The history of Apple Inc. is a captivating narrative intricately woven with innovation, technological brilliance, and the indomitable spirit of its co-founders, Steve Jobs and Steve Wozniak. From its unassuming beginnings in a suburban garage to its current status as one of the world’s most influential and iconic tech companies, the trajectory of Apple Inc. is nothing short of remarkable. In this exploration of the history of Apple, we will delve into the captivating journey of a company that has not only shaped the way we interact with technology but has also redefined our very concept of innovation.
Apple Inc. was conceived in the heart of Silicon Valley in 1976 when Steve Jobs, Steve Wozniak, and Ronald Wayne embarked on a journey to revolutionize personal computing. Their first creation, the Apple I, was a mere motherboard kit, but it laid the foundation for a global technological phenomenon. As we navigate the intricate history of Apple, it is impossible to ignore the pivotal roles played by Jobs and Wozniak. Steve Jobs became the driving force behind Apple’s meteoric rise with his visionary leadership and unyielding commitment to design excellence. On the other hand, Steve Wozniak provided the technical genius that powered the company’s earliest innovations.
The story of Apple Inc. is not merely a tale of products and profits; it is a testament to the relentless pursuit of innovation and the willingness to challenge the status quo. With each product launch, from the Apple II to the Macintosh, iPod, iPhone, and iPad, Apple reshaped entire industries and set new standards for user experience. These innovations didn’t just change how we work and communicate; they altered the fabric of our daily lives.
In this exploration of the history of Apple, we will traverse through the company’s highs and lows, the departure and return of Steve Jobs, and the iconic products that have defined generations. We will also examine how Apple Inc. continues to evolve and impact the world, emphasizing the enduring legacy of a company that has consistently pushed the boundaries of technology and design. Join us on this journey through the History of Apple as we uncover the roots of innovation and the indelible mark it has left on our digital landscape.
Table of Contents
What is Apple Inc. famous for?

Apple Inc. is famous for many groundbreaking contributions to technology and consumer electronics. At its core, Apple is renowned for its relentless commitment to innovation, design excellence, and user-friendly interfaces. Here are some key areas for which Apple is celebrated:
Iconic Hardware
Apple has consistently produced iconic hardware, including the Macintosh computers, iPods, iPhones, iPads, and MacBooks. These devices are known for their sleek design, premium build quality, and cutting-edge technology.
iOS Ecosystem
Apple’s iOS ecosystem, centered around the iPhone, is famous for its user-friendly interface, the App Store, and seamless device integration. The iPhone revolutionized the smartphone industry and set high standards for mobile devices.
Software Innovations
Apple is renowned for its operating systems, such as macOS and iOS, and software applications like iTunes, iMovie, and GarageBand. These tools have empowered users to easily create, consume, and manage digital content.
App Store
The App Store transformed how we access and use software, offering a vast marketplace for third-party apps catering to various needs and interests.
User Experience
Apple prioritizes user experience in all its products, ensuring they are intuitive, reliable, and aesthetically pleasing. This focus on user-centric design has garnered a dedicated customer base.
Retail Stores
Apple’s distinctive retail stores, with their minimalist design and iconic glass facades, have redefined the concept of physical retail in the tech industry.
Ecosystem Integration
The Apple ecosystem seamlessly connects devices and services, allowing users to sync data, access content across platforms, and benefit from features like iCloud, AirDrop, and Continuity.
Innovation in Services
Apple has expanded into services like Apple Music, Apple TV+, Apple Arcade, and Apple Fitness+, providing users with diverse digital content and entertainment.
Overall, Apple Inc. is famous for its ability to create cutting-edge hardware and software and for its commitment to delivering a holistic user experience that spans devices, services, and an expansive ecosystem. This experience ultimately shapes the way we live, work, and communicate in the digital age.
What was Apple’s first successful product?
Apple’s first truly successful product was the Apple II, introduced in 1977. While the Apple I laid the company’s foundation, the Apple II catapulted Apple Inc. into the mainstream and established its reputation as a leading player in the emerging personal computer industry.
The Apple II was a groundbreaking machine for its time, offering several key innovations. It was one of the first personal computers with color graphics and an open architecture, allowing users to expand and customize their systems with various hardware and software options. This openness made it popular among hobbyists, educators, and businesses alike.

One of the critical factors behind the Apple II’s success was its user-friendly design and accessible interface, which made it more approachable than many other early computers. This approachability, with its software library and the launch of the VisiCalc spreadsheet program, helped the Apple II gain traction in homes and offices.
The Apple II’s success provided the financial stability Apple needed to continue developing innovative products, ultimately leading to the introduction of the Macintosh, iPod, iPhone, iPad, and more. It laid the foundation for Apple’s enduring commitment to user-friendly technology and innovative design, setting the stage for the company’s remarkable journey of technological advancement and consumer impact over the decades.
A Journey of Innovation and Transformation
The history of Apple Inc. is a story of innovation, entrepreneurship, and remarkable technological advancements. The company was founded by Steve Jobs, Steve Wozniak, and Ronald Wayne in a garage in Cupertino, California, on April 1, 1976, and has undergone several phases of growth and transformation. Here’s a detailed overview of Apple’s history:
In The Early Days (1976-1980)
In the annals of technological history, Apple Computer, Inc.’s birth is a pivotal moment. Founded in 1976 by the visionary duo of Steve Jobs and Steve Wozniak, along with Ronald Wayne, Apple Inc. emerged from the humble confines of a garage in Cupertino, California. Their first foray into the tech world was the Apple I, a pioneering creation meticulously crafted by Wozniak. Sold as a motherboard kit, the Apple I marked the genesis of the company’s journey into personal computing.
The true turning point, however, came in 1977 with the introduction of the Apple II. This personal computer was a game-changer, boasting features like color graphics and an open architecture that allowed users to expand and customize their systems. The Apple II became a resounding success, finding a place in homes, schools, and businesses across the nation, and it played a pivotal role in propelling Apple’s early growth.
Regrettably, Ronald Wayne, one of the original co-founders, decided to part ways with the company in 1978. He sold his 10% stake in Apple back to Jobs and Wozniak for a mere $800, a decision that would later be regarded as one of the most expensive in the annals of corporate history.
This early phase of Apple’s history laid the groundwork for what would become one of the most iconic and influential technology companies in the world. The Apple I and Apple II demonstrated the founders’ ingenuity and foreshadowed the company’s future commitment to innovation and user-friendly technology, which would continue to shape the digital landscape for decades to come.
Introduction of the Macintosh (1984-1985)
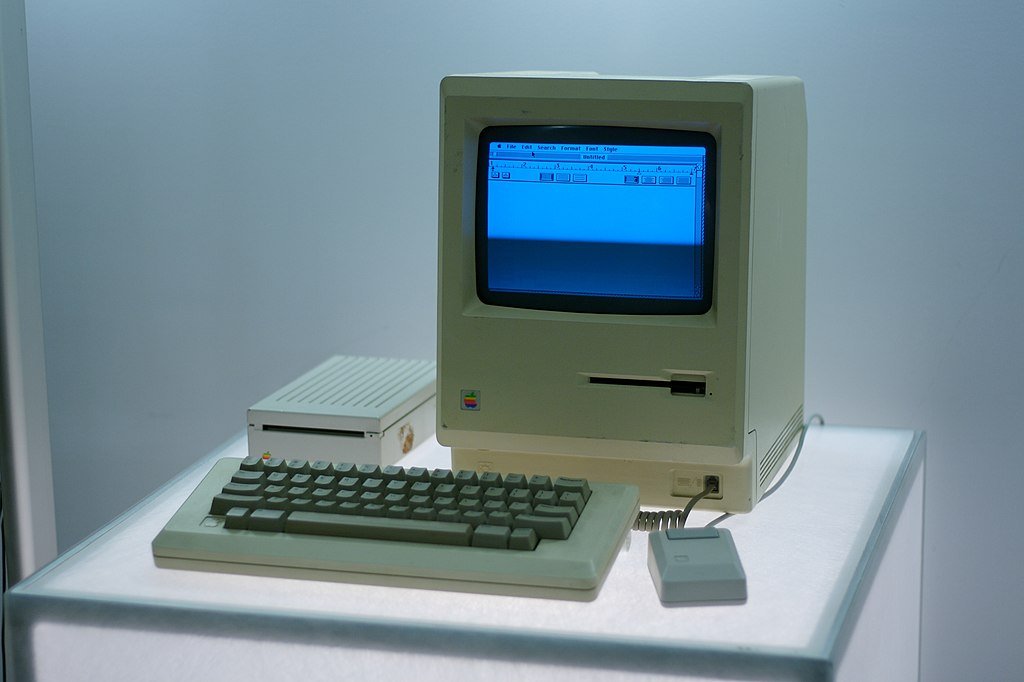
In 1984, Apple’s introduction of the Macintosh marked a watershed moment in the history of computing. The Macintosh was revolutionary because it brought to the masses what was then a cutting-edge technology: a graphical user interface (GUI) and a mouse. Prior to the Macintosh, most personal computers relied on command-line interfaces, which required users to type specific commands to perform tasks. The GUI, in contrast, allowed users to interact with the computer using a more intuitive and visual approach.
The Macintosh’s GUI was not only groundbreaking but also highly influential. It borrowed many concepts from Xerox’s Palo Alto Research Center (PARC), which had developed a GUI-based system called the Xerox Alto. Apple’s implementation, however, made it accessible and user-friendly, and it quickly became the standard for personal computing.

Apple aired the now-famous “1984” Super Bowl commercial during Super Bowl XVIII to introduce this revolutionary product to the world. Directed by Ridley Scott, the commercial depicted a dystopian, Orwellian world where conformity reigned supreme. A lone female athlete, representing the Macintosh, hurled a hammer at a giant screen displaying a Big Brother-like figure, symbolizing IBM. The ad’s message was clear: Apple’s Macintosh was here to break free from the established norms and empower individuals with computing technology.
This commercial generated immense buzz and attention, solidifying Apple’s reputation as a company that dared to challenge the status quo. The Macintosh’s introduction, combined with the iconic Super Bowl ad, set the stage for Apple’s ascent in the personal computer market and left an indelible mark on advertising and technology history. It was a defining moment that signaled the beginning of a new era in computing, one driven by user-friendly interfaces and innovative design.
The Sculley Era (1985-1993)
In 1985, a seismic shift occurred at Apple Inc. when the company’s co-founder and visionary leader, Steve Jobs, was ousted from his position as chairman by the board of directors. This decision resulted from a power struggle and differences in management philosophies, particularly between Jobs and John Sculley, whom Jobs had recruited to be Apple’s CEO.
With Jobs no longer at the helm, Apple faced significant challenges, including mounting competition from industry giants like IBM and the rapid rise in popularity of Microsoft Windows. IBM’s push into the personal computer market posed a formidable threat, particularly in the business sector, where Apple had initially made inroads with the Apple II and early Macintosh models.
During this period, the Macintosh product line continued evolving to stay competitive and relevant. Apple introduced models like the Macintosh SE and Macintosh II to address various user needs and preferences. While innovative as one of the earliest portable Macs, the Macintosh Portable faced challenges in terms of size and battery life, highlighting the company’s struggle to maintain its position in a rapidly changing market.
These developments marked a transitional phase in Apple’s history, marked by internal tensions and external competitive pressures. They set the stage for Steve Jobs’ eventual return to the company, a move that would ultimately lead to a renaissance of innovation and the creation of iconic products that would define Apple’s future success.
The Return of Steve Jobs (1997-2011)
In 1997, Apple made a pivotal move by acquiring NeXT, Steve Jobs’ new venture, bringing him back into the company he co-founded. This reunion began a remarkable era in Apple’s history, with groundbreaking product launches that reshaped entire industries and revolutionized consumer technology.
Under Steve Jobs’ visionary leadership, Apple embarked on a relentless innovation journey. In 1998, they unveiled the iMac, a colorful and innovative all-in-one computer that combined powerful computing capabilities and showcased Apple’s commitment to cutting-edge design and aesthetics. The iMac’s unique form factor and vibrant colors made it an instant hit, appealing to many users.
In 2001, Apple introduced the iPod, a portable digital music player that would fundamentally transform how we listen to music. With its sleek design and the revolutionary iTunes software debuting in 2001, users could easily purchase, organize, and sync their music libraries. This digital media ecosystem became a cornerstone of Apple’s strategy and paved the way for its dominance in the music industry.
Then, in 2007, Apple unveiled the iPhone, a game-changing smartphone featuring a touch screen and a new level of mobile computing capabilities. The iPhone redefined the smartphone market and set the stage for the mobile app revolution, transforming how we communicate, work, and entertain ourselves.
Finally, in 2010, Apple introduced the iPad, a tablet computer that redefined the tablet market. With its sleek design, intuitive interface, and vast ecosystem of apps, the iPad became a versatile tool for work and leisure, further solidifying Apple’s position as a leader in consumer electronics.
These iconic products, brought to life under Jobs’ leadership, not only fueled Apple’s growth but also left an indelible mark on the technology landscape, shaping how we live, work, and connect in the 21st century.
The Post-Jobs Era (2011-Present)
Following Steve Jobs’s passing in 2011, Tim Cook assumed the role of CEO at Apple Inc., facing the formidable challenge of filling the shoes of a legendary visionary. Under Cook’s leadership, Apple continued to thrive, maintaining its reputation for innovation and excellence.
During this period, Apple unveiled a series of groundbreaking products that further solidified its dominance in the tech industry. Multiple iterations of the iPhone continued to captivate consumers worldwide, while the introduction of the MacBook Air showcased Apple’s commitment to sleek design and portability. The Apple Watch and AirPods represented forays into new product categories, demonstrating the company’s ability to create and dominate markets.
Simultaneously, Apple strategically expanded its services division, diversifying its revenue streams beyond hardware. Apple Music, Apple TV+, Apple Arcade, and Apple News+ enriched the Apple ecosystem and established the company as a significant player in the digital content and entertainment industries.
Financially, Apple achieved unprecedented success. Its market capitalization soared to record highs, making it one of the most valuable companies globally. It is a testament to its ability to consistently deliver products and services that resonate with consumers and investors alike.

One of the most significant milestones during this period was Apple’s announcement in 2020 of its transition from Intel processors to Apple Silicon. This marked a pivotal moment as the company began using custom-designed ARM-based chips for its Mac computers, promising increased performance and efficiency while further integrating its hardware and software ecosystem.
Recent Developments (2020-Present)
In June 2020, Apple made a historic announcement at its first virtual Worldwide Developers Conference (WWDC). CEO Tim Cook unveiled the company’s plan to transition from Intel processors to its custom-designed Apple Silicon for Macs. This transition aimed to enhance performance and energy efficiency across the Mac lineup, underlining Apple’s commitment to innovation.
In September 2020, Apple introduced the iPhone 12 series, including the iPhone 12, 12 Pro, and 12 Pro Max. Notably, these devices were the first iPhones to support 5G connectivity, a significant leap in mobile technology, promising faster data speeds and improved network capabilities.
In November 2020, Apple marked a significant shift by releasing the first Macs featuring its in-house Apple M1 chip. The Mac mini, MacBook Air, and MacBook Pro all received this groundbreaking chip, emphasizing Apple’s dedication to redefining computing experiences with improved performance and energy efficiency.
Apple continued its innovative streak in April 2021 with the launch of the M1-powered iPad and a visually striking M1-powered iMac, available in seven vibrant colors. These releases further blurred the lines between tablets and traditional computers.
Throughout 2021 and 2022, Apple maintained its tradition of unveiling four new iPhone models each September. The iPhone 13 and iPhone 13 Pro series were introduced in 2021, followed by the iPhone 14 and iPhone 14 Pro in 2022. The latter incorporated a “dynamic island” design separating the top screen edge from the Face ID sensors.
In 2022, Apple announced a new line of Macs powered by the M2 chip, showcasing its commitment to delivering cutting-edge performance and efficiency. A specialized Apple Watch series, the Apple Watch Ultra, was also introduced for outdoor enthusiasts.
In March 2023, Apple expanded its services with the launch of ‘Apple Pay Later.’ This buy now, pay later service, available to Apple Wallet users, allows convenient loans for online or in-app purchases. Repayments are spread over four installments in six weeks without interest or fees.
Apple’s unwavering dedication to innovation continues to redefine technology and user experiences across various domains.
Throughout its history, Apple Inc. has consistently stood out for its steadfast commitment to design excellence, user-friendly interfaces, and creating a cohesive ecosystem encompassing hardware, software, and services. This dedication has become synonymous with the brand, setting it apart in the tech industry.
Apple’s impact on the computing world is undeniable. From the early success of the Apple II to the groundbreaking Macintosh with its graphical user interface, Apple has continuously pushed the boundaries of what personal computers can do. The introduction of the iPhone revolutionized the telecommunications industry, ushering in the era of smartphones and changing how we communicate, work, and play.
In music, the iPod and iTunes transformed how we listen to and purchase music. These innovations led to the digital music revolution and paved the way for the streaming era dominated by services like Apple Music.
As a pivotal player in the global tech landscape, Apple’s legacy of innovation and its ability to shape industries remain central to its identity. While developments beyond September 2021 are not covered here, Apple can expect to continue its tradition of setting trends and pushing technological boundaries.