In the ever-evolving world of technology and innovation, few narratives are as captivating as the tale of Artificial Intelligence (AI) mastering the art of games. The interplay between human intelligence and artificial intellect has yielded remarkable stories of progress, culminating in AI’s ascendancy in the realm of competitive games. Among the pivotal chapters in this saga, the name “Deep Blue” looms large, marking a defining moment in the history of AI and games.
Artificial Intelligence, often abbreviated as AI, has been the catalyst for revolutionary breakthroughs across various domains, but it’s within the domain of games that its prowess truly shines. From the early days when computer scientists first ventured into the world of chess to the recent triumphs in the complex strategic game of Go, AI has consistently demonstrated its capacity to surpass human capabilities.
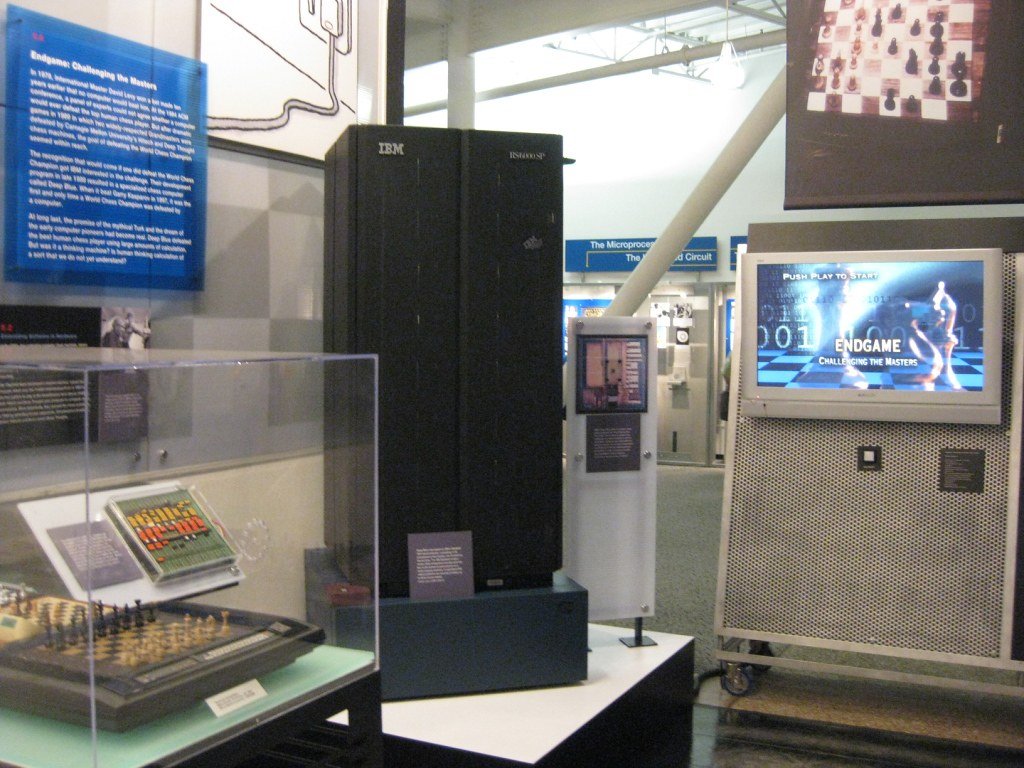
Deep Blue, an IBM creation, emerged as a harbinger of AI’s potential in gaming during the late 1990s. Its epic battle against the reigning world chess champion, Garry Kasparov, captured people’s imaginations worldwide. In 1997, Deep Blue made history by defeating Kasparov in a full-fledged match, heralding a new era where AI’s strategic acumen could rival and sometimes surpass human intellect.
The journey of AI’s ascendancy in games is a testament to human ingenuity, relentless technological advancements, and the ceaseless quest to push the boundaries of what is possible. In this exploration, we delve into the annals of AI’s engagement with games, tracing its evolution from the earliest chess programs to the contemporary dominance in eSports, showcasing the extraordinary strides made in bridging the gap between artificial and human intelligence. The legacy of AI in games is not merely a testament to the triumph of technology; it is a profound reflection of our ever-expanding understanding of intelligence and our willingness to embrace the challenges posed by the machines we create.
Table of Contents
What was the first AI to beat a human?
The first AI to beat a human in a notable competition was IBM’s “Deep Thought” in 1989. Deep Thought was a chess-playing computer program developed by IBM researchers, inspired by the ambition to conquer one of the most intellectually demanding board games.
Deep Thought’s historic victory came when it defeated the reigning world chess champion, Garry Kasparov, in a single game. While this victory was significant, it was not a full match, and Deep Thought needed to be consistently dominant.
The watershed moment in the history of AI defeating humans in chess occurred in 1997 when IBM’s “Deep Blue” defeated Garry Kasparov in a six-game match. Deep Blue marked a substantial leap in AI capabilities, employing advanced algorithms and massively parallel processing to evaluate millions of positions per second. This achievement was groundbreaking, marking the first time a reigning world chess champion was defeated under standard tournament conditions by a computer.
Deep Blue’s victory over Garry Kasparov marked a pivotal moment not only in the history of AI but also in the broader context of human-computer competition, demonstrating that machines were capable of surpassing human expertise in complex intellectual tasks, paving the way for future advancements in AI across various domains.
What was the first AI-based game?
The distinction of the first AI-based game can be attributed to “OxO” or “Noughts and Crosses,” also known as “Tic-Tac-Toe.” This simple yet classic game dates back to the mid-20th century and was one of the earliest instances of computer-based gaming.

In 1952, British computer scientist Alexander S. Douglas developed “OxO” on the EDSAC (Electronic Delay Storage Automatic Calculator), one of the first stored-program digital computers. The game was essentially a digital version of Tic-Tac-Toe, where players take turns marking ‘X’ or ‘O’ on a 3×3 grid, aiming to form a line of their symbol horizontally, vertically, or diagonally. Douglas programmed the EDSAC to allow human players to play against the computer, making it one of the first instances of human-computer interaction in a gaming context.
While “OxO” may seem rudimentary by today’s standards, it laid the foundation for the future of AI in gaming. It demonstrated how computers could be programmed to follow rules and interact with users in a gaming environment. This pioneering effort paved the way for the development of more sophisticated AI-based games over the decades, culminating in the powerful AI engines that now dominate complex games like chess, Go, and video games, showcasing the extraordinary progress in the field of artificial intelligence.
What is the history of artificial intelligence?
The history of Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a journey spanning over half a century, characterized by significant milestones and continuous evolution. It began in the mid-20th century when computer scientists and researchers embarked on the quest to create machines that could mimic human intelligence.
1950s-1960s
The inception of AI can be traced to this period, marked by the development of the first computer programs designed to perform tasks like playing chess (IBM’s IBM 701) and solving mathematical problems (the Logic Theorist by Allen Newell and Herbert A. Simon). The term “Artificial Intelligence” was coined in 1956 at the Dartmouth Conference.
1970s-1980s
The initial enthusiasm around AI led to the “AI winter,” a reduced funding and progress period. Expert systems, which utilized knowledge-based rules, gained attention during this time.
1990s-2000s
AI experienced a resurgence with advancements in machine learning, neural networks, and natural language processing. IBM’s Deep Blue defeating Garry Kasparov in chess (1997) and the rise of search engines like Google were significant milestones.
2010s-Present
The last decade has witnessed remarkable breakthroughs. Machine learning techniques, and intense learning, fueled progress in image recognition, speech synthesis, and autonomous vehicles. AI-powered applications have become commonplace in various industries, including healthcare, finance, and transportation.
Throughout its history, AI has seen periods of boom and bust but has consistently progressed. Today, AI is a pervasive force integrated into our daily lives through virtual assistants, recommendation systems, and autonomous robots. Its potential continues to expand, promising to shape the future of technology and society in unprecedented ways.
A History of AI Dominating Human Games
The history of artificial intelligence (AI) schooling humans in their own games is a fascinating journey showcasing AI technologies’ rapid advancement. Here’s a brief overview of some key moments in this history:
Early Chess Programs (1950s-1960s)
The origins of AI in gaming date back to the 1950s, when computer scientists first ventured into the world of chess programs. Claude Shannon, the father of modern digital circuit design and information theory, played a pivotal role in this early endeavor. In 1950, he wrote a paper titled “Programming a Computer for Playing Chess,” outlining the foundational principles of chess programming.
However, it was only in the 1960s that significant progress was made, and computers began to show their mettle by challenging human chess players. This period marked the inception of AI’s journey into strategic board games, setting the stage for subsequent advancements in AI’s domination of various other games and fields.
IBM’s Deep Thought (1980s)
Deep Thought, IBM’s brainchild, indeed represented a significant advancement in chess-playing AI. In 1989, it made headlines by achieving a remarkable feat—defeating Grandmaster Garry Kasparov, one of the world’s most renowned chess players. This victory was a testament to AI’s progress in understanding and simulating human strategic thinking. However, it’s worth noting that Deep Thought, while impressive, was not yet the dominant force it would later become.
Its victory was a glimpse into the potential of AI, foreshadowing the future where more powerful chess-playing AI systems like IBM’s Deep Blue would rise to even greater prominence, ultimately reshaping the landscape of competitive chess and setting the stage for AI’s continued evolution in gaming and beyond.
IBM’s Deep Blue (1990s)
Deep Blue’s historic victory in 1997 was a watershed moment in the history of Artificial Intelligence (AI). This IBM creation, a powerful chess-playing computer, achieved what was once considered an unattainable milestone by defeating Garry Kasparov, the reigning world chess champion. This triumph showcased the rapid advancements in computing power and AI algorithms, signaling that machines had not only caught up with human intelligence in chess but had also surpassed it.

Deep Blue’s win highlighted the potential of AI to tackle complex strategic tasks, setting the stage for further AI achievements in various domains and sparking discussions about the intersection of human and artificial intelligence.
Checkers and Chinook (1990s)
In the world of checkers (draughts), a pivotal moment arrived in 1994 when the AI program Chinook, painstakingly developed by Jonathan Schaeffer and his dedicated team, achieved an extraordinary milestone. Chinook didn’t just excel at playing checkers; it achieved the seemingly unattainable goal of solving the game. This meant that through an exhaustive analysis of every possible move and countermove, Chinook determined that with perfect play, it was invincible.
In essence, it cracked the code of checkers, affirming that no human or machine adversary could ever defeat it under ideal circumstances. Chinook’s remarkable accomplishment showcased AI’s formidable capabilities in mastering complex games and highlighted the boundless potential of AI in problem-solving domains.
Jeopardy! and Watson (2011)
IBM’s Watson’s triumph in the quiz show Jeopardy! in 2011 marked a watershed moment in the history of Artificial Intelligence. Watson demonstrated its ability to excel in natural language processing and general knowledge by defeating human champions Brad Rutter and Ken Jennings. Its significance lies in its ability to rapidly analyze vast information databases, process intricate language nuances, and generate accurate responses in real time.
This feat showcased AI’s potential as a knowledge repository and tool for information retrieval and problem-solving across many industries, from healthcare and customer service to research and data analysis. Watson’s victory catalyzed a new era of AI applications, underlining its transformative impact on human society.
Go and AlphaGo (2016)
Indeed, one of the most pivotal milestones in the history of AI was the development of AlphaGo by Google’s DeepMind, which made history in 2016 by defeating the reigning world Go champion, Lee Sedol. This event reverberated across the AI community and the world at large because Go, with its vast number of potential moves, had long been considered an insurmountable challenge for computers.
AlphaGo’s victory was a testament to the remarkable capabilities of deep learning algorithms, neural networks, and reinforcement learning techniques. It not only showcased AI’s ability to tackle complex, strategic games but also ignited a renewed interest in the limitless possibilities of artificial intelligence across various domains, from healthcare and finance to autonomous systems and beyond.
eSports and OpenAI (2018-2020)
AI’s incursion into the realm of esports marks a remarkable achievement in the field of artificial intelligence. OpenAI’s groundbreaking accomplishments, particularly with its Dota 2 venture, showcased the astonishing capabilities of AI-driven gaming agents. OpenAI Five, a team composed of AI-controlled heroes in Dota 2, exhibited not only individual prowess but also an unparalleled capacity for teamwork and strategy.
These achievements not only demonstrated AI’s ability to compete at the highest level of professional esports but also underscored its adaptability in complex, dynamic environments. Beyond just winning games, these AI systems provided invaluable insights into teamwork, decision-making, and adaptability, contributing to our understanding of AI’s potential applications in diverse fields beyond gaming. The success of OpenAI in esports marks a pivotal moment where machines challenged and sometimes outperformed human expertise in a highly competitive and unpredictable domain.
Chess and Stockfish (ongoing)
Chess engines like Stockfish represent the pinnacle of AI-powered gaming. With each iteration, they push the boundaries of what’s achievable in the game of chess. These engines possess an uncanny ability to analyze positions with lightning speed, exploring vast move trees and calculating with a precision beyond human reach.
Their superhuman level of play has not only challenged top chess players but also become indispensable tools for analysis and preparation. They’ve revolutionized chess theory by uncovering new strategies, refining openings, and offering deep insights into the intricacies of the game. In the realm of chess, Stockfish and its peers have ushered in an era of unparalleled excellence and understanding, bridging the gap between man and machine.
Video Games and Reinforcement Learning (ongoing)
AI’s evolution in video games is marked by the application of reinforcement learning techniques. These methods enable AI agents to excel not only in classic Atari games but also in intricate 3D virtual worlds like Dota 2 and Minecraft. Through reinforcement learning,
AI systems learn by interacting with their environment, making decisions, and receiving rewards or penalties based on their actions. This iterative process empowers AI to develop strategies, adapt to changing game dynamics, and eventually outperform human players. As AI continues to push the boundaries of what’s achievable in gaming, it not only enhances player experiences but also contributes to the broader field of artificial intelligence and its practical applications.
Robotics and Physical Games (ongoing)
AI’s foray into the realm of physical games marks a remarkable extension of its capabilities. In addition to conquering digital challenges, robots and AI systems have been meticulously engineered to engage in real-world sports and games. Whether it’s dominating table tennis with astonishing reflexes and precision, mastering the intricate strategies of badminton, or outwitting human adversaries in the nuances of poker, AI has showcased its adaptability and strategic prowess.
These feats underscore the versatility of AI, transcending the virtual domain to interact with the tangible world, blurring the line between human and artificial intelligence while offering valuable insights into the potential for automation and enhanced performance in various physical activities and competitive endeavors.
The history of AI’s triumphs in human games stands as a testament to the relentless advancement of machine learning, deep learning, and reinforcement learning techniques. These achievements highlight the extraordinary capabilities that AI has acquired over the years, from mastering chess and Go to dominating esports and complex strategy games.
Beyond the realm of games, these strides in AI have profound implications for society. They have ignited a robust discourse on the ethical and philosophical dimensions of technology’s role in our lives. Questions about the ethical use of AI, its potential impact on employment, and the necessity of regulating AI systems have gained prominence.
Furthermore, AI’s game prowess has served as a proving ground for its broader applications. The decision-making, pattern recognition, and strategic thinking exhibited by AI in gaming contexts have found practical utility in healthcare, where AI assists in diagnosis and treatment planning, and in autonomous vehicles, where it navigates complex environments safely. The history of AI schooling humans in games is a testament to human ingenuity and the transformative potential of artificial intelligence across diverse domains.