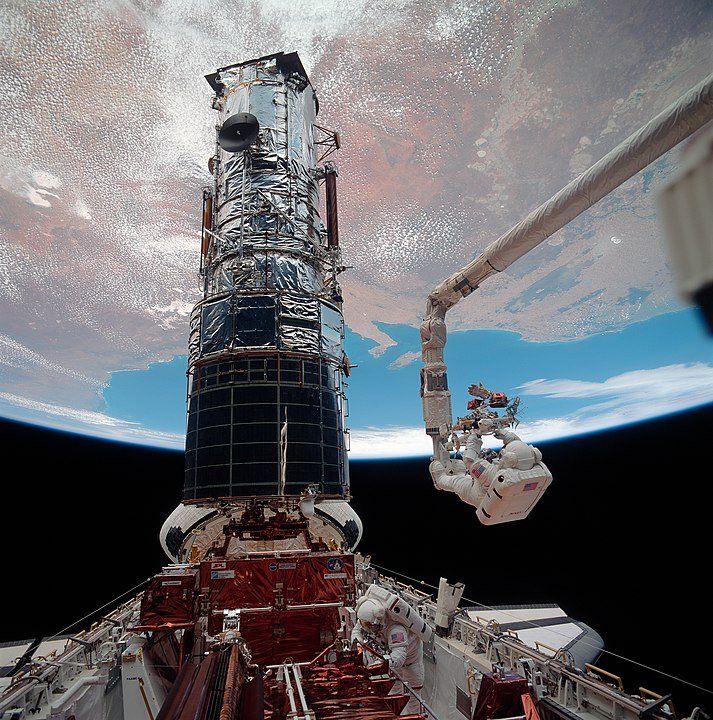
The Hubble Space Telescope has stood as an unparalleled beacon of scientific exploration and astronomical wonder since its launch in 1990. Its orbiting vantage point, far above Earth’s atmosphere, has enabled it to capture breathtaking Hubble images of distant galaxies, exoplanets, and cosmic phenomena with unparalleled clarity. This remarkable telescope has expanded our understanding of the universe and ignited our collective curiosity about the cosmos.
Space exploration has been an essential component of human interest for centuries, driving us to venture beyond our home planet in search of answers to age-old questions. Astronomy, the study of celestial objects and the universe as a whole serves as our guide on this cosmic journey, and the Hubble Space Telescope has been at the forefront of this quest for knowledge.
Since its inception, the Hubble Space Telescope has unveiled the cosmos in unimaginable ways. Its keen eye has peered into the heart of galaxies millions of light-years away, revealing their intricate structures, vibrant colors, and mysterious behaviors. It has allowed us to witness the birth and death of stars, capture the intricate dance of distant galaxies, and even glimpse the atmospheres of planets orbiting other stars, marking groundbreaking achievements in exoplanet research.
As we delve deeper into this exploration of the Hubble Space Telescope’s contributions to space exploration and astronomy, we will embark on a journey through the universe, guided by the awe-inspiring Hubble images that have reshaped our understanding of the cosmos. Join us as we uncover the mysteries of the universe and celebrate the remarkable achievements of the Hubble Space Telescope.
Table of Contents
Why is it called the Hubble Space Telescope?
The Hubble Space Telescope is named after the American astronomer Edwin Hubble, who made groundbreaking contributions to our understanding of the universe. Edwin Hubble is famously known for his observations that provided evidence for the expansion of the universe, a foundational concept in modern cosmology.

The choice to name the telescope after Edwin Hubble pays homage to his pioneering work, which revolutionized our perception of the cosmos. The telescope’s mission was to observe the universe with unparalleled clarity and precision, just as Hubble’s observations had done decades earlier. By using advanced technology and positioning itself above Earth’s atmosphere to avoid atmospheric interference, the Hubble Space Telescope has continued Hubble’s legacy of pushing the boundaries of our knowledge about the universe.
In essence, naming the telescope after Edwin Hubble is a tribute to his significant contributions to astronomy. It emphasizes its mission to continue its legacy by exploring the depths of space and expanding our understanding of the universe.
What type of telescope is the Hubble Space Telescope?
The Hubble Space Telescope (HST) is a space-based, optical, ultraviolet, and near-infrared telescope. It is often referred to as a “space telescope” because it operates in the vacuum of space, free from the distortions and limitations of Earth’s atmosphere. This unique vantage point allows Hubble to capture incredibly sharp and clear images of celestial objects.
Hubble primarily operates in the visible and ultraviolet regions of the electromagnetic spectrum, enabling it to observe a wide range of astronomical phenomena, including galaxies, stars, nebulae, and planets. Its scientific instruments include cameras, spectrographs, and detectors, which collectively provide versatile observational capabilities.
One of Hubble’s most significant advantages is its ability to capture high-resolution images, making it an invaluable tool for detailed scientific research and public outreach. Over the years, it has made numerous groundbreaking discoveries and contributed to our understanding of the universe’s age, expansion rate, and the properties of distant galaxies and exoplanets.
The Hubble Space Telescope is a multi-purpose observatory that has revolutionized astronomy by providing unparalleled views of the cosmos from its unique vantage point in space.
Hubble Space Telescope’s Extraordinary Discoveries
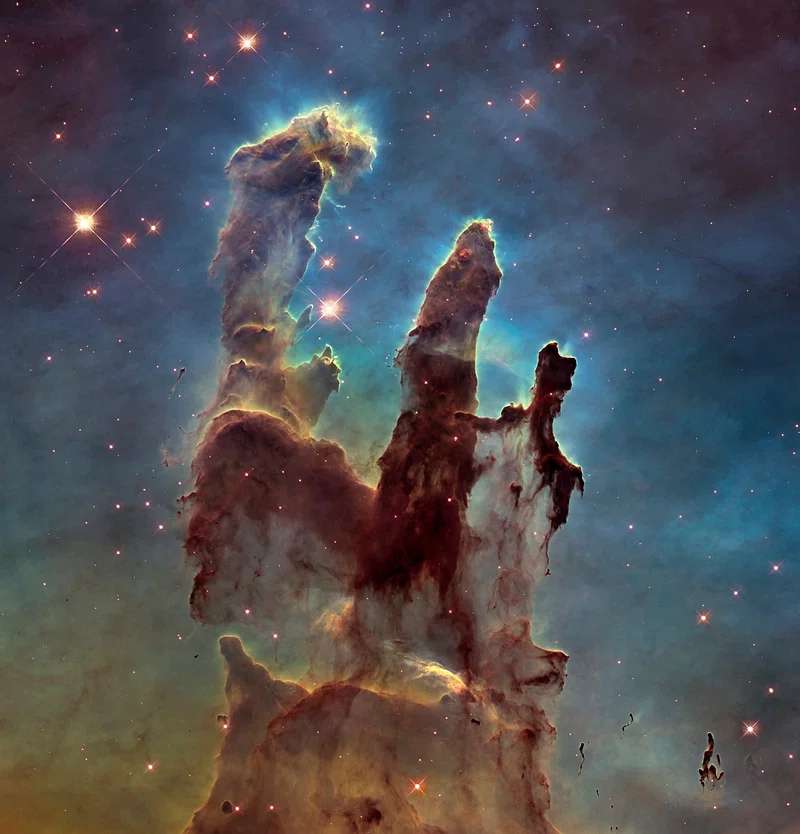

The Hubble Space Telescope’s “voyage of discovery” refers to its mission and ongoing efforts to explore and observe distant objects in the universe from its vantage point in space. Launched into orbit by the Space Shuttle Discovery on April 24, 1990, the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) has provided invaluable insights into various aspects of the cosmos.
Key aspects of the Hubble Space Telescope’s “voyage of discovery” include:
Observing distant galaxies
Hubble’s awe-inspiring images of galaxies beyond our Milky Way have been nothing short of transformative in the field of astronomy. By capturing these stunning visuals, Hubble has not only unveiled the intricate beauty of distant galaxies but has also become a time machine, allowing us to glimpse their ancient past. These images have illuminated the complex processes governing galaxy formation and evolution, revealing the interplay of stars, gas, and dark matter in these cosmic structures. They have also provided crucial insights into the nature of the universe itself, aiding in our quest to understand its origins, expansion, and the fundamental forces that shape its destiny.
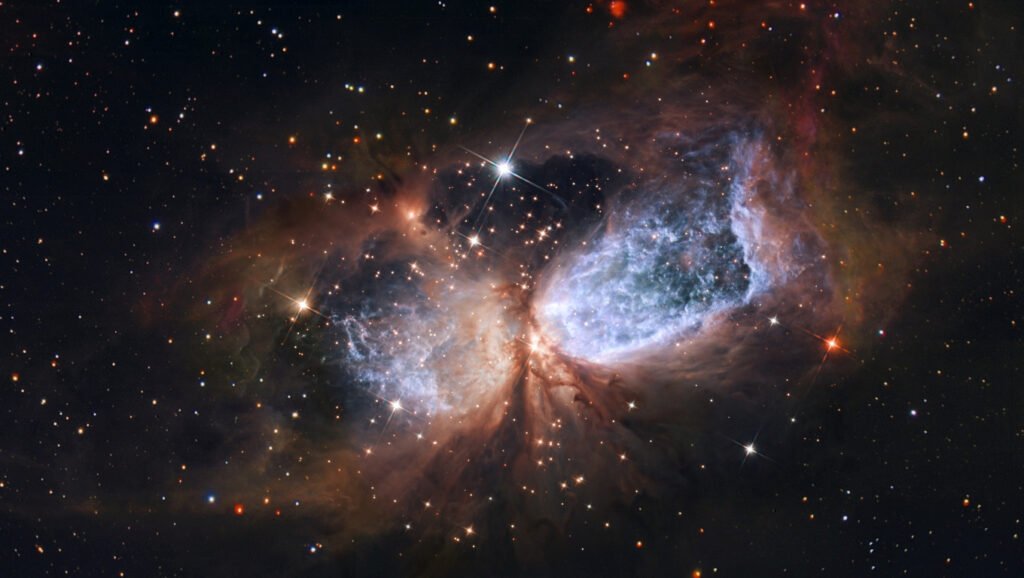

Studying exoplanets
Hubble’s role in exoplanet research is instrumental in advancing our understanding of worlds beyond our solar system. By carefully observing exoplanet transit events, during which these distant planets pass in front of their host stars, Hubble can analyze the starlight that passes through the exoplanet’s atmosphere. This analysis reveals the atmosphere’s chemical composition, including the presence of elements like hydrogen, helium, and water vapor.
These findings provide critical insights into exoplanet atmospheres, their potential habitability, and the potential presence of conditions conducive to life. Hubble’s contribution to exoplanet characterization is a testament to its versatility and its profound impact on expanding our knowledge of the universe and the search for other habitable worlds.
Investigating the early universe
Hubble’s remarkable ability to peer back in time has been instrumental in unraveling the mysteries of the early universe. It offers a glimpse into the universe’s infancy by capturing light from galaxies and celestial objects that existed billions of years ago. This capability allows astronomers to study galaxies’ conditions, structures, and evolution when the cosmos was much younger, shedding light on the processes that shaped the universe we observe today. Hubble’s observations of these ancient galaxies provide crucial data for cosmological models, helping refine our understanding of the Big Bang, the formation of galaxies, and the cosmic timeline, ultimately advancing our knowledge of the universe’s early stages.
Measuring cosmic expansion
Hubble played a pivotal role in measuring the rate of the universe’s expansion, a fundamental parameter known as the Hubble Constant. By observing distant galaxies and measuring their redshift, a result of the universe’s expansion, Hubble provided crucial data that allowed scientists to refine their understanding of the universe’s age, size, and evolution. This constant has profound implications for cosmology, as it informs theories about the Big Bang and the universe’s fate. Hubble’s precise measurements of the Hubble Constant continue to be a cornerstone in the field, shaping our comprehension of the cosmos and the forces driving its ever-accelerating expansion.
Exploring planetary bodies
The Hubble Space Telescope has played a crucial role in advancing our understanding of planets and moons within our own solar system. By carefully observing these celestial bodies, Hubble has provided valuable insights into their atmospheres, surface features, and geology. It has captured images of Mars during its dust storms, revealing details about its ever-changing surface. Hubble has also scrutinized Jupiter’s turbulent atmosphere and its ever-shifting cloud patterns, shedding light on the gas giant’s meteorology. Furthermore, it has studied the unique moons of outer planets like Saturn and Uranus, unveiling their diverse characteristics and orbital dynamics. Through its observations, Hubble continues contributing to our knowledge of the solar system’s complex and dynamic nature.
Unveiling the mysteries of dark matter

Hubble’s observations have indeed played a pivotal role in advancing our understanding of the universe’s mass distribution through gravitational lensing studies. Gravitational lensing is a phenomenon predicted by Einstein’s theory of general relativity, where massive objects like galaxies and galaxy clusters can bend the path of light from more distant objects behind them, effectively acting as cosmic lenses. This distortion of light allows astronomers detect and study objects that would otherwise be too faint or distant to observe directly.
Hubble’s high-resolution imaging capabilities have enabled precise measurements of gravitational lensing effects, unveiling hidden structures and magnifying foreign background objects. These studies have provided critical insights into the distribution of dark matter, the invisible and mysterious substance that makes up a significant portion of the universe’s mass. By mapping the gravitational lensing patterns, Hubble has contributed to our understanding of the large-scale structure of the cosmos, helping scientists unravel the cosmic web of galaxies and dark matter that shapes the universe’s architecture.
Investigating the life cycles of stars:
The Hubble Space Telescope has been a celestial witness to the dynamic and dramatic processes that govern the life cycles of stars. Its keen eye has peered into stellar nurseries, capturing the birth of stars as they emerge from vast clouds of gas and dust. It has chronicled the evolution of these young stars, tracking their growth and the formation of planetary systems around them. Moreover, Hubble has caught the awe-inspiring spectacle of supernova explosions, the explosive deaths of massive stars that release immense energy and forge heavy elements. These observations have deepened our Understanding stellar evolution provided critical insights into the elemental makeup of the universe itself.
Mapping the cosmos
Indeed, the Hubble Space Telescope has played a pivotal role in advancing our comprehension of the structures and dynamics of various celestial objects. Hubble has meticulously charted the intricate details of galaxies, star clusters, and nebulae through its high-resolution imaging capabilities and sophisticated instruments. These detailed maps have offered profound insights into these cosmic entities’ formation, evolution, and interactions. They have allowed astronomers to study the distribution of stars within galaxies, the birth and death of stars within star clusters, and the complex, dynamic processes shaping nebulae. Hubble’s visual revelations have not only deepened our understanding of the universe but have also inspired awe and wonder about the beauty and complexity of the cosmos.
Since its launch in 1990, the Hubble Space Telescope has undeniably been one of the most transformative instruments in the history of astronomy. Its relentless pursuit of knowledge has yielded countless scientific breakthroughs, unveiling the cosmos in unprecedented detail. It has deepened our understanding of the universe’s vastness, origins, and evolution over billions of years. With each passing year, Hubble’s ongoing mission continues to astonish us with breathtaking Hubble images, revealing distant galaxies, unraveling the enigma of dark matter, and probing the atmospheres of exoplanets. It remains a beacon of human ingenuity, pushing the boundaries of our comprehension and inspiring generations of scientists and stargazers alike.