serving as more than just communication tools. They are now our personal assistants, entertainment hubs, cameras, navigation devices, and gateways to vast information stores. This transformation has reshaped daily life and driven innovation across various industries, from healthcare to education and beyond.
Artificial Intelligence and Robotics (20th century to present)
The remarkable advances in artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and robotics have ushered in a new era of technological innovation. These cutting-edge technologies have given rise to transformative developments such as self-driving cars, which have the potential to revolutionize transportation by increasing safety and efficiency. Virtual assistants powered by AI have become integral in our daily lives, enhancing convenience and productivity. Furthermore, automation driven by AI and robotics has found applications across diverse industries, streamlining processes, reducing costs, and improving precision. These innovations reflect the power of modern technology and promise to reshape how we live and work in the years to come.
Biotechnology and Medicine (20th century to present)
Progress in biotechnology, genetic engineering, and medical technology has ushered in a profound healthcare revolution, reshaping the landscape of medicine and human well-being. Breakthroughs in these fields have enabled the development of cutting-edge treatments, ranging from targeted therapies for previously untreatable diseases to innovative regenerative medicine techniques. Diagnostics have been transformed with the advent of precision medicine, allowing personalized treatment plans tailored to individual genetic profiles. Moreover, decoding the human genome has unveiled the intricate genetic blueprint of our species, opening up new vistas of understanding disease susceptibility, drug responses, and the potential for gene editing to prevent hereditary conditions. This ongoing revolution holds immense promise for the future of healthcare, promising longer and healthier lives for individuals worldwide.

Renewable Energy and Sustainability (late 20th century to present)
Growing environmental concerns, fueled by the recognition of climate change and the negative impacts of traditional fossil fuel-based energy sources, have galvanized global efforts to shift towards cleaner and more sustainable alternatives. This imperative has driven significant developments in renewable energy sources like solar and wind power. Solar panels and wind turbines have become increasingly efficient and affordable, making them viable options for widespread energy generation.
Moreover, the urgency to address environmental challenges has led to innovations in sustainable technologies and practices across various sectors. From energy-efficient building designs and electric vehicles to eco-friendly materials and recycling processes, the drive for sustainability has spurred a wave of creativity and investment. These innovations mitigate environmental harm and promote a more sustainable and responsible approach to technology and industry, ultimately paving the way for a greener and more sustainable future.
These are just some of the key highlights in the history of modern technology. Technological advancement continues to accelerate, with ongoing developments in fields like nanotechnology, quantum computing, and biotechnology shaping the future.