In the tapestry of human progress, few threads are as vibrant and intricate as the evolution of technology. The fascinating interplay between innovation and human ingenuity has woven the complex narrative of the History of Technology. This journey spans the epochs, from the earliest sparks of human innovation to the dynamic present, encompassing various Types of Technology that have reshaped societies, economies, and cultures.
The history of technology explores how humans have harnessed their curiosity and creativity to fashion tools, machines, and systems that transcend mere necessity. It delves into the saga of how each era’s challenges and aspirations birthed innovative solutions, from the first rudimentary tools of our ancient ancestors to the awe-inspiring frontiers of Artificial Intelligence and nanotechnology.
At its heart, the History of Technology is an odyssey of human innovation, revealing the resilience and adaptability that define us as a species. Through this voyage, we uncover the tapestry of interconnected breakthroughs that have catalyzed progress, from the Industrial Revolution’s seismic shifts to the Information Age’s digital transformations.
This exploration not only delves into the chronological unfolding of technological advancements but also unveils the myriad Types of Technology that have emerged. From the digital realms of Information and Communication Technology to the transformative potentials of Biotechnology and the sustainable promises of Energy Technology, each category represents a unique facet of human creativity to improve our lives and understand the world around us.
Embark with us on this journey through time and innovation as we unravel the intertwined threads of the History of Technology and the myriad Types of Technology that have shaped our past, present, and the boundless horizons of our future.
Table of Contents
When was technology introduced?
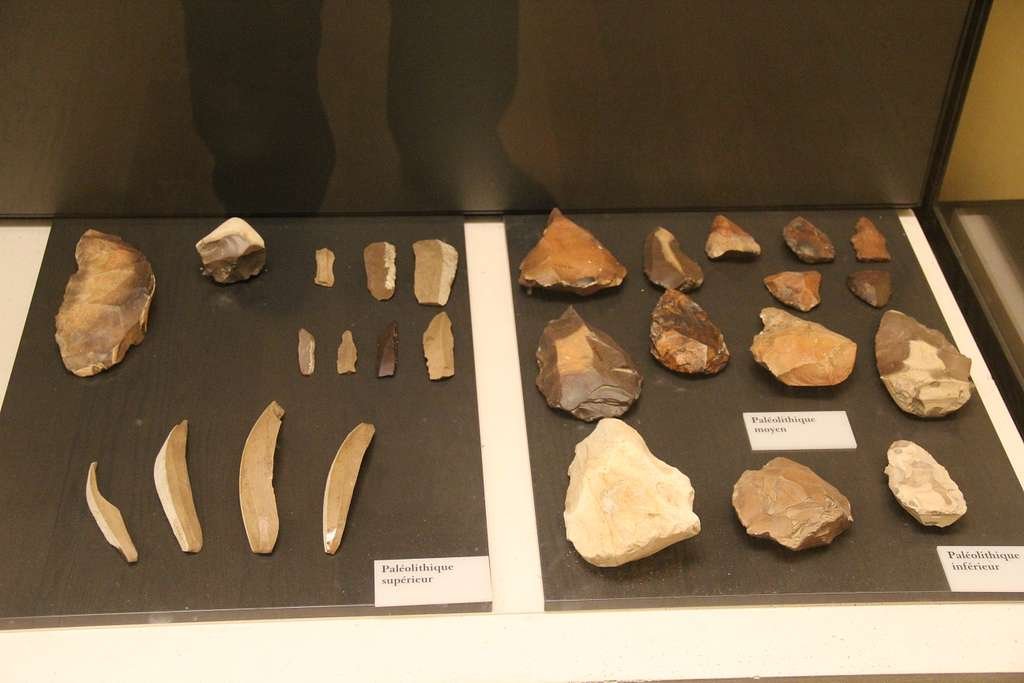

Technology was introduced early in human history, dating back to prehistoric times. The earliest humans developed basic tools, such as sharpened stones and simple weapons, to aid hunting, protection, and survival. The mastery of fire also marked a significant technological leap, offering warmth, protection, and the ability to cook food. These foundational advancements, occurring over millions of years, laid the groundwork for the evolution of technology.
More complex technologies emerged as human societies transitioned from nomadic to settled lifestyles. Around 10,000 BCE, agriculture was developed, allowing humans to cultivate crops and domesticate animals. This marked a pivotal shift from relying solely on nature to actively shaping and manipulating the environment.
The invention of the wheel around 3500 BCE revolutionized transportation and facilitated trade. In the following millennia, advancements like writing systems, metallurgy, and early engineering techniques further propelled technological progress. The construction of monumental structures, such as the Egyptian pyramids and Roman aqueducts, demonstrated sophisticated engineering prowess.
The introduction of technologies accelerated with the Industrial Revolution in the late 18th century. Steam engines, mechanized textile production, and improved transportation networks ushered in a new era of mass production and urbanization. This marked a turning point where technology became a driving force for societal change and economic growth.
In conclusion, technology was introduced gradually throughout human history, evolving from basic tools to intricate machinery and digital systems. It reflects humanity’s innate curiosity and problem-solving abilities, shaping cultures and civilizations.
What are types of technology?

Technology encompasses various tools, methods, and systems humans create and employ to solve problems, enhance efficiency, and improve their lives. It can be broadly categorized into several types:
Information and Communication Technology (ICT)
This category includes information processing and communication technologies. Computers, smartphones, the internet, and software applications are all part of ICT, enabling global connectivity, data sharing, and rapid communication.
Biotechnology
Biotechnology involves using biological systems, organisms, or derivatives to develop new products or processes. Genetic engineering, pharmaceuticals, and medical devices fall under this category, influencing healthcare, agriculture, and the environment.
Energy Technology
Energy technologies focus on efficiently harnessing and utilizing various energy sources. Renewable technologies (solar, wind, hydro), nuclear power, and advancements in energy storage systems contribute to sustainable energy production and consumption.
Manufacturing Technology
Manufacturing technologies pertain to techniques and tools used in production processes. Automation, robotics, 3D printing, and advanced materials shape modern manufacturing, increasing productivity and precision.
Transportation Technology
Transportation technology involves innovations in how people and goods move. From automobiles to high-speed trains and electric vehicles to autonomous drones, advancements in transportation technology impact mobility, logistics, and urban planning.
Medical Technology
Medical technologies encompass medical devices, equipment, and procedures that enhance healthcare diagnosis, treatment, and patient outcomes. MRI machines, surgical robots, prosthetics, and telemedicine are examples of this type.
Agricultural Technology
Agricultural technologies aim to improve crop yield, livestock production, and sustainable farming practices. Irrigation systems, genetically modified crops, precision agriculture, and automated farm equipment fall within this category.
Environmental Technology
Environmental technologies address ecological challenges and promote sustainability. Waste management, water purification, air pollution control, and renewable energy solutions create a cleaner and more sustainable environment.
Aerospace and Space Technology
This category encompasses aviation, aerospace engineering, and space exploration technologies. Aerospace technology has transformed global travel and communication from commercial airplanes to spacecraft and satellite communication.
Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology involves manipulating matter at the nanoscale (very small dimensions) to create new materials and devices with unique properties. It has applications in electronics, medicine, materials science, and more.
These types of technology are not mutually exclusive; they often intersect and synergize to drive further innovation. As technology advances, it shapes virtually every aspect of human existence, transforming how we live, work, and interact with the world around us.

History Of Technology
The History of Technology is a fascinating journey through time that explores the evolution of human innovation and its impact on society, culture, and how we live our lives. From the earliest tools and inventions to today’s advanced technologies, this field of study provides insights into how human ingenuity has shaped the world around us.
Prehistoric and Ancient Technologies
The history of technology traces its origins to the ingenious innovations crafted by our prehistoric forebears. These innovative developments, including primitive stone tools and the mastery of fire, marked pivotal milestones that enabled early humans to navigate and flourish within their environments. Over time, as civilizations took root, ingenuity expanded, and ancient societies such as the Egyptians, Greeks, and Romans pioneered new technological frontiers. They devised sophisticated agricultural methods to ensure sustenance, erected monumental structures through advanced construction techniques, and established communication systems to bridge distances. These advancements laid the foundation for the intricate tapestry of technology weaves today, revealing the enduring link between human curiosity, progress, and the tools that have continually propelled us toward more significant achievements.
Medieval and Renaissance Innovations
During the medieval period, from the 5th to the 15th century, society witnessed a notable refinement of existing technologies and the emergence of novel innovations that would later play pivotal roles in shaping the course of human progress. This era was characterized by a burgeoning curiosity about the natural world, which fueled the gradual transformation of societal norms.
The medieval landscape witnessed the rise of ingenious inventions like windmills, watermills, and mechanical clocks. These engineering marvels harnessed natural forces with increasing efficiency, revolutionizing agricultural production, timekeeping, and how communities organized their lives. The introduction of these technologies marked a significant shift towards mechanization and a burgeoning interest in optimizing human labor through machinery.
As the medieval era transitioned into the Renaissance, a period spanning the 14th to 17th centuries, a vibrant intellectual awakening swept across Europe. The Renaissance breathed new life into scientific inquiry and experimentation as scholars and thinkers rediscovered ancient wisdom and challenged traditional dogmas. This revival of interest in science gave rise to transformative breakthroughs in various domains.
In optics, pioneers like Alhazen and Leonardo da Vinci explored the properties of light and vision, paving the way for developing lenses and telescopes. Astronomical discoveries during this period, including Nicolaus Copernicus’ heliocentric model, shattered long-held cosmological beliefs and paved the way for our modern understanding of the universe. The invention of the printing press by Johannes Gutenberg revolutionized communication and learning, enabling the dissemination of knowledge on an unprecedented scale.
With their advancements and intellectual ferment, the medieval and Renaissance periods laid a solid foundation for the subsequent technological revolutions that would profoundly reshape the world. These eras exemplify the power of human curiosity and innovation, driving progress that continues to influence our lives today.
Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution, a transformative era from the late 18th to the 19th century, is a pivotal chapter in the annals of technological advancement. This era of profound change was propelled by a trifecta of innovations that resonated across society’s fabric.
At its heart, the Industrial Revolution harnessed the potent energy of steam engines, igniting a shift in power from human and animal labor to machines. This revolutionary technology not only supercharged manufacturing processes but also facilitated the creation of mechanized marvels that drove industries to unprecedented heights.
Among these marvels, mechanized textile production emerged as a cornerstone, unleashing a torrent of efficiency that had never before been witnessed. Factories burgeoned, becoming hives of ceaseless activity as machines replaced manual labor, reshaping production dynamics and rendering the impossible possible.
This metamorphosis extended beyond the confines of factories, heralding the transition from rural economies to industrial powerhouses. A confluence of inventions and innovations redefined the essence of work, urbanization, and commerce, ultimately culminating in the radical transformation of society’s structure.
Yet, as machinery thundered and chimneys exhaled plumes of progress, profound social and economic implications echoed. A burgeoning working class, urbanization’s juggernaut, and debates over labor conditions painted a complex portrait of change. The Industrial Revolution sowed seeds of unprecedented wealth alongside glaring inequalities, spurring discussions that resonate through modern socio-economic discourse.
In retrospect, the Industrial Revolution remains an unforgettable testament to humanity’s capacity to harness innovation’s winds and navigate uncharted territories. Its impact is a cornerstone of the modern world, an era where the engines of technology propelled civilization into the future, forever altering the trajectory of progress.
19th and 20th Century Innovations
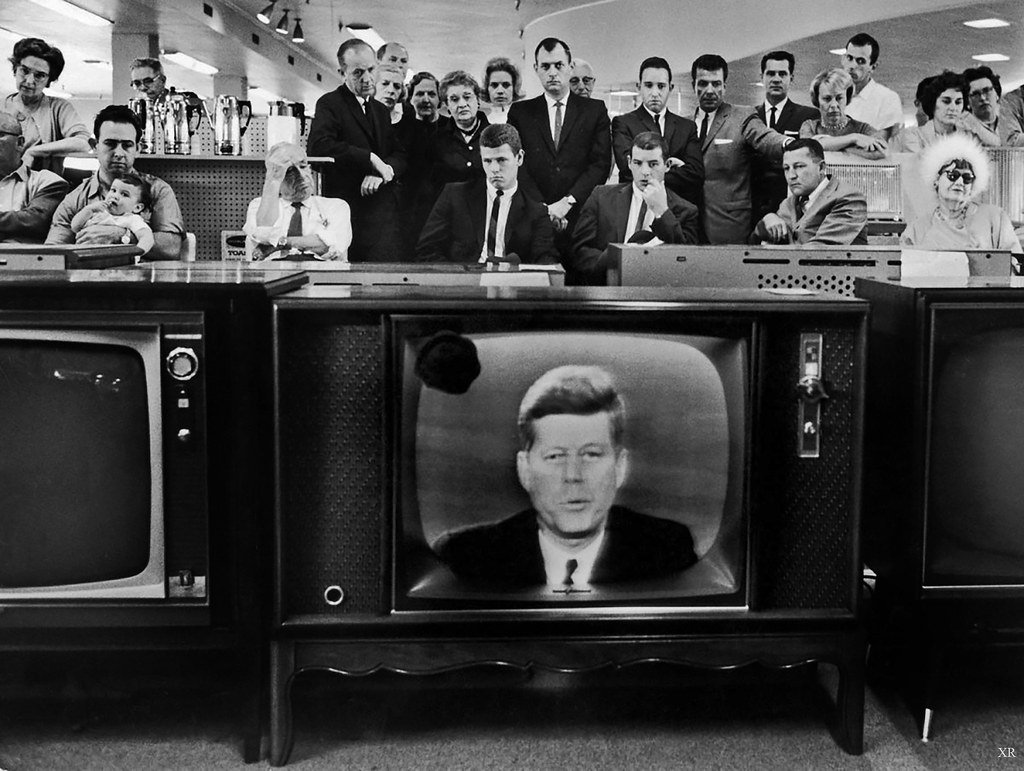
The 19th and 20th centuries stand as a pivotal juncture in the history of human progress, marked by an extraordinary surge in technological advancements that reshaped the very fabric of society. The emergence of electricity, telegraphy, the telephone, and the automobile propelled communication and transportation into uncharted territories. These innovations dissolved geographical barriers, enabling unprecedented exchanges of information and goods.
Moreover, the canvas of entertainment and information dissemination underwent a profound transformation with the development of radio, television, and cinema. These mediums brought distant events and stories to life and nurtured a shared global culture, revolutionizing how we perceive the world.
However, the groundbreaking invention of the computer set the stage for the most significant leap yet—the advent of the internet. This revolutionary duo ushered in the Information Age, intertwining humanity in an intricate web of connectivity. Suddenly, knowledge, communication, and commerce transcended physical boundaries, paving the way for a new era of collaboration, exploration, and innovation.
These technological marvels of the 19th and 20th centuries laid the foundation for today’s interconnected digital world. They epitomize the indomitable spirit of human innovation, demonstrating our capacity to reshape reality and pave pathways to an ever-evolving future.

Modern Technologies
The 21st century is a testament to the relentless march of technological progress, with a cascade of innovations that have redefined every facet of human existence. Among the most conspicuous are mobile devices, smartphones, and wearable technology, which have metamorphosed communication and information retrieval into seamless, ubiquitous experiences.
Yet, the transformation runs far more profound. The surge of renewable energy sources marks a pivotal shift towards sustainability, altering how we power our world. Genetic engineering unveils potentials that could revolutionize healthcare, agriculture, and beyond, though accompanied by ethical considerations. Artificial intelligence and robotics orchestrate an intricate dance across industries, promising unparalleled efficiency while prompting discussions on automation’s impact on employment and society’s fabric.
The nexus of technology and human life has grown inseparable in this era. The breathtaking pace of change forces us to grapple with the possibilities and responsibilities these advancements bestow upon us. As we navigate this terrain, we are tasked with harnessing these innovations to uplift humanity while thoughtfully addressing the ethical, societal, and economic landscapes they reshape.
Societal Implications
The history of technology transcends mere technical advancement; it delves into the intricate tapestry of societal, cultural, and ethical dimensions woven by these innovations. Beyond the marvel of invention lies a realm of profound social and cultural transformation. The rapid integration of technology into daily life has spurred discussions on multifaceted issues. Privacy and data security concerns have become paramount in an interconnected world, while debates over automation’s influence on employment patterns challenge traditional work paradigms. The digital divide raises questions of equitable access to opportunities in an increasingly digital landscape.
Moreover, ethical considerations surface as technology advances, with dilemmas ranging from AI-driven decision-making to genetic engineering. The imperative of environmental sustainability amplifies as well, as tech’s ecological footprint becomes more evident. In comprehending technology’s multifarious role, addressing these issues is imperative for shaping a future where innovation harmonizes with the values and needs of humanity.
The history of technology is an ongoing story of human creativity and adaptation. By examining the past, we gain insights into how we arrived at our current technological landscape and can make informed decisions about the future. It’s a field that highlights the intertwined relationship between innovation, culture, and progress, ultimately shaping the way we navigate the world around us.