In the world of digital currencies, Bitcoin has emerged as a trailblazer, influencing the course of financial transactions. This blog aims to take you through an intriguing exploration of Bitcoin’s history, from its mysterious inception to its profound impact on finance. Join us as we unravel the intricacies of its creation and delve into the initial applications that paved the way for the cryptocurrency revolution.
Table of Contents
Before delving into the blog, let’s address some fundamental questions about Bitcoin:
What is the history of Bitcoin and its uses?
Bitcoin, introduced in 2009 by an unknown person or group using the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto, marked the inception of decentralized digital currency. Initially conceived as a peer-to-peer electronic cash system, its blockchain technology ensures secure and transparent transactions. Over time, Bitcoin has evolved beyond its role as a medium of exchange to become a store of value akin to digital gold. Its decentralized nature, limited supply of 21 million coins, and global acceptance contribute to its growing significance in diversifying investment portfolios and challenging traditional financial norms.

What was the original idea of Bitcoin?
The original idea behind Bitcoin, introduced in a 2008 whitepaper by the pseudonymous Satoshi Nakamoto, aimed to create a decentralized digital currency. Nakamoto envisioned a peer-to-peer electronic cash system that eliminated the need for traditional financial intermediaries. The key innovation was the use of blockchain technology, a distributed ledger, to record and verify transactions securely. Bitcoin’s design intended to provide financial autonomy, borderless transactions, and a finite supply to prevent inflation. By combining cryptographic principles and decentralized control, the original idea of Bitcoin sought to revolutionize the way people engage in financial transactions, fostering a trustless and censorship-resistant system.
What was the initial price of Bitcoin?
When Bitcoin debuted in 2009, it had no established market value, as its initial transactions were exchanged between early adopters on a peer-to-peer basis. The first recorded price for a Bitcoin transaction occurred in May 2010 when a programmer named Laszlo Hanyecz paid 10,000 Bitcoins for two pizzas, valuing each Bitcoin at a fraction of a cent. However, the first significant recorded exchange on a cryptocurrency market took place in October 2010, with one Bitcoin reaching parity with the US dollar. This marked the beginning of Bitcoin’s price discovery, setting the stage for its subsequent volatile journey in the financial markets.
With these questions in mind, let’s now delve deeper into the genesis of Bitcoin.
Genesis of Bitcoin
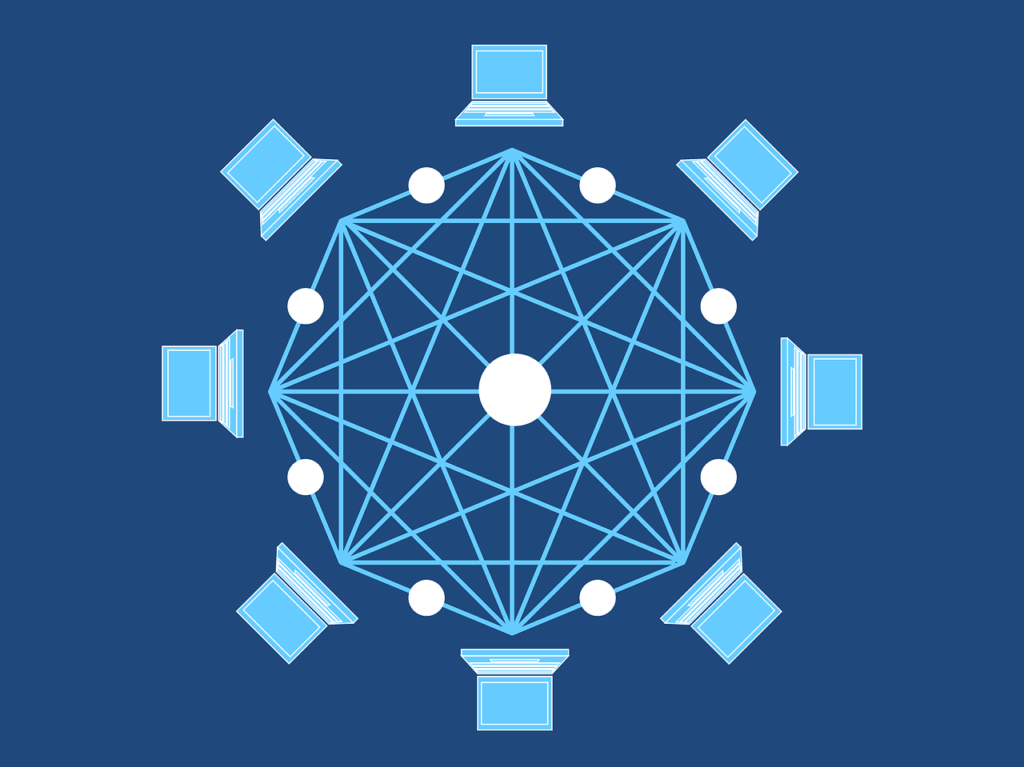

The Mystery Behind Satoshi Nakamoto
Identity Enigma
The enigma of Satoshi Nakamoto, the mysterious creator of Bitcoin, adds a compelling layer to the cryptocurrency’s genesis. Despite extensive speculation and investigations, Nakamoto’s true identity remains concealed, fueling ongoing intrigue and curiosity. This intentional anonymity has become an integral part of Bitcoin’s narrative, sparking debates about the motivations behind such secrecy. Whether driven by a desire for privacy, concerns about legal repercussions, or a commitment to decentralization, Nakamoto’s decision to stay in the shadows contributes to the enduring mystique of Bitcoin’s origin, searching for the identity of this elusive figure a central theme in the ongoing lore of cryptocurrency.
Whitepaper Revolution
Satoshi Nakamoto’s whitepaper, released in 2008, stands as a revolutionary document that introduced the concept of a decentralized digital currency. The whitepaper outlined the principles of peer-to-peer transactions and cryptographic techniques, setting the stage for the development of Bitcoin as a groundbreaking financial innovation.
The Birth of the Blockchain
Decentralized Ledger System
The blockchain, as the technological backbone of Bitcoin, operates as a decentralized ledger system. It records and verifies transactions across a network of computers, ensuring that no single entity has control. This decentralized nature enhances security and transparency in the financial ecosystem.
Transparency and Security
At its core, the blockchain guarantees transparency and security in every transaction. By providing a tamper-resistant record of all transactions, the blockchain eliminates the need for trust in centralized authorities. This innovation establishes a foundation for a secure and transparent digital financial environment.
Mining and Circulation
Decoding the Mining Process
Bitcoin mining is the mechanism by which new bitcoins are brought into circulation, and transactions are validated on the decentralized network.
Creation of New Bitcoins
Bitcoin mining is the mechanism by which new bitcoins are brought into existence. Miners, individuals, or groups with specialized computer hardware compete to solve complex mathematical puzzles. Successfully solving a puzzle allows them to add a new block to the blockchain, and in return, they are rewarded with newly minted bitcoins.
Transaction Verification
Miners play a crucial role in validating and confirming transactions on the Bitcoin network. By solving cryptographic puzzles, they ensure the integrity of the transactions and contribute to the decentralized nature of the system.
Security Features
The mining process adds a layer of security to the Bitcoin network. The computational power required for mining makes it economically unfeasible for any single entity to control the entire network, thus preventing centralized manipulation.
Bitcoin Halving and its Implications
Bitcoin halving is a programmed event that reduces the rate at which new bitcoins are created, occurring approximately every four years.
Supply Control
Bitcoin halving is a programmed event that occurs approximately every four years, reducing the reward that miners receive by half. This mechanism is designed to control the overall supply of bitcoins, mimicking the scarcity and deflationary nature of precious metals like gold.
Economic Impact
Bitcoin halving has profound economic implications. As the rate of new bitcoin creation diminishes, scarcity increases, potentially leading to increased demand and upward price pressure. This event reflects the balance between supply and demand in the cryptocurrency market.
Market Sentiment
Bitcoin halving often captures the attention of investors and enthusiasts, influencing market sentiment. Anticipation of reduced supply can trigger speculative activities and contribute to price volatility in the lead-up to and aftermath of the halving.
Early Use Cases of Bitcoin

The Pizza That Changed Everything
The purchase of two pizzas for 10,000 bitcoins in 2010 is a seminal moment in Bitcoin’s history, symbolizing its initial transition from a conceptual digital currency to a medium of exchange. This seemingly insignificant event holds profound significance for these key reasons:
Pioneering Real-world Transactions
The pizza transaction marked one of the first instances of Bitcoin being used for a tangible, real-world exchange. It showcased the potential for a decentralized digital currency to facilitate everyday transactions, no matter how small. This laid the foundation for Bitcoin’s evolution from a speculative asset to a practical means of value transfer.
Establishing a Valuation Benchmark
While the 10,000 bitcoins spent on pizzas may now seem extravagant, it established an early benchmark for the valuation of Bitcoin. This transaction planted the seed for discussions around the value of Bitcoin in terms of everyday goods and services, ultimately contributing to its acceptance and integration into mainstream commerce.
Silk Road and the Dark Web
Bitcoin’s association with the Silk Road marketplace represents a darker chapter in its history, highlighting the cryptocurrency’s dual nature.
Controversy and Illicit Transactions
The Silk Road, an online marketplace for illegal goods and services, accepted Bitcoin as its primary form of payment. This association brought Bitcoin into the spotlight for its potential use in facilitating illicit transactions, prompting regulatory scrutiny and concerns about its anonymity features.
Impact on Reputation
The Silk Road controversy significantly impacted Bitcoin’s reputation, leading to skepticism and negative perceptions in mainstream media. However, it also spurred conversations about the need for regulatory frameworks and accountability within the cryptocurrency space. Despite the negative connotations, this episode played a role in shaping discussions around the responsible use of digital currencies and the importance of distinguishing between legal and illegal applications.
Bitcoin’s Evolution and Mainstream Adoption
Rise of Bitcoin Exchanges
The evolution of Bitcoin exchanges has been a crucial factor in the cryptocurrency’s journey towards mainstream adoption. Key elements define this transformation:
Facilitating Transactions
Bitcoin exchanges played a pivotal role in establishing platforms where users could seamlessly buy and sell bitcoins. These exchanges provided a bridge between the traditional financial system and the emerging world of cryptocurrencies, offering a secure environment for transactions. This development marked a significant step in making Bitcoin more accessible to the general public.
Challenges and Breakthroughs
The journey of Bitcoin exchanges was challenging. Security concerns, regulatory uncertainties, and technological challenges were obstacles that these platforms had to overcome. Breakthroughs in security protocols, regulatory clarity, and technological advancements contributed to the resilience and legitimacy of Bitcoin exchanges, fostering trust among users and paving the way for broader adoption of Bitcoin as a legitimate digital asset.
Bitcoin’s Rollercoaster Ride in Value
Bitcoin’s early years were marked by extreme price volatility, transitioning from near worthlessness to unprecedented values. Understanding this rollercoaster ride involves examining these key aspects:
Market Dynamics and Influencing Factors
The fluctuating value of Bitcoin was influenced by a myriad of factors, including market demand, macroeconomic trends, regulatory developments, and technological advancements. The decentralized and relatively nascent nature of the cryptocurrency market amplified these dynamics, contributing to rapid and sometimes unpredictable changes in Bitcoin’s valuation.
Role of Speculators
Speculators played a significant role in Bitcoin’s price volatility. The speculative nature of early Bitcoin markets attracted investors looking for quick returns, contributing to price bubbles and subsequent corrections. Over time, as the market matured and institutional players entered the scene, Bitcoin’s value became less susceptible to extreme fluctuations, marking a transition toward a more stabilized and developed market.
Bitcoin Today and Future Prospects

Mainstream Acceptance and Institutional Interest
Bitcoin has undergone a remarkable transformation from a niche technology to gaining widespread acceptance among mainstream investors and businesses. Several key factors have fueled this shift:
Increasing Trust and Legitimacy
Over the years, Bitcoin has gained trust and legitimacy as a viable investment and store of value. Mainstream investors, including hedge funds and corporations, have recognized its potential as a hedge against inflation and a diversification tool for investment portfolios. This acceptance has elevated Bitcoin from a speculative asset to a recognized and respected component of the financial landscape.
Institutional Involvement
Institutional interest in Bitcoin has grown significantly. Notable financial institutions, asset management firms, and even publicly traded companies have entered the space. Institutional involvement is not limited to investment; it also extends to providing custodial services, creating investment products, and integrating Bitcoin into traditional financial platforms. This influx of institutional interest has further legitimized Bitcoin as an asset class, boosting its credibility and broadening its appeal.
Innovations and Scaling Solutions
Bitcoin’s ecosystem continues to evolve with ongoing innovations addressing scalability challenges and enhancing transaction efficiency. The key solutions driving this evolution are the Lightning Network and Segregated Witness (SegWit):
Lightning Network
The Lightning Network is a second-layer scaling solution built on top of the Bitcoin blockchain. It enables faster and cheaper transactions by creating off-chain payment channels. Users can transact directly with each other off-chain, reducing the burden on the main blockchain and significantly improving scalability. This innovation has the potential to make microtransactions feasible and enhance the overall speed of the Bitcoin network.
Segregated Witness (SegWit)
SegWit is a protocol upgrade that separates transaction signatures from the transaction data, effectively increasing the block size limit without a hard fork. This optimization not only improves the overall efficiency of the Bitcoin network but also enhances security and enables the implementation of further technological advancements. SegWit has been widely adopted, contributing to a more scalable and robust Bitcoin network.
Bitcoin’s transformative journey, from Satoshi Nakamoto’s whitepaper to its global influence, signifies a paradigm shift in finance. The blockchain’s advent revolutionized transparency, while mining and halving events added layers of economic intrigue. Early transactions, including the famous pizza purchase, showcased the practicality of this digital currency. Despite controversies, Bitcoin’s value surged, attracting mainstream acceptance and institutional interest. Ongoing innovations like the Lightning Network reflect a commitment to scalability. As Bitcoin evolves, it remains a pioneering force, shaping the future of digital currencies and challenging traditional financial norms with resilience, innovation, and global impact.